2.34 MPU6050 Module¶
Overview¶
In this lesson, you will learn how to use MPU6050. MPU-6050 is a 6-axis (combined 3-axis Gyroscope, 3-axis Accelerometer) motion tracking devices. It is often used for augmented reality and electronic image stabilization (EIS: Electronic Image Stabilization), optical image stabilization (OIS: Optical Image Stabilization), “Zero touch” gesture user interface.
Components Required¶
Fritzing Circuit¶
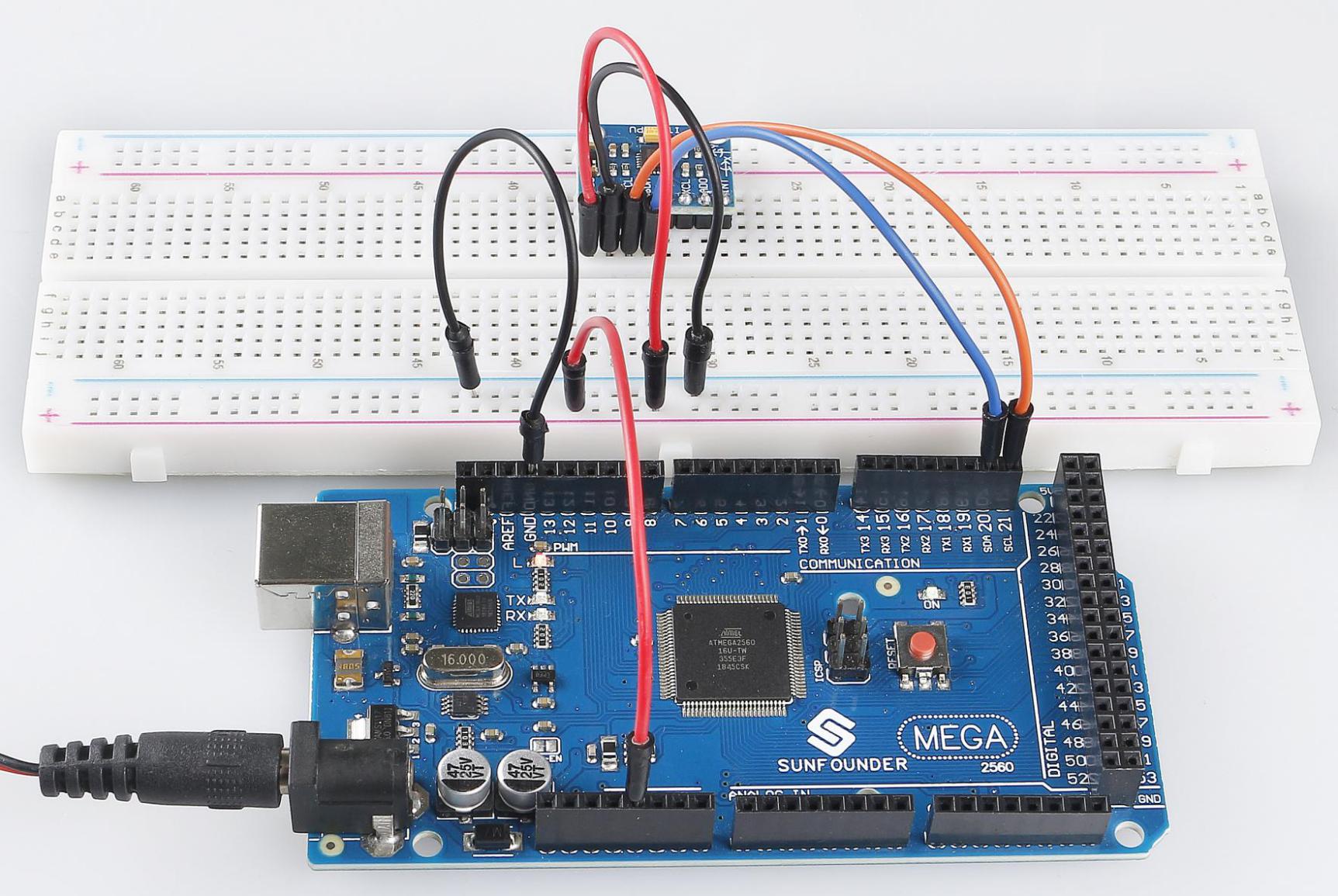
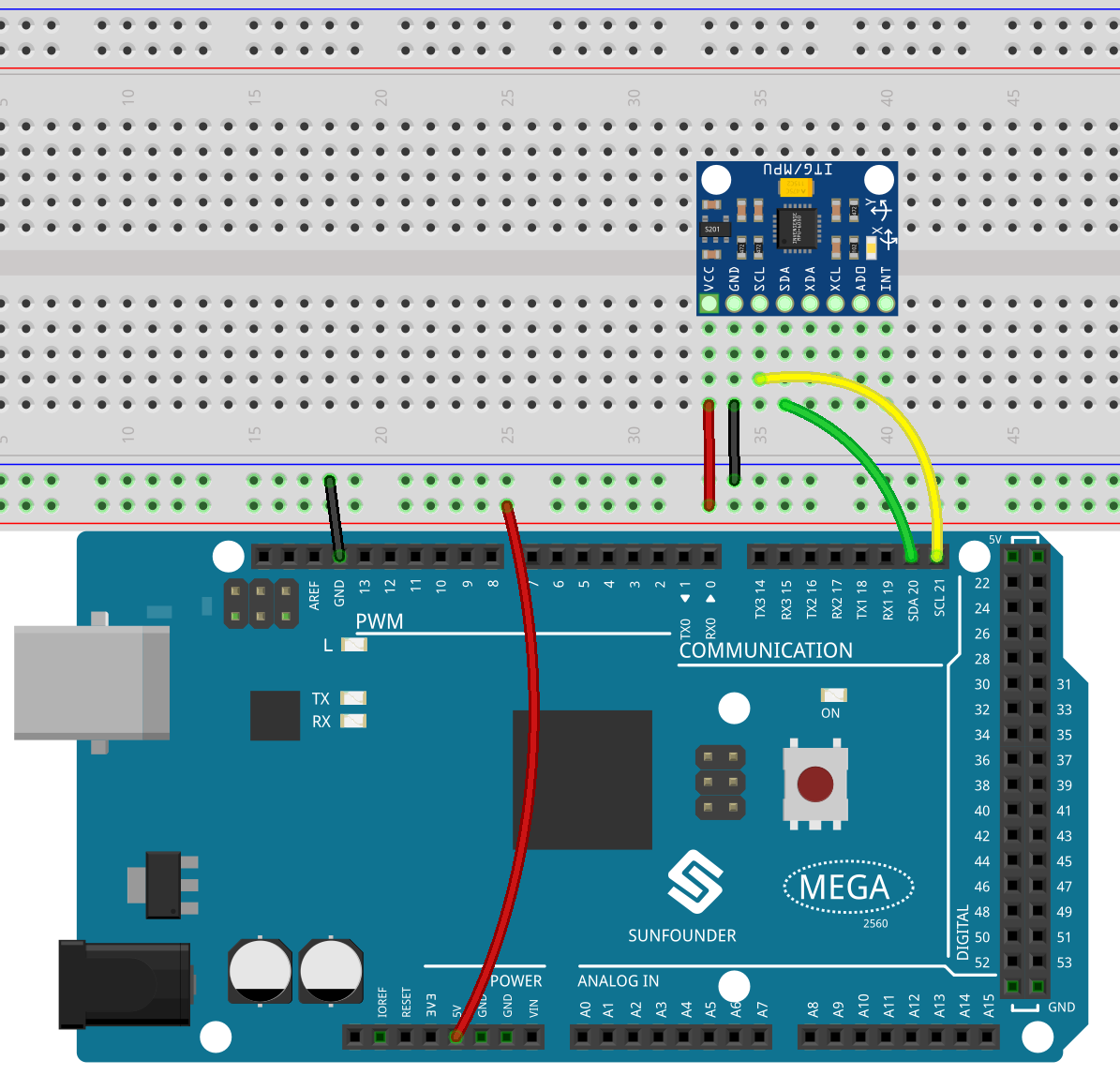
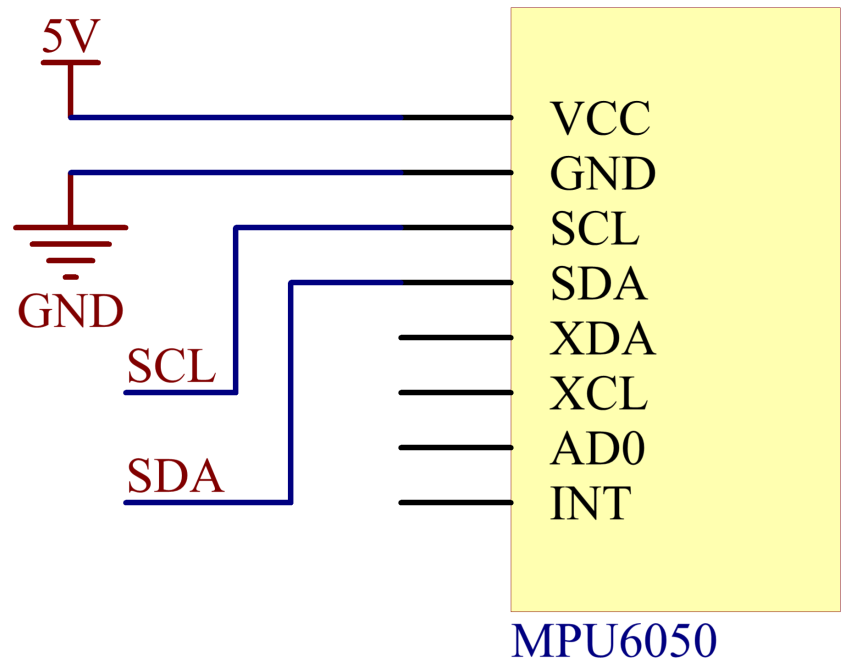
In this example, we drive MPU6050 with IIC. We inset MPU6050 into the breadboard; get the VCC connected to 5V, GND to GND, SCL to pin SCL 21, and SDA to the pin SDA 20.
Schematic Diagram¶
Code¶
Note
You can open the file
2.34_MPU6050.inounder the path ofsunfounder_vincent_kit_for_arduino\code\2.34_MPU6050directly.Or copy this code into Arduino IDE.
After uploading the codes to the Mega2560 board, you can open the serial monitor to see the gravity acceleration and angular velocity of MPU6050 in each direction.
Code Analysis¶
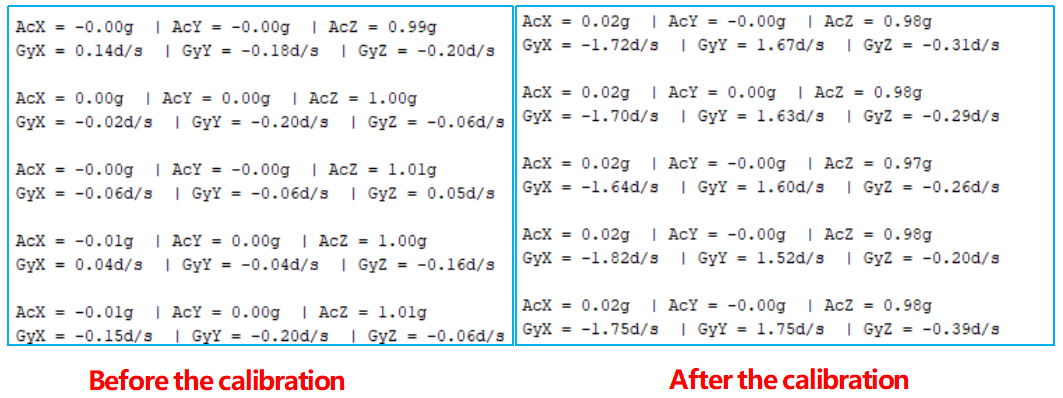
In the stationary desktop state, the Z-axis acceleration is 1 gravity unit, and the X and Y axes are 0.
Before your use, you need to calibrate the module, the methods are as follows:
MPU6050 modules are placed horizontally on the desktop and then you can fix them with clamps or adhesive tape.
Run the sample codes to get the RAW DATA of MPU6050 when it is static.
Add compensation according to the readings when MPU6050 is static.
Take MPU6050 we use as an example, and the results of compensation are as follows:
Serial.print(AcX / 65536 * ACCELE_RANGE - 0.02);
Serial.print(AcY / 65536 * ACCELE_RANGE + 0);
Serial.print(AcZ/65536 * ACCELE_RANGE + 0.02);
Serial.print(GyX / 65536 * GYROSC_RANGE + 1.70);
Serial.print(GyY/65536 * GYROSC_RANGE - 1.70);
Serial.print(GyZ/65536*GYROSC_RANGE + 0.25);
Phenomenon Picture¶