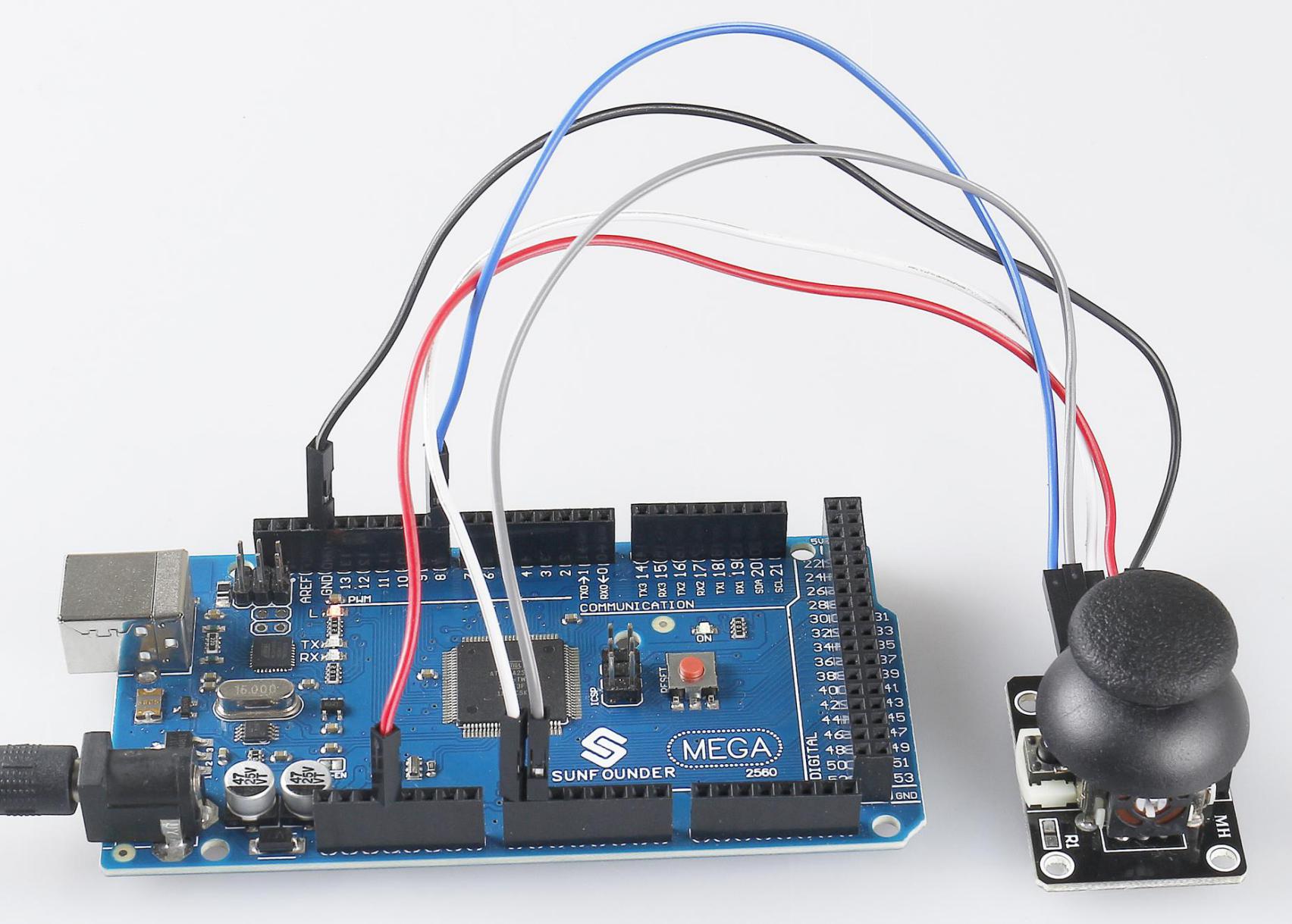
2.23 Joystick Module¶
Overview¶
In this lesson, you will learn something about Joystick. The basic idea of a joystick is to translate the movement of a stick into electronic information that a computer can process. It can be applied to work as the controller of devices, such as robot.
Components Required¶
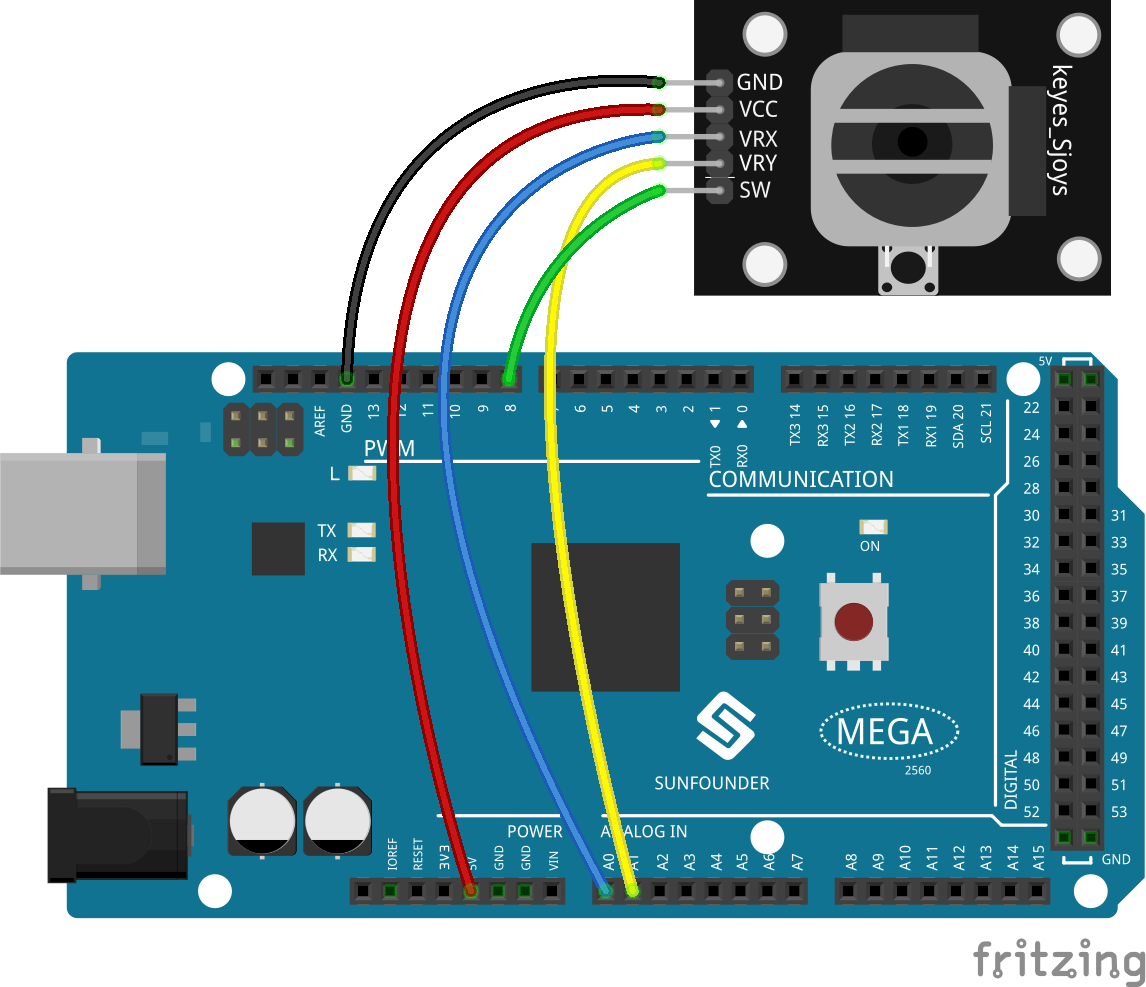
Fritzing Circuit¶
In this example, we get the GND of the Joystick extended to connect with GND, VCC with 5V, VRX with pin A0. After that, we make VRY connect with pin A1, SW connect with pin 8.
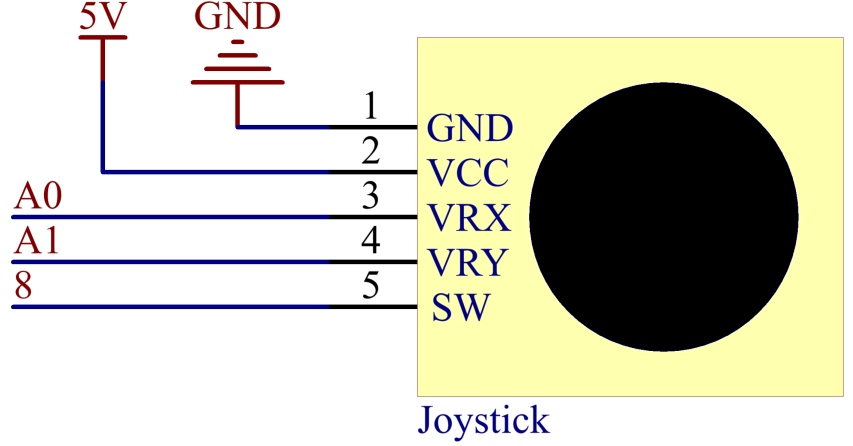
Schematic Diagram¶
Code¶
Note
You can open the file
2.23_joystick.inounder the path ofsunfounder_vincent_kit_for_arduino\code\2.23_joystickdirectly.Or copy this code into Arduino IDE.
Uploaded the codes to the Mega2560 board, you can open the serial monitor to see readings on the X-axis and Y-axis of Joystick, as well as the button status of Z-axis. The values of the X-axis and Y-axis are the analog values, which vary within the range「0」~「1023」. The Z-axis shows numerical value and the state is either 「1」 or 「0」. Refer to 1.5 Analog Read and 1.4 Digital Read to check the code explanation.
Phenomenon Picture¶