Lesson 28 Humiture Sensor¶
Introduction
The digital temperature and humidity sensor DHT11 is a composite sensor that contains a calibrated digital signal output of temperature and humidity. The technology of a dedicated digital modules collection and the temperature and humidity sensing technology are applied to ensure that the product has high reliability and excellent long-term stability.
Required Components
1 * Raspberry Pi
1 * Breadboard
1 * Humiture module
1 * 3-Pin anti-reverse cable
Experimental Principle
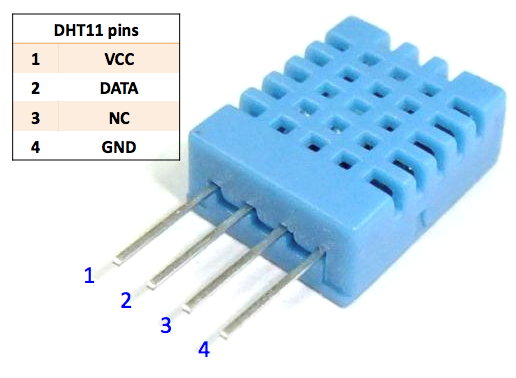
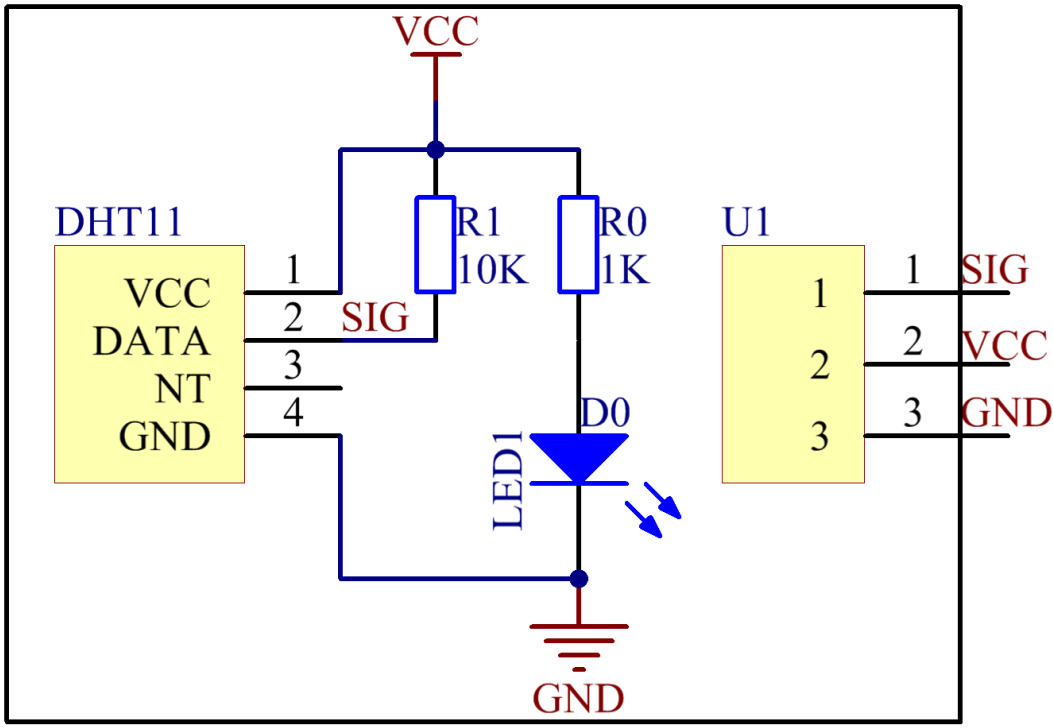
Only three pins are available for use: VCC, GND, and DATA. The communication process begins with the DATA line sending start signal to DHT11, and DHT11 receives the signal and returns an answer signal, then the host receives the answer signal and begins to receive 40-bit humiture data (8-bit humidity integer + 8-bit humidity decimal + 8-bit temperature integer + 8-bit temperature decimal + 8-bit checksum). For more information, please refer to the datasheet of DHT11.
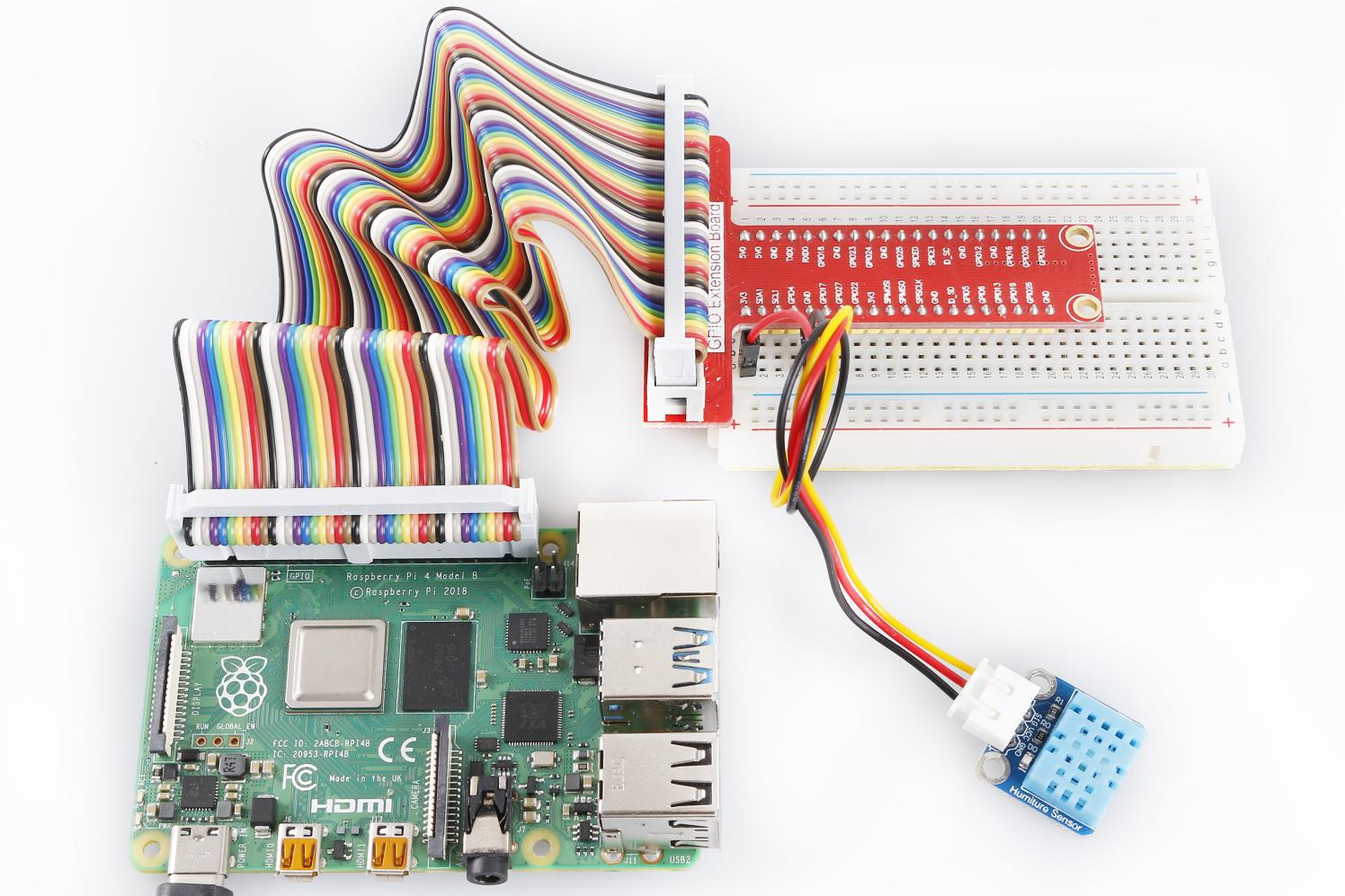
Experimental Procedures
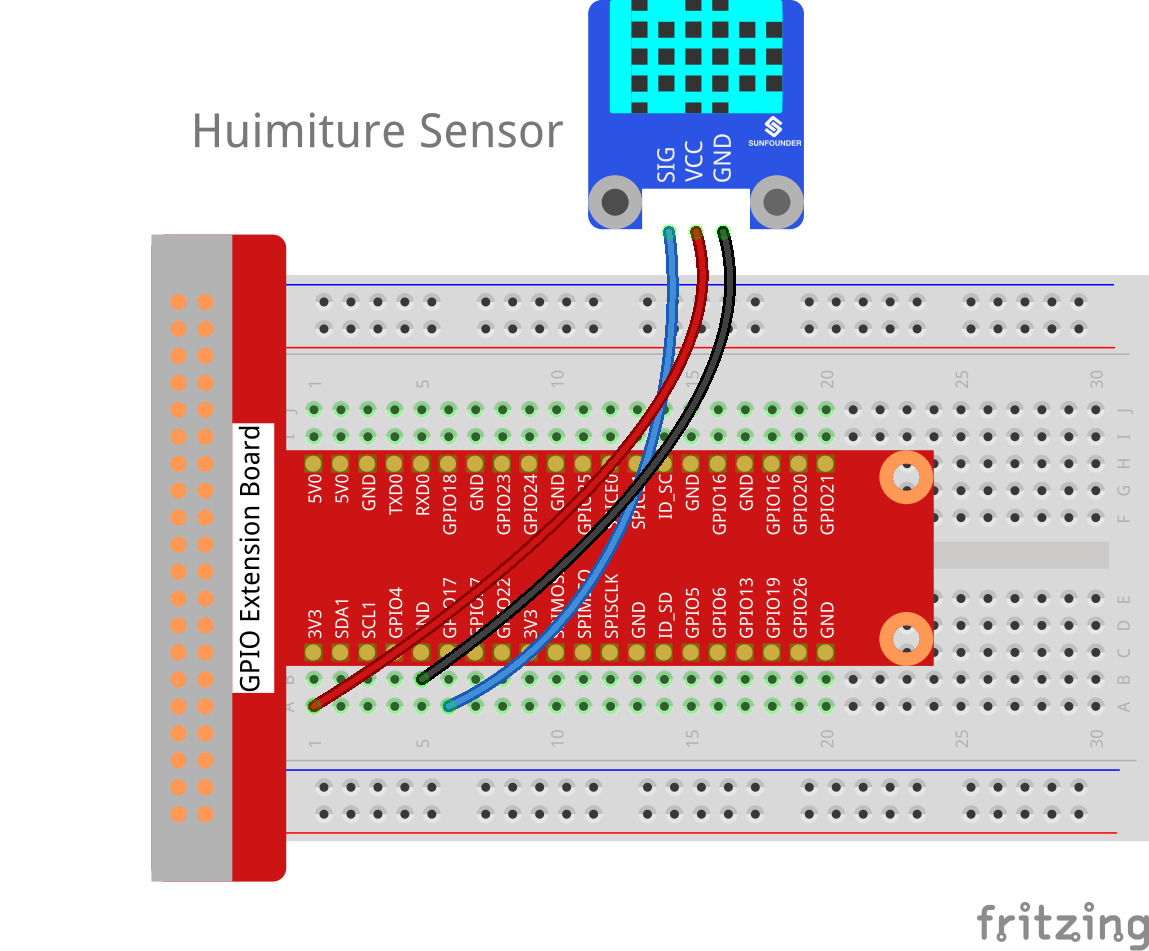
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Raspberry Pi |
GPIO Extension Board |
Humiture Module |
GPIO0 |
GPIO17 |
SIG |
3.3V |
3V3 |
VCC |
GND |
GND |
GND |
For C Users:
Step 2: Change directory.
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/C/28_humiture/
Step 3: Compile.
gcc humiture.c -lwiringPi
Note
If it does not work after running, or there is an error prompt wiringPi.h: No such file or directory, please refer to WiringPi to install it.
Step 4: Run.
sudo ./a.out
Code
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define MAXTIMINGS 85
#define DHTPIN 0
int dht11_dat[5] = {0,0,0,0,0};
void read_dht11_dat()
{
uint8_t laststate = HIGH;
uint8_t counter = 0;
uint8_t j = 0, i;
float f; // fahrenheit
dht11_dat[0] = dht11_dat[1] = dht11_dat[2] = dht11_dat[3] = dht11_dat[4] = 0;
// pull pin down for 18 milliseconds
pinMode(DHTPIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(DHTPIN, LOW);
delay(18);
// then pull it up for 40 microseconds
digitalWrite(DHTPIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(40);
// prepare to read the pin
pinMode(DHTPIN, INPUT);
// detect change and read data
for ( i=0; i< MAXTIMINGS; i++) {
counter = 0;
while (digitalRead(DHTPIN) == laststate) {
counter++;
delayMicroseconds(1);
if (counter == 255) {
break;
}
}
laststate = digitalRead(DHTPIN);
if (counter == 255) break;
// ignore first 3 transitions
if ((i >= 4) && (i%2 == 0)) {
// shove each bit into the storage bytes
dht11_dat[j/8] <<= 1;
if (counter > 16)
dht11_dat[j/8] |= 1;
j++;
}
}
if ((j >= 40) &&
(dht11_dat[4] == ((dht11_dat[0] + dht11_dat[1] + dht11_dat[2] + dht11_dat[3]) & 0xFF)) ) {
f = dht11_dat[2] * 9. / 5. + 32;
printf("Humidity = %d.%d %% Temperature = %d.%d *C (%.1f *F)\n",
dht11_dat[0], dht11_dat[1], dht11_dat[2], dht11_dat[3], f);
}
}
int main (void)
{
printf ("Raspberry Pi wiringPi DHT11 Temperature test program\n") ;
if (wiringPiSetup () == -1)
exit (1) ;
while (1)
{
read_dht11_dat();
delay(1000); // wait 1sec to refresh
}
return 0 ;
}
For Python Users:
Step 2: Change directory.
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_SensorKit_for_RPi2/Python/
Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 28_humiture.py
Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
DHTPIN = 17
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
MAX_UNCHANGE_COUNT = 100
STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN = 1
STATE_INIT_PULL_UP = 2
STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN = 3
STATE_DATA_PULL_UP = 4
STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN = 5
def read_dht11_dat():
GPIO.setup(DHTPIN, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(DHTPIN, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.05)
GPIO.output(DHTPIN, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.02)
GPIO.setup(DHTPIN, GPIO.IN, GPIO.PUD_UP)
unchanged_count = 0
last = -1
data = []
while True:
current = GPIO.input(DHTPIN)
data.append(current)
if last != current:
unchanged_count = 0
last = current
else:
unchanged_count += 1
if unchanged_count > MAX_UNCHANGE_COUNT:
break
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN
lengths = []
current_length = 0
for current in data:
current_length += 1
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_UP:
if current == GPIO.HIGH:
state = STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_UP:
if current == GPIO.HIGH:
current_length = 0
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
lengths.append(current_length)
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if len(lengths) != 40:
#print ("Data not good, skip")
return False
shortest_pull_up = min(lengths)
longest_pull_up = max(lengths)
halfway = (longest_pull_up + shortest_pull_up) / 2
bits = []
the_bytes = []
byte = 0
for length in lengths:
bit = 0
if length > halfway:
bit = 1
bits.append(bit)
#print ("bits: %s, length: %d" % (bits, len(bits)))
for i in range(0, len(bits)):
byte = byte << 1
if (bits[i]):
byte = byte | 1
else:
byte = byte | 0
if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0):
the_bytes.append(byte)
byte = 0
#print (the_bytes)
checksum = (the_bytes[0] + the_bytes[1] + the_bytes[2] + the_bytes[3]) & 0xFF
if the_bytes[4] != checksum:
#print ("Data not good, skip")
return False
return the_bytes[0], the_bytes[2]
def main():
print ("Raspberry Pi wiringPi DHT11 Temperature test program\n")
while True:
result = read_dht11_dat()
if result:
humidity, temperature = result
print ("humidity: %s %%, Temperature: %s C" % (humidity, temperature))
time.sleep(1)
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup()
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
Now, you can see humidity and temperature value printed on the screen.