6.6 Digital Dice¶
This project builds upon the 2.5 Number Display project by adding a button to control the digit displayed on the seven-segment display.
When the button is pressed, the 7-segment display scrolls through the numbers 1-6, and when the button is released, it displays a random number.
This cycle continues each time the button is pressed.
Required Components
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
ESP32 Starter Kit |
320+ |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
|
Schematic
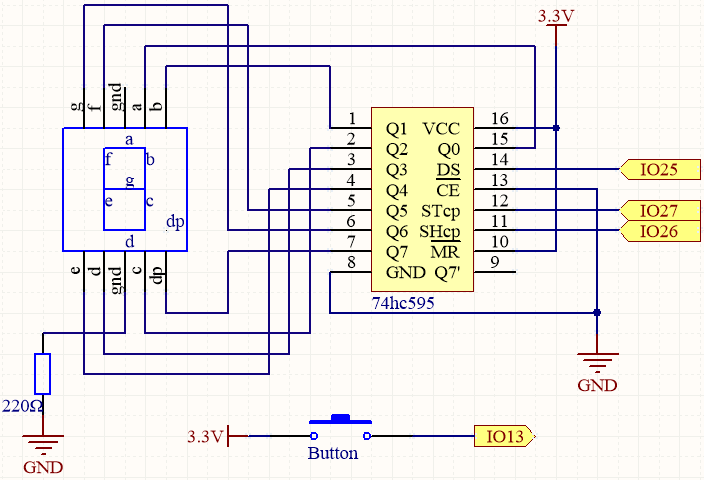
This project builds upon the 2.5 Number Display project by adding a button to control the digit displayed on the seven-segment display.
The button is directly connected to IO13 without an external pull-up or pull-down resistor because IO13 has an internal pull-up resistor of 47K, eliminating the need for an additional external resistor.
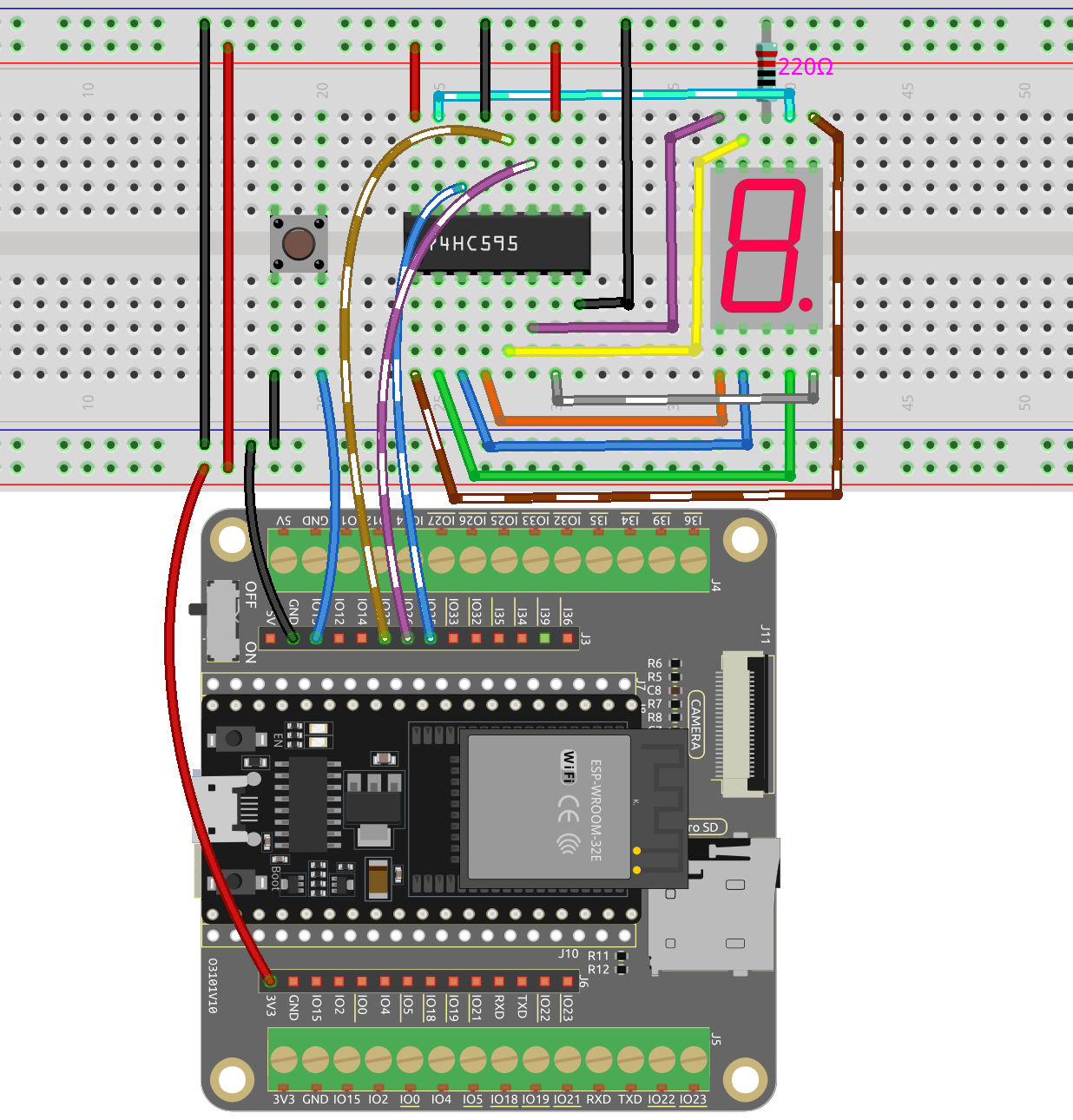
Wiring
Code
Note
Open the
6.6_digital_dice.pyfile located in theesp32-starter-kit-main\micropython\codespath, or copy and paste the code into Thonny. Then, click “Run Current Script” or press F5 to execute it.Make sure to select the “MicroPython (ESP32).COMxx” interpreter in the bottom right corner.
import machine
import time
import random
# Define the segment code for a common anode 7-segment display
SEGCODE = [0x3f, 0x06, 0x5b, 0x4f, 0x66, 0x6d, 0x7d, 0x07, 0x7f, 0x6f]
# Initialize the pins for the 74HC595 shift register
sdi = machine.Pin(25, machine.Pin.OUT) # DS
rclk = machine.Pin(27, machine.Pin.OUT) # STcp
srclk = machine.Pin(26, machine.Pin.OUT) # SHcp
button = machine.Pin(13, machine.Pin.IN) # Button pin
# Define the hc595_shift function to shift data into the 74HC595 shift register
def hc595_shift(dat):
# Set the RCLK pin to low
rclk.off()
# Iterate through each bit (from 7 to 0)
for bit in range(7, -1, -1):
# Extract the current bit from the input data
value = 1 & (dat >> bit)
# Set the SRCLK pin to low
srclk.off()
# Set the value of the SDI pin
sdi.value(value)
# Clock the current bit into the shift register by setting the SRCLK pin to high
srclk.on()
# Latch the data into the storage register by setting the RCLK pin to high
rclk.on()
# Initialize the random seed
random.seed(time.ticks_us())
num = 1
button_state = False
# Define the button callback function to toggle the button state
def button_callback(pin):
global button_state
button_state = not button_state
# Attach the button callback function to the falling edge of the button pin
button.irq(trigger=machine.Pin.IRQ_FALLING, handler=button_callback)
# Continuously display the current digit on the 7-segment display, scrolling if button is not pressed
while True:
# Display the current digit on the 7-segment display
hc595_shift(SEGCODE[num])
# If the button is pressed and button state is True
if button_state:
pass
# If the button is pressed again and button state is False, generate a new random digit
if not button_state:
num = random.randint(1, 6)
time.sleep_ms(10) # Adjust this value to control the display refresh rate
While the program is running, pressing the button will make the 7-segment display scroll and randomly display a number between 1 and 6.
Upon pressing the button again, the 7-segment display will stop and reveal a specific number. Press the button once more, and the 7-segment display will resume scrolling through the digits.