2.1 Hello, LED!¶
Just as printing “Hello, world!” is the first step in learning to program, using a program to drive an LED is the traditional introduction to learning physical programming.
Required Components
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
ESP32 Starter Kit |
320+ |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
|
Available Pins
Here is a list of available pins on the ESP32 board for this project.
Available Pins |
IO13, IO12, IO14, IO27, IO26, IO25, IO33, IO32, IO15, IO2, IO0, IO4, IO5, IO18, IO19, IO21, IO22, IO23 |
Schematic
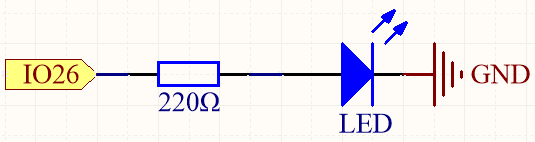
This circuit works on a simple principle, and the current direction is shown in the figure. The LED will light up after the 220ohm current limiting resistor when pin26 outputs high level. The LED will turn off when pin26 outputs low level.
Wiring
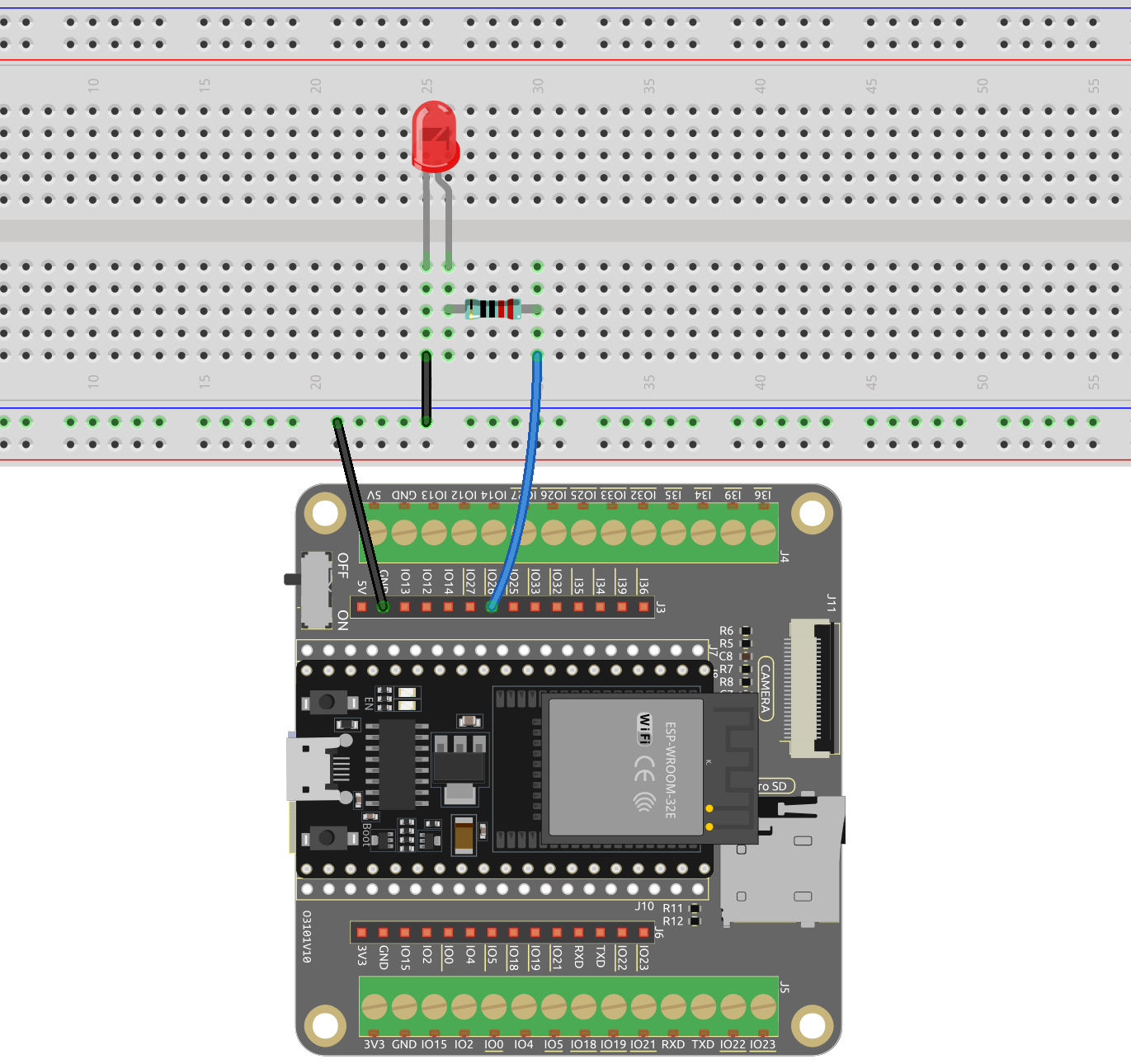
Run the Code
Open the
2.1_hello_led.pyfile located in theesp32-starter-kit-main\micropython\codespath, or copy and paste the code into Thonny.# Import the necessary libraries import machine import time # Set up the LED on pin 26 as an output pin led = machine.Pin(26, machine.Pin.OUT) # Start an infinite loop while True: # Turn on the LED by setting its value to 1 (HIGH) led.value(1) # Wait for 1 second (1000 milliseconds) while the LED is on time.sleep(1) # Turn off the LED by setting its value to 0 (LOW) led.value(0) # Wait for 0.5 seconds (500 milliseconds) while the LED is off time.sleep(0.5)
Connect the ESP32 WROOM 32E to your computer using a Micro USB cable.
Then click on the “MicroPython (ESP32).COMXX” interpreter in the bottom right corner.
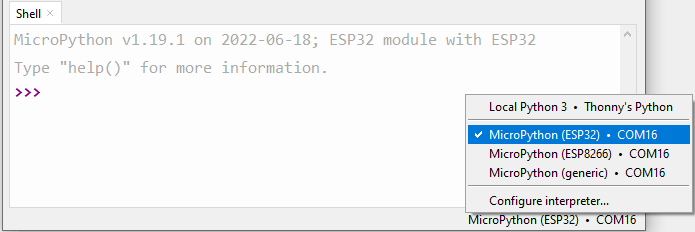
Finally, click “Run Current Script” or press F5 to execute it.
After the code runs, you will see the LED blinking.
How it works?
It imports two modules,
machineandtime. Themachinemodule provides low-level access to the microcontroller’s hardware, while thetimemodule provides functions for time-related operations.import machine import time
Then set up the pin26 as an output pin using the
machine.Pin()function with themachine.Pin.OUTargument.led = machine.Pin(26, machine.Pin.OUT)
In the
While Trueloop, the LED is turned on for one second by setting the value of the pin26 to 1 usingled.value(1)and then set to 0(led.value(0)) to turn it off for one second, and so on in an infinite loop.while True: # Turn on the LED by setting its value to 1 (HIGH) led.value(1) # Wait for 1 second (1000 milliseconds) while the LED is on time.sleep(1) # Turn off the LED by setting its value to 0 (LOW) led.value(0) # Wait for 0.5 seconds (500 milliseconds) while the LED is off time.sleep(0.5)
Learn More
In this project, we used MicroPython’s machine and time module, we can find more ways to use them here.