Servo¶
Overview¶
In this lesson, you will explore the use of Arduino and Servo Motors. Focusing on the Arduino Uno and the SG90 servo motor, you’ll learn how to program the Arduino to control the servo’s sweeping motion. This technique is essential in various applications like robotics and automated systems.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Elite Explorer Kit |
300+ |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
|
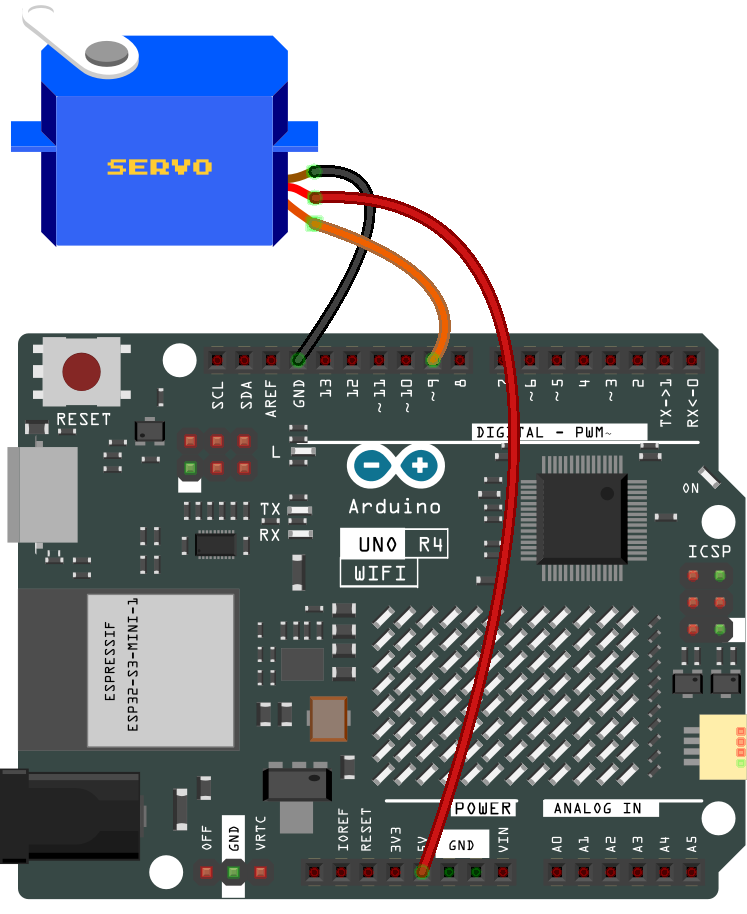
Wiring¶
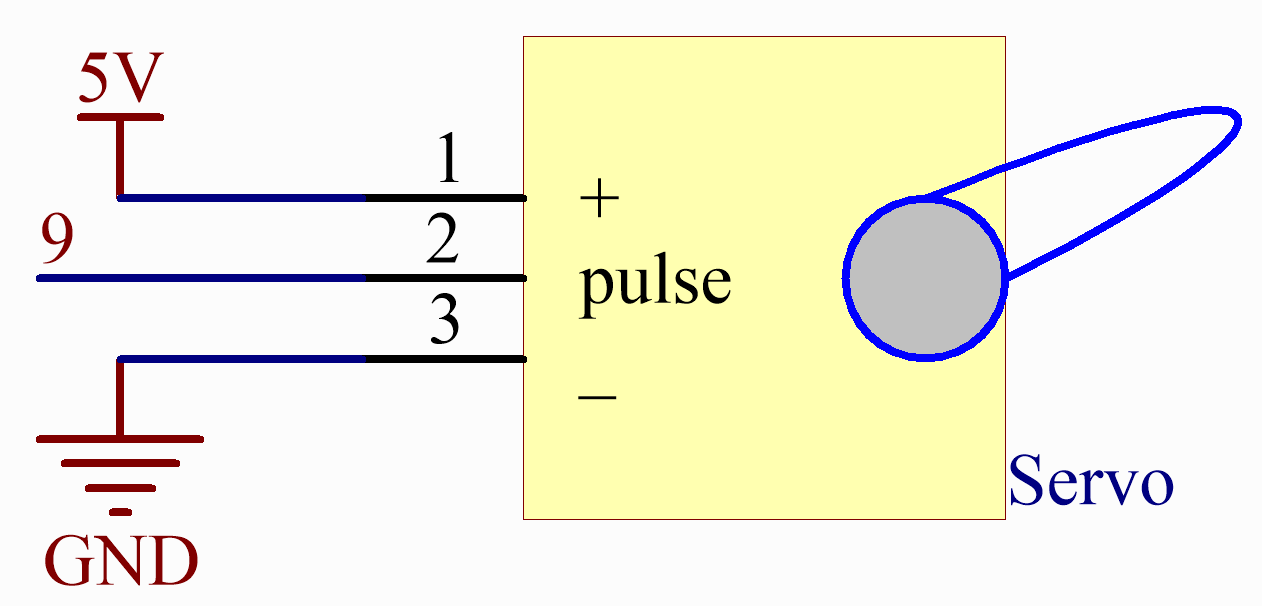
Schematic Diagram¶
Code¶
Note
You can open the file
27-servo.inounder the path ofelite-explorer-kit-main\basic_project\27-servodirectly.Or copy this code into Arduino IDE.
Code Analysis¶
Here, the
Servolibrary is included which allows for easy control of the servo motor. The pin connected to the servo and the initial angle of the servo are also defined.#include <Servo.h> const int servoPin = 9; // Define the servo pin int angle = 0; // Initialize the angle variable to 0 degrees Servo servo; // Create a servo object
The
setup()function runs once when the Arduino starts. The servo is attached to the defined pin using theattach()function.void setup() { servo.attach(servoPin); }
The main loop has two
forloops. The first loop increases the angle from 0 to 180 degrees, and the second loop decreases the angle from 180 to 0 degrees. Theservo.write(angle)command sets the servo to the specified angle. Thedelay(15)causes the servo to wait for 15 milliseconds before moving to the next angle, controlling the speed of the scanning movement.void loop() { // scan from 0 to 180 degrees for (angle = 0; angle < 180; angle++) { servo.write(angle); delay(15); } // now scan back from 180 to 0 degrees for (angle = 180; angle > 0; angle--) { servo.write(angle); delay(15); } }