Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
4.1.14 Password Lock¶
Introduction¶
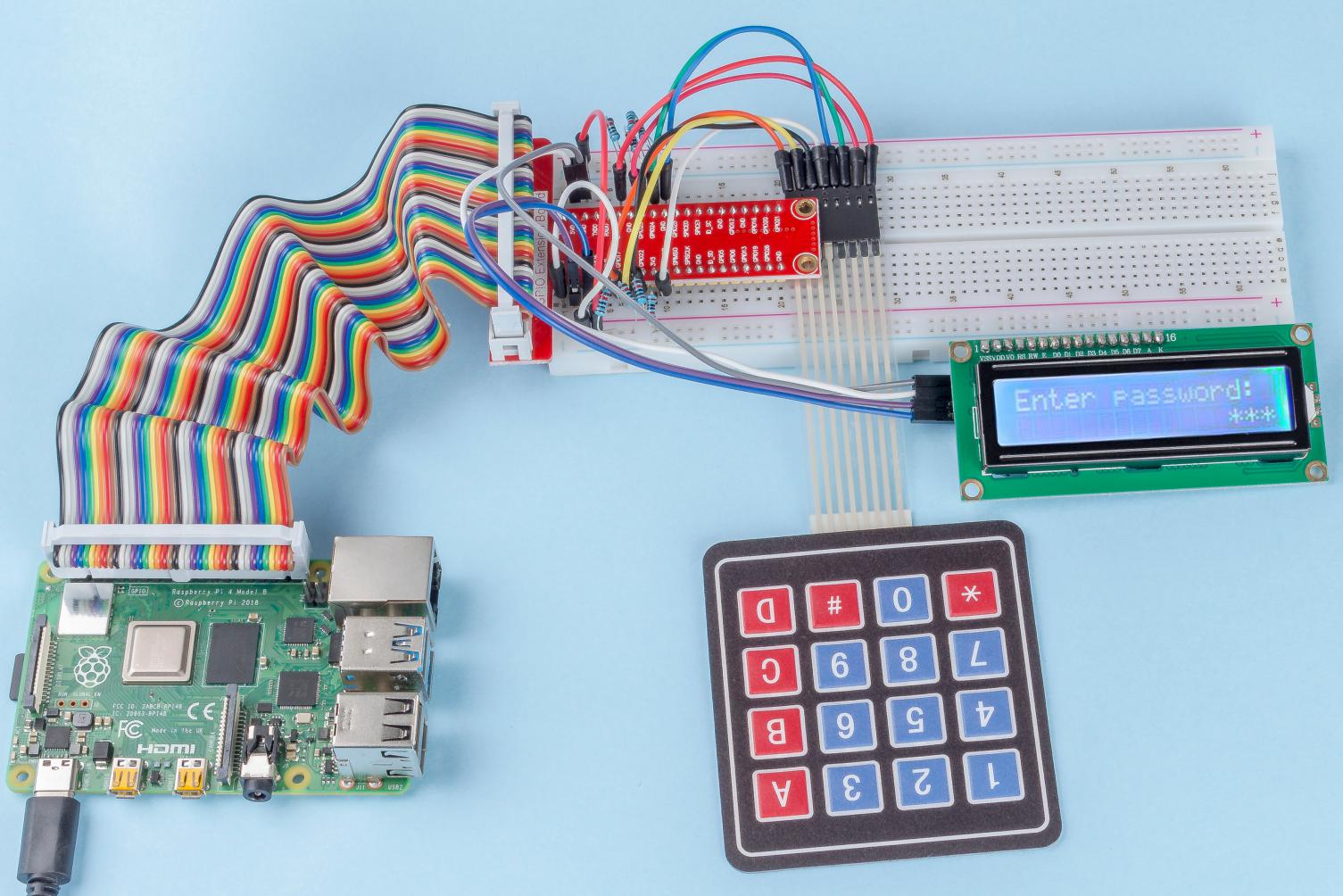
In this project, we will use a keypad and a LCD to make a combination lock. The LCD will display a corresponding prompt for you to type your password on the Keypad. If the password is input correctly, “Correct” will be displayed.
On the basis of this project, we can add additional electronic components, such as buzzer, LED and so on, to add different experimental phenomena for password input.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
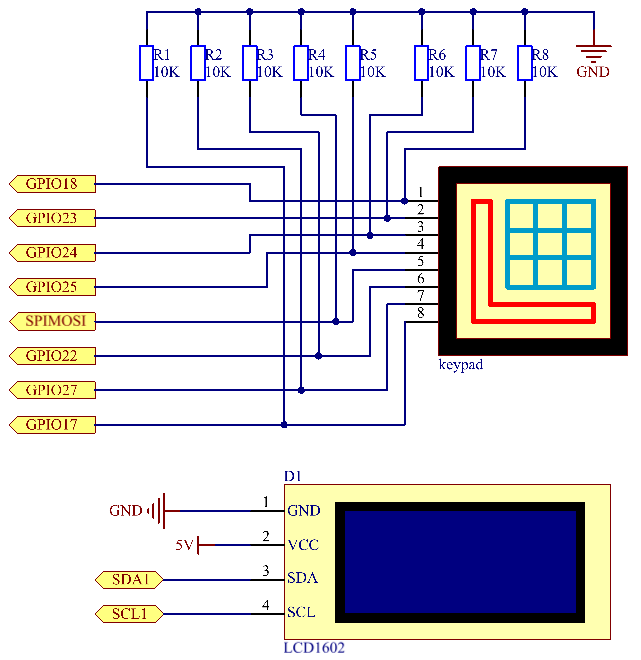
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO23 |
Pin 16 |
4 |
23 |
GPIO24 |
Pin 18 |
5 |
24 |
GPIO25 |
Pin 22 |
6 |
25 |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
SPIMOSI |
Pin 19 |
12 |
10 |
SDA1 |
Pin 3 |
||
SCL1 |
Pin 5 |
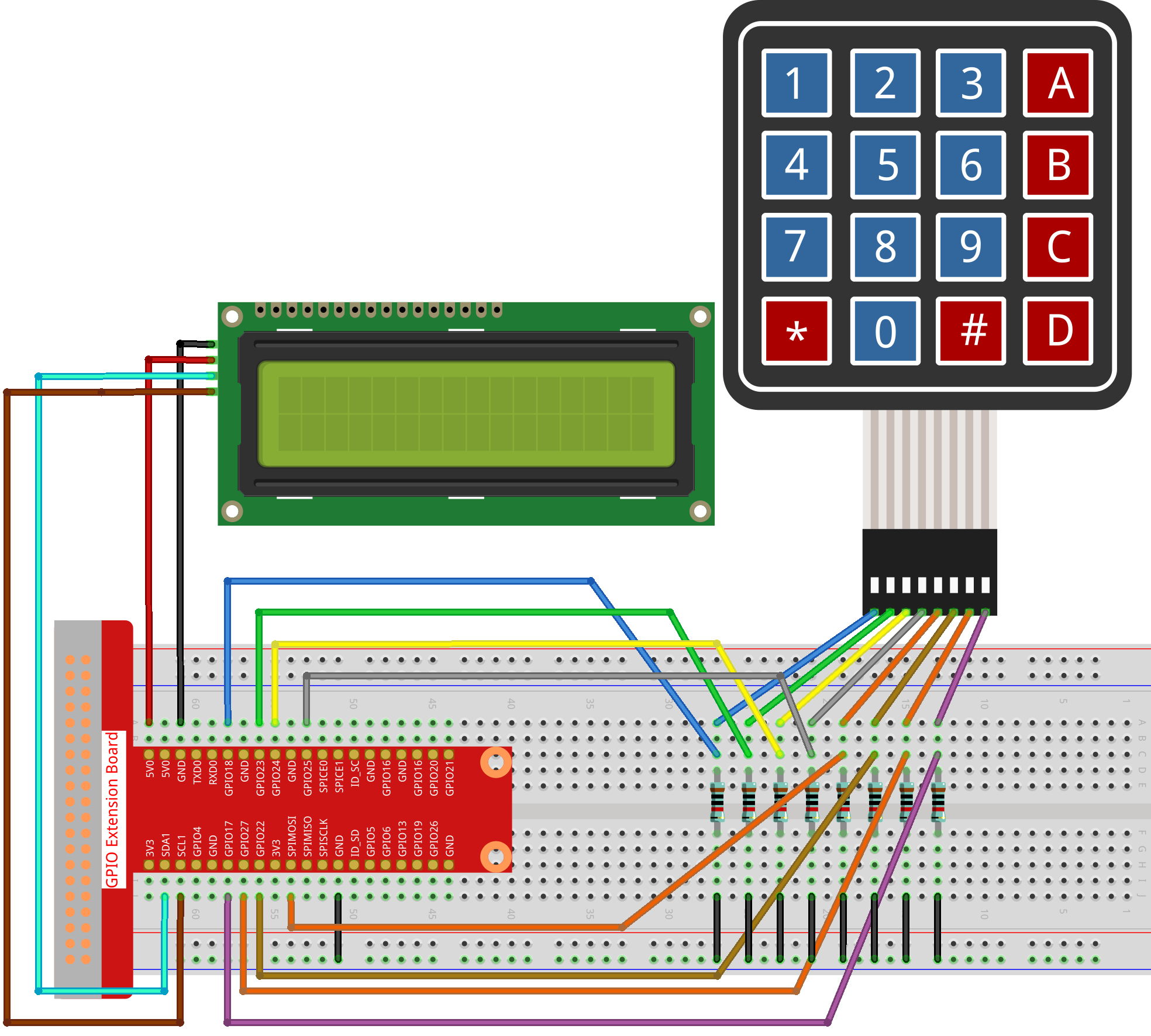
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Change directory.
cd ~/raphael-kit/python/
Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 4.1.14_PasswordLock.py
After the code runs, keypad is used to input password: 1984. If the “CORRECT” appears on LCD1602, there is no wrong with the password; otherwise, “WRONG KEY” will appear.
Note
If you get the error
FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/dev/i2c-1', you need to refer to I2C Configuration to enable the I2C.If you get
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'smbus2'error, please runsudo pip3 install smbus2.If the error
OSError: [Errno 121] Remote I/O errorappears, it means the module is miswired or the module is broken.If the code and wiring are fine, but the LCD still does not display content, you can turn the potentiometer on the back to increase the contrast.
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like raphael-kit/python. After modifying the code, you can run it directly to see the effect.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import LCD1602
##################### HERE IS THE KEYPAD LIBRARY TRANSPLANTED FROM Arduino ############
#class Key:Define some of the properties of Key
class Keypad():
def __init__(self, rowsPins, colsPins, keys):
self.rowsPins = rowsPins
self.colsPins = colsPins
self.keys = keys
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(self.rowsPins, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.setup(self.colsPins, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN)
def read(self):
pressed_keys = []
for i, row in enumerate(self.rowsPins):
GPIO.output(row, GPIO.HIGH)
for j, col in enumerate(self.colsPins):
index = i * len(self.colsPins) + j
if (GPIO.input(col) == 1):
pressed_keys.append(self.keys[index])
GPIO.output(row, GPIO.LOW)
return pressed_keys
################ EXAMPLE CODE START HERE ################
LENS = 4
password=['1','9','8','4']
testword=['0','0','0','0']
keyIndex=0
def check():
for i in range(0,LENS):
if(password[i]!=testword[i]):
return 0
return 1
def setup():
global keypad, last_key_pressed
rowsPins = [18,23,24,25]
colsPins = [10,22,27,17]
keys = ["1","2","3","A",
"4","5","6","B",
"7","8","9","C",
"*","0","#","D"]
keypad = Keypad(rowsPins, colsPins, keys)
last_key_pressed = []
LCD1602.init(0x27, 1) # init(slave address, background light)
LCD1602.clear()
LCD1602.write(0, 0, 'WELCOME!')
LCD1602.write(2, 1, 'Enter password')
time.sleep(2)
def destroy():
LCD1602.clear()
GPIO.cleanup()
def loop():
global keyIndex
global LENS
global keypad, last_key_pressed
while(True):
pressed_keys = keypad.read()
if len(pressed_keys) != 0 and last_key_pressed != pressed_keys:
LCD1602.clear()
LCD1602.write(0, 0, "Enter password:")
LCD1602.write(15-keyIndex,1, pressed_keys)
testword[keyIndex]=pressed_keys
keyIndex+=1
if (keyIndex is LENS):
if (check() is 0):
LCD1602.clear()
LCD1602.write(3, 0, "WRONG KEY!")
LCD1602.write(0, 1, "please try again")
else:
LCD1602.clear()
LCD1602.write(4, 0, "CORRECT!")
LCD1602.write(2, 1, "welcome back")
keyIndex=keyIndex%LENS
last_key_pressed = pressed_keys
time.sleep(0.1)
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
try:
setup()
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
Code Explanation
LENS = 4
password=['1','9','8','4']
...
rowsPins = [18,23,24,25]
colsPins = [10,22,27,17]
keys = ["1","2","3","A",
"4","5","6","B",
"7","8","9","C",
"*","0","#","D"]
Here, we define the length of the password LENS, the array keys that store the matrix keyboard keys, and the array password that stores the correct password.
class Keypad():
def __init__(self, rowsPins, colsPins, keys):
self.rowsPins = rowsPins
self.colsPins = colsPins
self.keys = keys
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(self.rowsPins, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.setup(self.colsPins, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN)
...
This class is the code that reads the values of the pressed keys. Refer to 2.1.8 Keypad of this document for more details.
while(True):
pressed_keys = keypad.read()
if len(pressed_keys) != 0 and last_key_pressed != pressed_keys:
LCD1602.clear()
LCD1602.write(0, 0, "Enter password:")
LCD1602.write(15-keyIndex,1, pressed_keys)
testword[keyIndex]=pressed_keys
keyIndex+=1
...
Read the key value and store it in the test array testword. If the number of stored key values is more than 4, the correctness of the password is automatically verified, and the verification results are displayed on the LCD interface.
def check():
for i in range(0,LENS):
if(password[i]!=testword[i]):
return 0
return 1
Verify the correctness of the password. Return 1 if the password is entered correctly, and 0 if not.
Phenomenon Picture¶