4.1.16 Morse Code Generator¶
Introduction¶
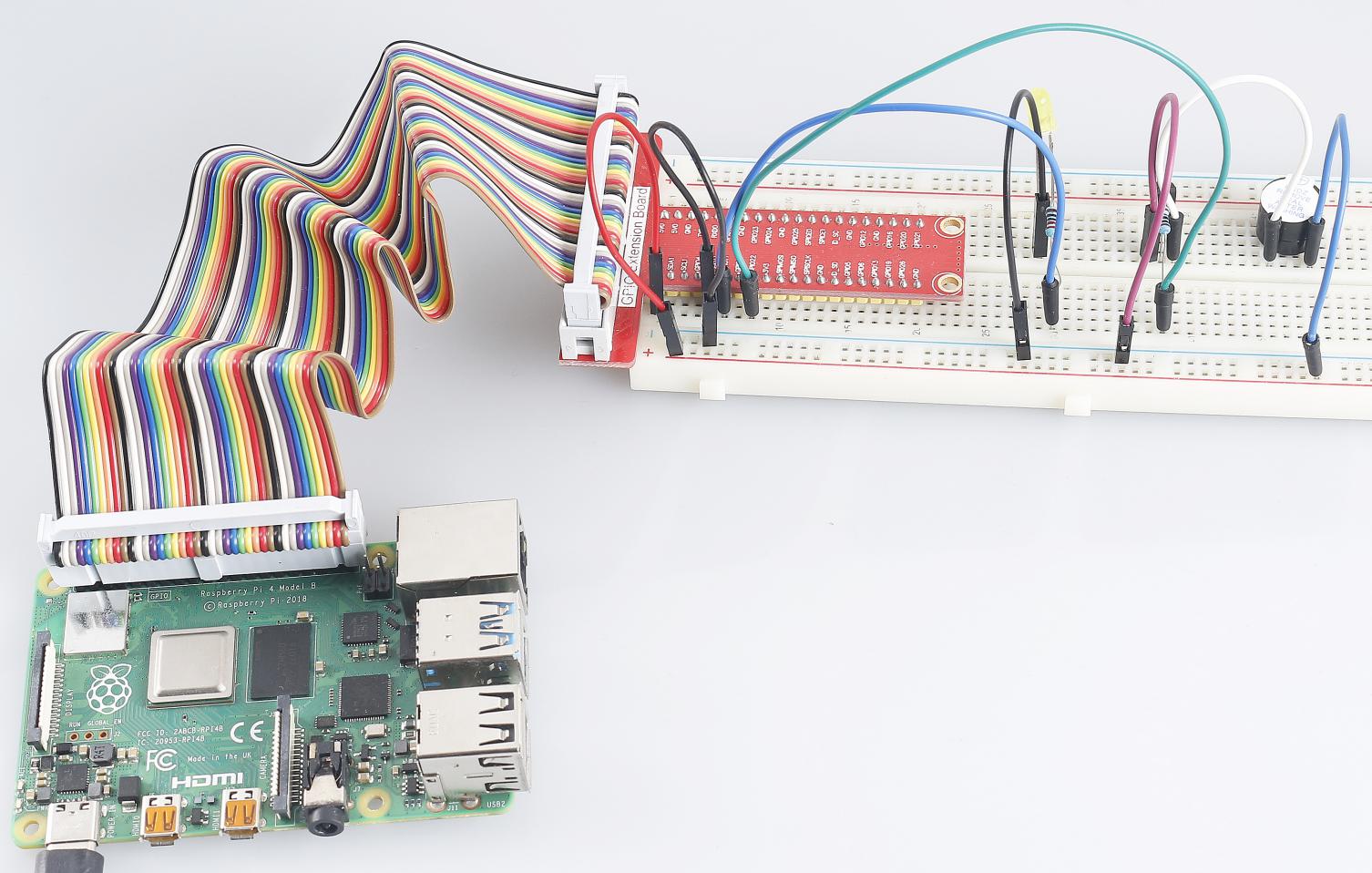
In this project, we’ll make a Morse code generator, where you type in a series of English letters in the Raspberry Pi to make it appear as Morse code.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
|
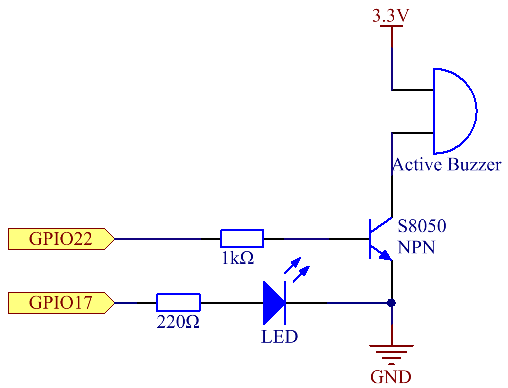
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
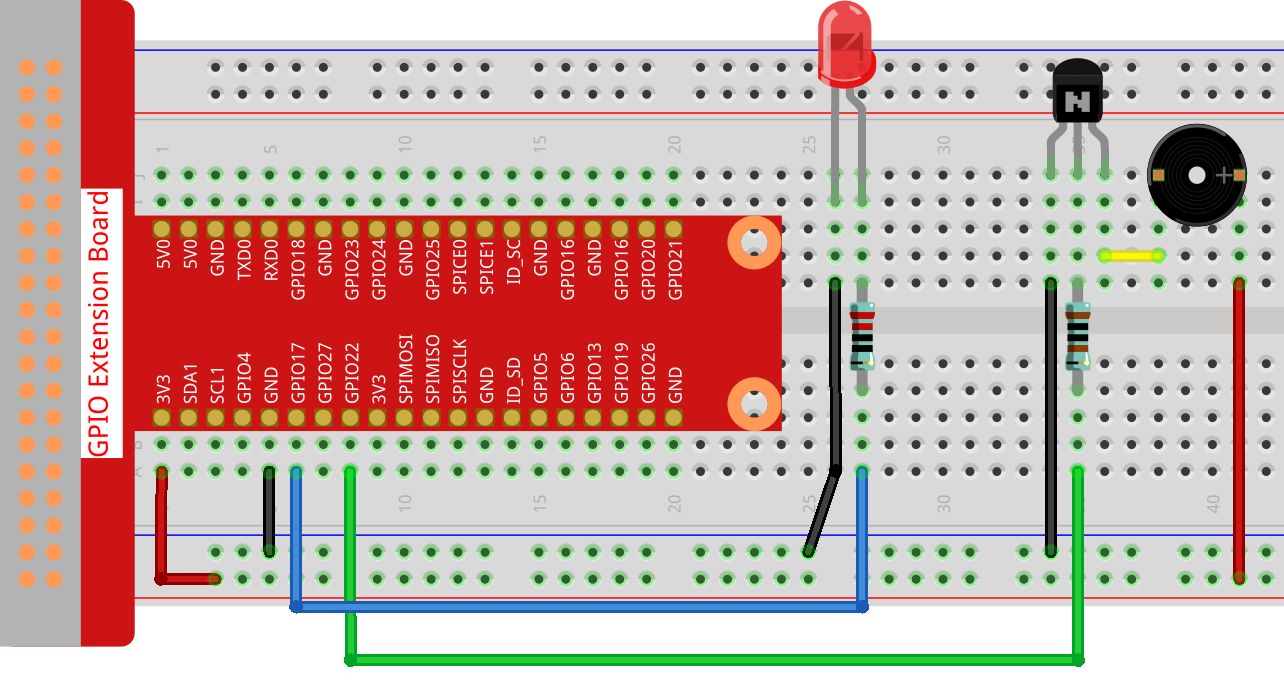
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit. (Pay attention to poles of the buzzer: The one with + label is the positive pole and the other is the negative.)
Step 2: Open the code file.
cd ~/raphael-kit/python
Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 4.1.16_MorseCodeGenerator.py
After the program runs, type a series of characters, and the buzzer and the LED will send the corresponding Morse code signals.
Code
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
BeepPin=22
ALedPin=17
MORSECODE = {
'A':'01', 'B':'1000', 'C':'1010', 'D':'100', 'E':'0', 'F':'0010', 'G':'110',
'H':'0000', 'I':'00', 'J':'0111', 'K':'101', 'L':'0100', 'M':'11', 'N':'10',
'O':'111', 'P':'0110', 'Q':'1101', 'R':'010', 'S':'000', 'T':'1',
'U':'001', 'V':'0001', 'W':'011', 'X':'1001', 'Y':'1011', 'Z':'1100',
'1':'01111', '2':'00111', '3':'00011', '4':'00001', '5':'00000',
'6':'10000', '7':'11000', '8':'11100', '9':'11110', '0':'11111',
'?':'001100', '/':'10010', ',':'110011', '.':'010101', ';':'101010',
'!':'101011', '@':'011010', ':':'111000',
}
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(BeepPin, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.setup(ALedPin,GPIO.OUT,initial=GPIO.LOW)
def on():
GPIO.output(BeepPin, 1)
GPIO.output(ALedPin, 1)
def off():
GPIO.output(BeepPin, 0)
GPIO.output(ALedPin, 0)
def beep(dt): # dt for delay time.
on()
time.sleep(dt)
off()
time.sleep(dt)
def morsecode(code):
pause = 0.25
for letter in code:
for tap in MORSECODE[letter]:
if tap == '0':
beep(pause/2)
if tap == '1':
beep(pause)
time.sleep(pause)
def main():
while True:
code=input("Please input the messenger:")
code = code.upper()
print(code)
morsecode(code)
def destroy():
print("")
GPIO.output(BeepPin, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(ALedPin, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.cleanup()
if __name__ == '__main__':
setup()
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
Code Explanation
MORSECODE = {
'A':'01', 'B':'1000', 'C':'1010', 'D':'100', 'E':'0', 'F':'0010', 'G':'110',
'H':'0000', 'I':'00', 'J':'0111', 'K':'101', 'L':'0100', 'M':'11', 'N':'10',
'O':'111', 'P':'0110', 'Q':'1101', 'R':'010', 'S':'000', 'T':'1',
'U':'001', 'V':'0001', 'W':'011', 'X':'1001', 'Y':'1011', 'Z':'1100',
'1':'01111', '2':'00111', '3':'00011', '4':'00001', '5':'00000',
'6':'10000', '7':'11000', '8':'11100', '9':'11110', '0':'11111',
'?':'001100', '/':'10010', ',':'110011', '.':'010101', ';':'101010',
'!':'101011', '@':'011010', ':':'111000',
}
This structure MORSE is the dictionary of the Morse code, containing characters A-Z, numbers 0-9 and marks “?” “/” “:” “,” “.” “;” “!” “@” .
def on():
GPIO.output(BeepPin, 1)
GPIO.output(ALedPin, 1)
The function on() starts the buzzer and the LED.
def off():
GPIO.output(BeepPin, 0)
GPIO.output(ALedPin, 0)
The function off() is used to turn off the buzzer and the LED.
def beep(dt): # x for dalay time.
on()
time.sleep(dt)
off()
time.sleep(dt)
Define a function beep() to make the buzzer and the LED emit sounds and
blink in a certain interval of dt.
def morsecode(code):
pause = 0.25
for letter in code:
for tap in MORSECODE[letter]:
if tap == '0':
beep(pause/2)
if tap == '1':
beep(pause)
time.sleep(pause)
The function morsecode() is used to process the Morse code of input
characters by making the “1” of the code keep emitting sounds or lights
and the “0”shortly emit sounds or lights, ex., input “SOS”, and there
will be a signal containing three short three long and then three short
segments “ · · · - - - · · · ”.
def main():
while True:
code=input("Please input the messenger:")
code = code.upper()
print(code)
morsecode(code)
When you type the relevant characters with the keyboard, upper() will
convert the input letters to their capital form.
printf() then prints the clear text on the computer screen, and the
morsecod() function causes the buzzer and the LED to emit Morse code.
Phenomenon Picture¶