Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
I2C LCD1602¶
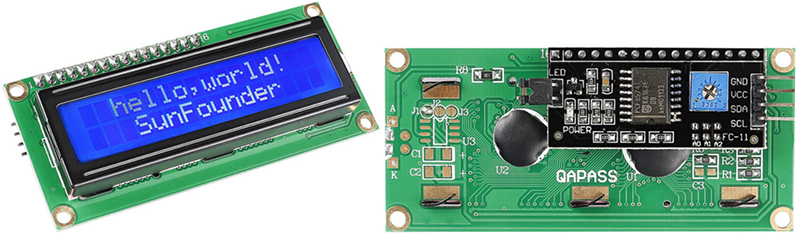
GND: Ground
VCC: Voltage supply, 5V.
SDA: Serial data line. Connect to VCC through a pullup resistor.
SCL: Serial clock line. Connect to VCC through a pullup resistor.
As we all know, though LCD and some other displays greatly enrich the man-machine interaction, they share a common weakness. When they are connected to a controller, multiple IOs will be occupied of the controller which has no so many outer ports. Also it restricts other functions of the controller.
Therefore, LCD1602 with an I2C module is developed to solve the problem. The I2C module has a built-in PCF8574 I2C chip that converts I2C serial data to parallel data for the LCD display.
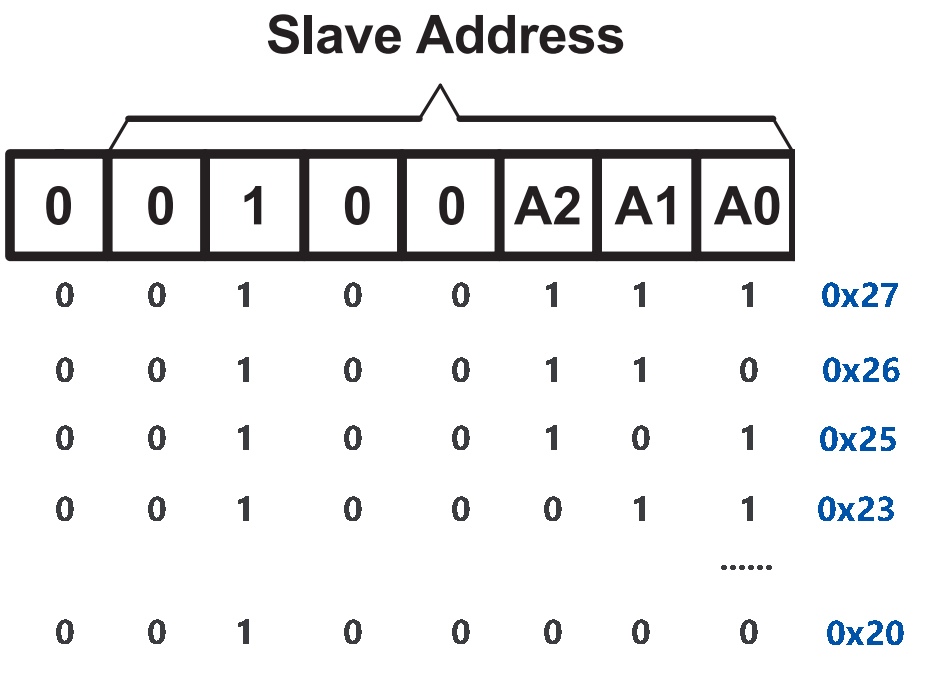
I2C Address
The default address is basically 0x27, in a few cases it may be 0x3F.
Taking the default address of 0x27 as an example, the device address can be modified by shorting the A0/A1/A2 pads; in the default state, A0/A1/A2 is 1, and if the pad is shorted, A0/A1/A2 is 0.
Backlight/Contrast
Backlight can be enabled by jumper cap, unplugg the jumper cap to disable the backlight. The blue potentiometer on the back is used to adjust the contrast (the ratio of brightness between the brightest white and the darkest black).
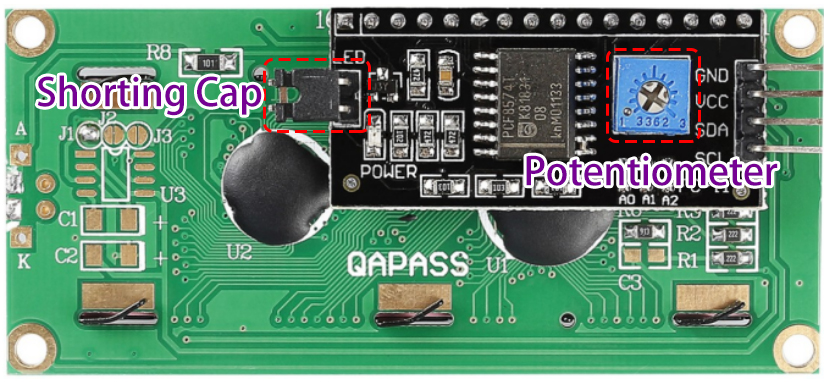
Shorting Cap: Backlight can be enabled by this cap,unplugg this cap to disable the backlight.
Potentiometer: It is used to adjust the contrast (the clarity of the displayed text), which is increased in the clockwise direction and decreased in the counterclockwise direction.
Example
1.1.7 I2C LCD1602 (C Project)
3.1.3 Reversing Alarm (C Project)
3.1.7 Overheat Monitor (C Project)
3.1.8 Password Lock (C Project)
3.1.11 GAME– Guess Number (C Project)
1.1.7 I2C LCD1602 (Python Project)
4.1.9 Reversing Alarm (Python Project)
4.1.13 Overheat Monitor (Python Project)
4.1.14 Password Lock (Python Project)
4.1.17 GAME– Guess Number (Python Project)