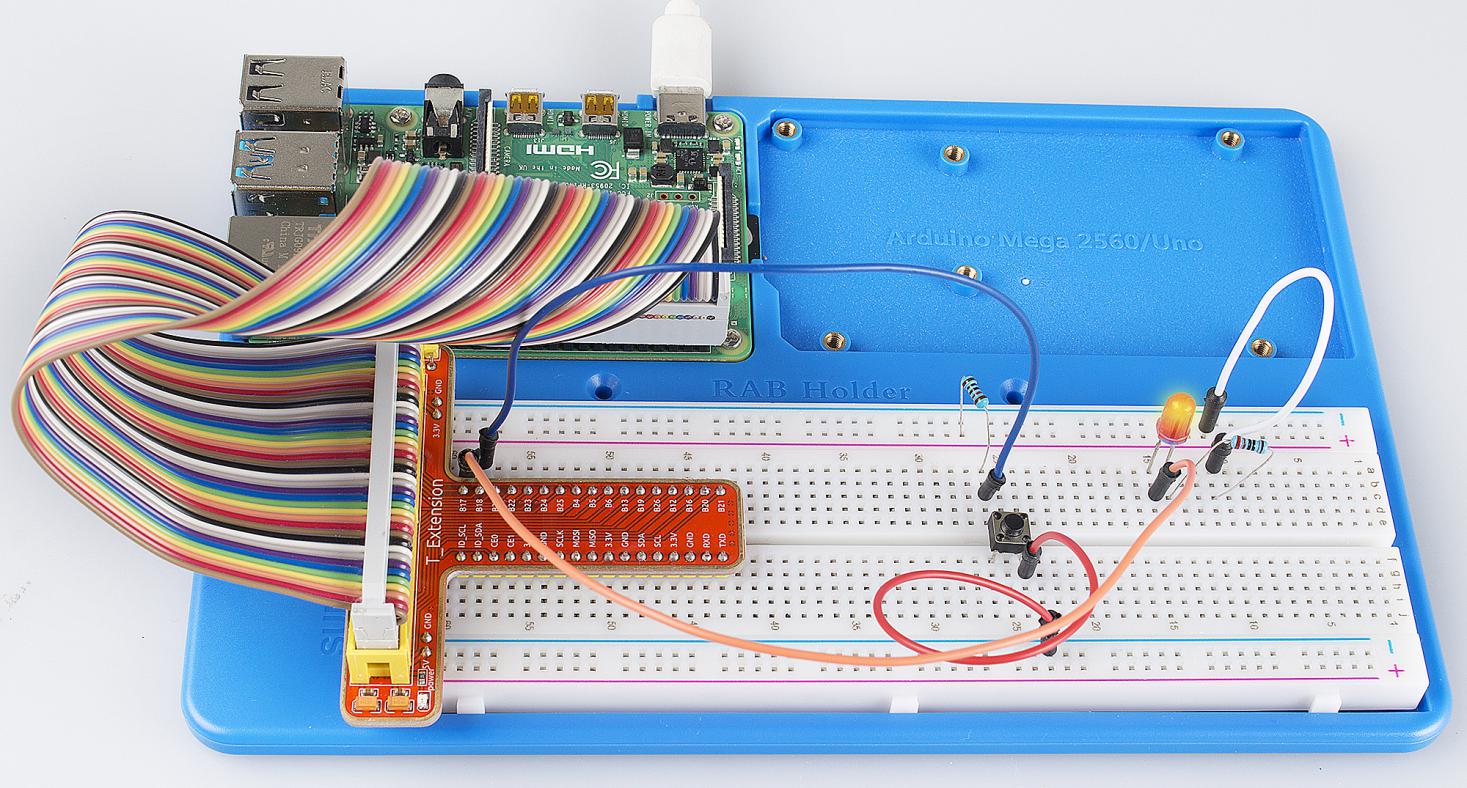
Lesson 2 Controlling an LED by a Button¶
Introduction¶
In this lesson, we will learn how to turn an LED on or off by a button.
Components¶
- 1 * Raspberry Pi
- 1 * Breadboard
- 1 * LED
- 1 * Button
- 2 * Resistor (220Ω, 10K)
- Jumper wires
- 1 * T-Extension Board
- 1 * 40-Pin Cable
Principle¶
Button
Buttons are a common component used to control electronic devices. They are usually used as switches to connect or disconnect circuits. Although buttons come in a variety of sizes and shapes, the one used here is a 6mm mini-button as shown in the following pictures. Pin 1 is connected to pin 2 and pin 3 to pin 4. So you just need to connect either of pin 1 and pin 2 to pin 3 or pin 4.
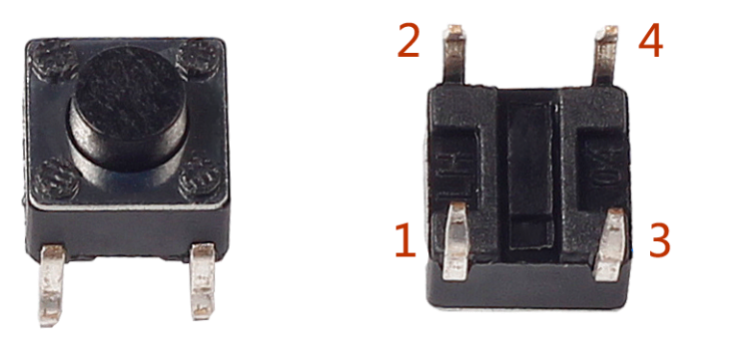
The following is the internal structure of a button. Since the pin 1 is connected to pin 2, and pin 3 to pin 4. The symbol on the right below is usually used to represent a button in circuits.
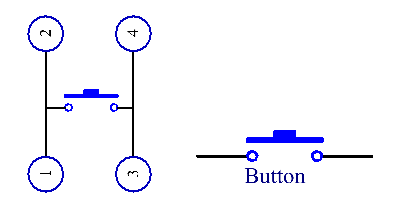
When the button is pressed, the 4 pins are connected, thus closing the circuit.
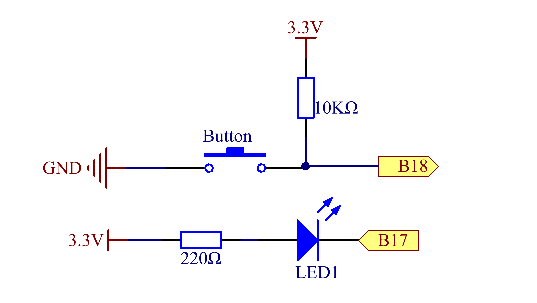
Use a normally open button as the input of Raspberry Pi, the detailed connection is as shown in the schematic diagram below. When the button is pressed, the B18 will turn into low level (0V). We can detect the state of the B18 through programming. That is, if the B18 turns into low level, it means the button is pressed. You can run the corresponding code when the button is pressed, and then the LED will light up.
Note
The longer pin of the LED is the anode and the shorter one is the cathode.
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
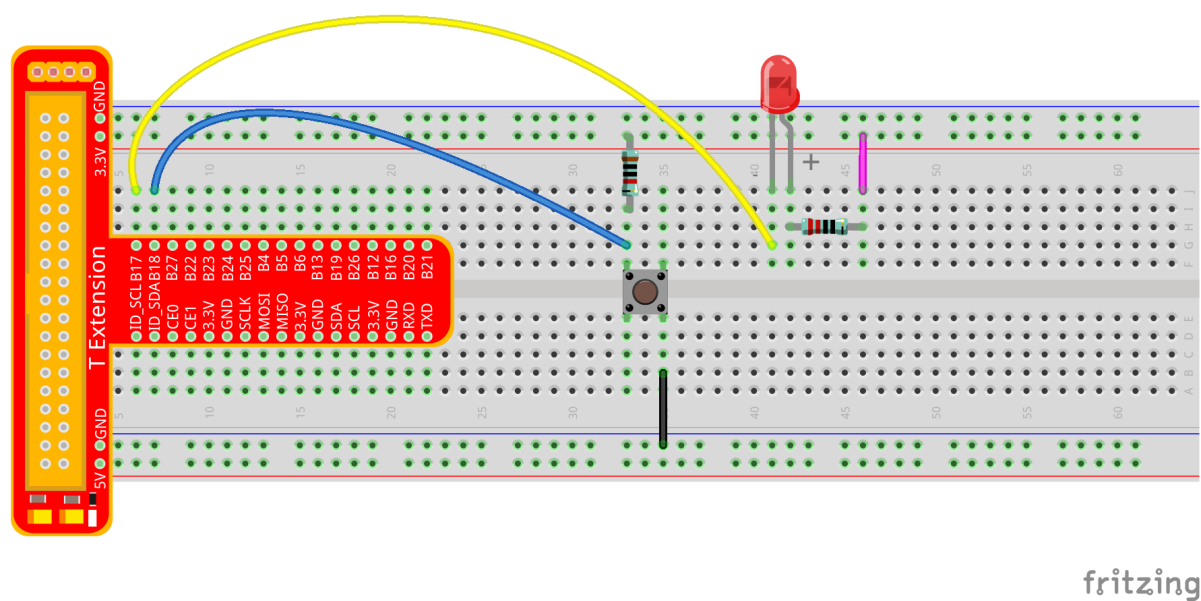
For C Language Users:¶
Step 2: Open the code file:
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_Super_Kit_V3.0_for_Raspberry_Pi/C
Note
Change directory to the path of the code in this experiment via cd.
Step 3: Compile the Code.
gcc 02_buttonControlLed.c -o 02_buttonControlLed -lwiringPi
or
make 02_buttonControlLed
Step 4: Run the executable file above.
sudo ./02_buttonControlLed
Note
If it does not work after running, or there is an error prompt: “wiringPi.h: No such file or directory”, please refer to C code is not working?.
Step 5: Check the code.
nano 02_buttonControlLed.c
Code
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define LedPin 0
#define ButtonPin 1
int main(void){
// When initialize wiring failed, print messageto screen
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
pinMode(LedPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ButtonPin, INPUT);
// Pull up to 3.3V,make GPIO1 a stable level
pullUpDnControl(ButtonPin, PUD_UP);
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("========================================\n");
printf("| Button control LED |\n");
printf("| ------------------------------ |\n");
printf("| LED connect to GPIO0 |\n");
printf("| Button connect to GPIO1 |\n");
printf("| |\n");
printf("| Press button to turn on LED. |\n");
printf("| |\n");
printf("| SunFounder|\n");
printf("========================================\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
printf("LED off...\n");
while(1){
// Indicate that button has pressed down
if(digitalRead(ButtonPin) == 0){
// Led on
digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW);
printf("...LED on\n");
delay(100);
}
else{
// Led off
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
printf("LED off...\n");
delay(100);
}
}
return 0;
}
Code Explanation
#define LedPin 0
/* Pin B17 in the T_Extension Board connects to the GPIO0.
GPIO0 corresponds to pin0 in the wiringPi pin figure. So in C program,
LedPin is defined as 0. */
#define ButtonPin 1
/* Pin B18 in the T_Extension Board connects to the
GPIO8. GPIO8 corresponds to pin1 in the wiringPi pin figure. So in C
program, LedPin is defined as 1.*/
pinMode(LedPin, OUTPUT) // Set LedPin as output to assign value to it.
pinMode(ButtonPin, INPUT) // Set ButtonPin as input to read the value of ButtonPin.
pullUpDnControl(ButtonPin, PUD_UP)
/* Set the ButtonPin as pull-up input.
When the button is not pressed, the I/O port is 3.3V. When the button is
pressed, the I/O port connects to GND (OV). You can judge the button
status by reading the level value of the I/O port.*/
while(1){
// indicate that button has pressed down
if(digitalRead(ButtonPin) == 0)
{
// LED on
digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW);
printf("...LED on\n");
delay(100);
}
else
{
// LED off
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
printf("LED off...\n");
delay(100);
}
/* digitalWrite (LedPin, HIGH) in while: close the LED. if (digitalRead(ButtonPin) == 0:
check whether the button has been pressed. Execute digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW)
when pressed to light up LED.*/
}
Press Ctrl+X to exit, if you have modified the code, there will be a prompt asking whether to save the changes or not. Type in Y (save) or N (don’t save). Then press Enter to exit. Repeat Step 3 and Step 4 to see the effect after modifying.
For Python Users:¶
Step 2: Open the code file.
cd /home/pi/SunFounder_Super_Kit_V3.0_for_Raspberry_Pi/Python
Step 3: Run the code.
sudo python3 02_buttonControlLed.py
Step 4: Check the code.
nano 02_buttonControlLed.py
Code
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
from sys import version_info
if version_info.major == 3:
raw_input = input
# Set #17 as LED pin
LedPin = 17
# Set #18 as button pin
BtnPin = 18
# Set Led status to True(OFF)
Led_status = True
# Define a function to print message at the beginning
def print_message():
print ("========================================")
print ("| Button control LED |")
print ("| ------------------------------ |")
print ("| LED connect to GPIO17 |")
print ("| Button connect to GPIO18 |")
print ("| |")
print ("| Press button to turn on/off LED. |")
print ("| |")
print ("| SunFounder|")
print ("========================================\n")
print ("Program is running...")
print ("Please press Ctrl+C to end the program...")
#raw_input ("Press Enter to begin\n")
# Define a setup function for some setup
def setup():
# Set the GPIO modes to BCM Numbering
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
# Set LedPin's mode to output,
# and initial level to high (3.3v)
GPIO.setup(LedPin, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.HIGH)
# Set BtnPin's mode to input,
# and pull up to high (3.3V)
GPIO.setup(BtnPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
# Set up a falling detect on BtnPin,
# and callback function to swLed
GPIO.add_event_detect(BtnPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=swLed)
# Define a callback function for button callback
def swLed(ev=None):
global Led_status
# Switch led status(on-->off; off-->on)
Led_status = not Led_status
GPIO.output(LedPin, Led_status)
if Led_status:
print ("LED OFF...")
else:
print ("...LED ON")
# Define a main function for main process
def main():
# Print messages
print_message()
while True:
# Don't do anything.
time.sleep(1)
# Define a destroy function for clean up everything after
# the script finished
def destroy():
# Turn off LED
# GPIO.output(LedPin, GPIO.HIGH)
# Release resource
GPIO.cleanup()
# If run this script directly, do:
if __name__ == '__main__':
destroy()
setup()
try:
main()
# When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program
# destroy() will be executed.
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
finally:
print("destroy")
destroy()
Code Explanation
LedPin = 17 # Set #17 as LED pin
BtnPin = 18 # Set #18 as button pin
# Set up a falling detect on BtnPin, and callback function to swled
GPIO.add_event_detect(BtnPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=swLED)
# Define a callback function for button callback, execute the function after the callback of the interrupt.
def swLed(ev=None):
global Led_status
# Switch Led status (on-->off; off-->on)
Led_status = not Led_status
GPIO.output(LedPin, Led_status)
if Led_status:
print ("LED OFF...")
else:
print ("...LED ON")
Now, press the button, and the LED will light up; press the button again, and the LED will go out. At the same time, the state of the LED will be printed on the screen.