Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
4.1.6 Battery Indicator¶
Introduction¶
In this project, we will make a battery indicator device that can visually display the battery level on the LED Bargraph.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
|
- |
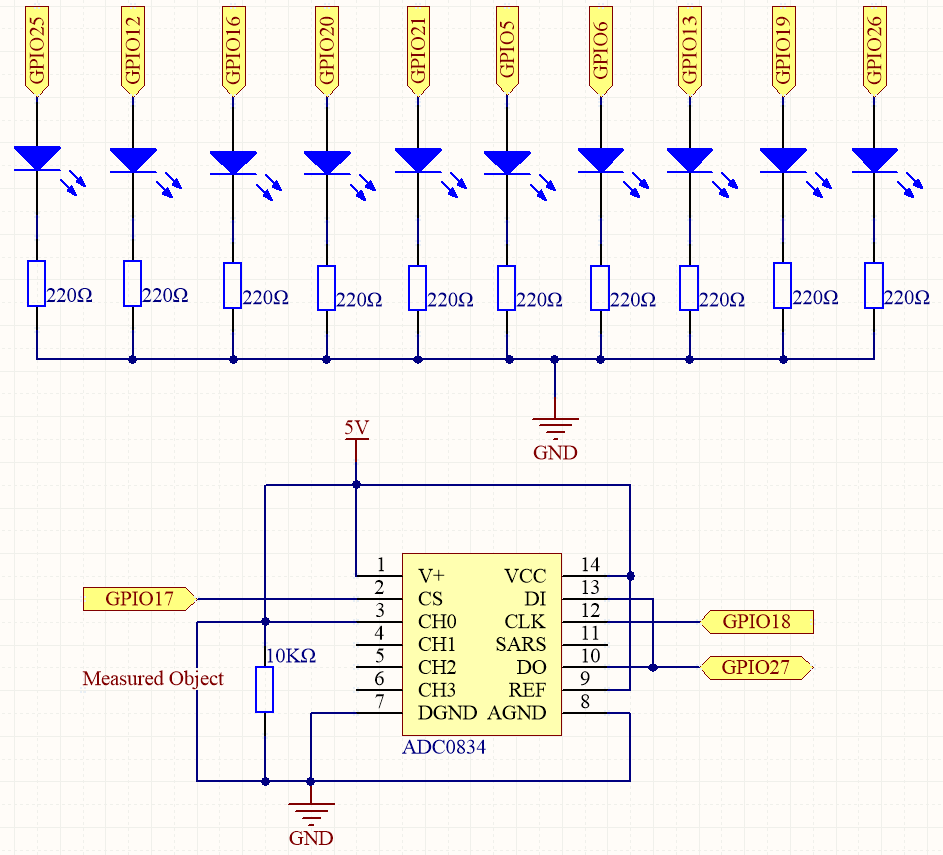
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO25 |
Pin 22 |
6 |
25 |
GPIO12 |
Pin 32 |
26 |
12 |
GPIO16 |
Pin 36 |
27 |
16 |
GPIO20 |
Pin 38 |
28 |
20 |
GPIO21 |
Pin 40 |
29 |
21 |
GPIO5 |
Pin 29 |
21 |
5 |
GPIO6 |
Pin 31 |
22 |
6 |
GPIO13 |
Pin 33 |
23 |
13 |
GPIO19 |
Pin 35 |
24 |
19 |
GPIO26 |
Pin 37 |
25 |
26 |
Experimental Procedures¶
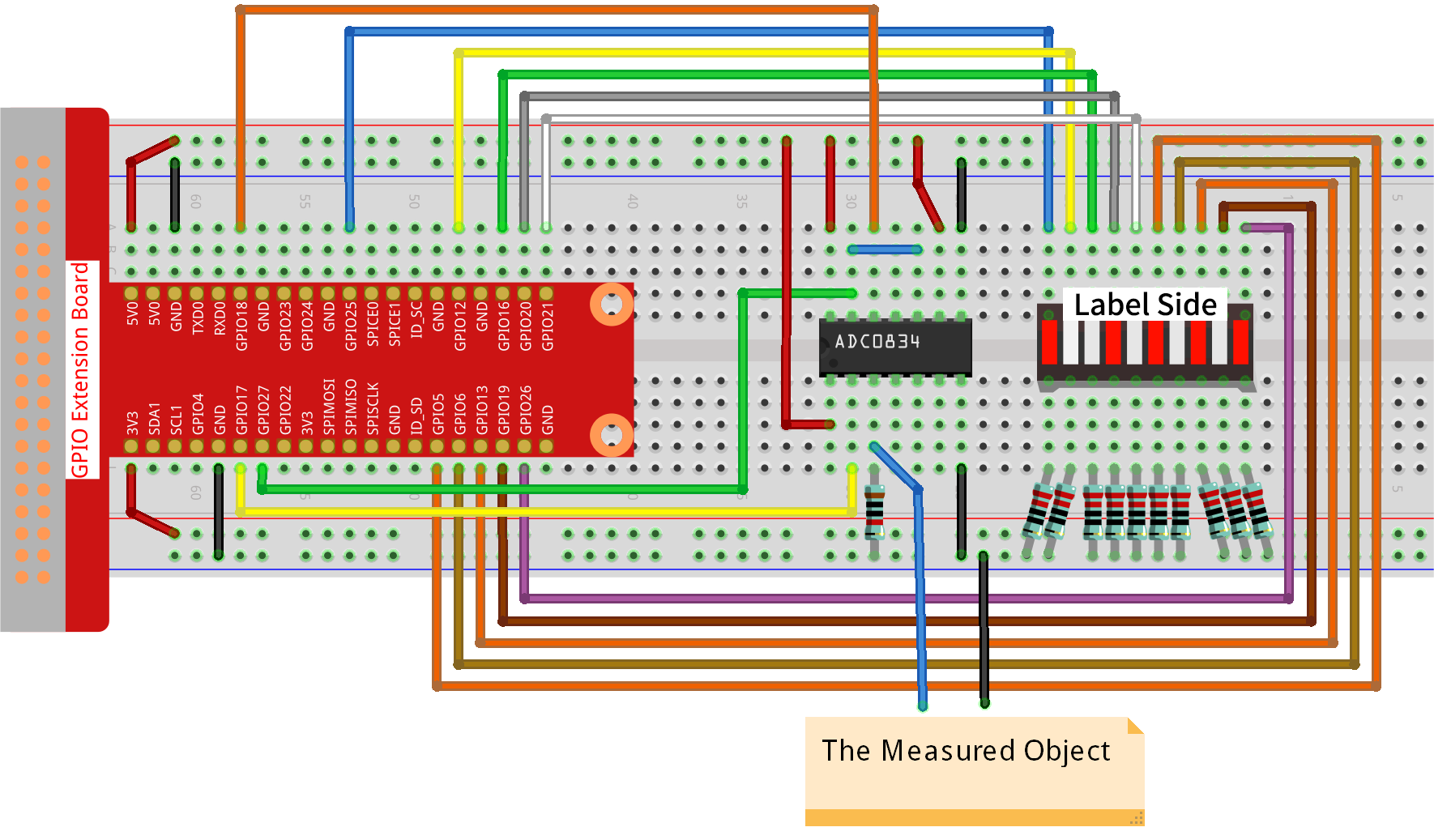
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/python-pi5
Step 3: Run the executable file.
sudo python3 4.1.11_BatteryIndicator_zero.py
After the program runs, give the 3rd pin of ADC0834 and the GND a lead-out wire separately and then lead them to the two poles of a battery separately. You can see the corresponding LED on the LED Bargraph is lit up to display the power level (measuring range: 0-5V).
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like raphael-kit/python-pi5. After modifying the code, you can run it directly to see the effect.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from gpiozero import LED
import ADC0834
import time
# List of GPIO pins to which LEDs are connected
ledPins = [25, 12, 16, 20, 21, 5, 6, 13, 19, 26]
# Initialize LED objects for each pin in the list
leds = [LED(pin) for pin in ledPins]
# Setup ADC0834 module
ADC0834.setup()
def LedBarGraph(value):
# Turn off all LEDs
for i in range(10):
leds[i].off()
# Turn on LEDs up to the specified value
for i in range(value):
leds[i].on()
try:
# Main loop to continuously update LED bar graph
while True:
# Read analog value from ADC0834
analogVal = ADC0834.getResult()
# Convert analog value to LED bar graph level
LedBarGraph(int(analogVal/25))
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# Turn off all LEDs when program is interrupted
for i in range(10):
leds[i].off()
Code Explanation
This section imports the necessary libraries.
gpiozerois for controlling the LEDs,ADC0834for interfacing with the ADC module, andtimefor time-related operations.#!/usr/bin/env python3 from gpiozero import LED import ADC0834 import time
Defines the GPIO pins to which the LEDs are connected and initializes an array of LED objects for each pin. This allows for easy control of each LED in the array.
# List of GPIO pins to which LEDs are connected ledPins = [25, 12, 16, 20, 21, 5, 6, 13, 19, 26] # Initialize LED objects for each pin in the list leds = [LED(pin) for pin in ledPins]
Initializes the ADC0834 module for analog-to-digital conversion.
# Setup ADC0834 module ADC0834.setup()
This function turns off all LEDs and then turns on a number of LEDs based on the input value, effectively creating a bar graph representation.
def LedBarGraph(value): # Turn off all LEDs for i in range(10): leds[i].off() # Turn on LEDs up to the specified value for i in range(value): leds[i].on()
Continuously reads the analog value from the ADC0834 and updates the LED bar graph based on this value. The analog value is scaled down to a range of 0-10 for the 10 LEDs.
try: # Main loop to continuously update LED bar graph while True: # Read analog value from ADC0834 analogVal = ADC0834.getResult() # Convert analog value to LED bar graph level LedBarGraph(int(analogVal/25))
Ensures all LEDs are turned off when the program is interrupted (e.g., by pressing Ctrl+C).
except KeyboardInterrupt: # Turn off all LEDs when program is interrupted for i in range(10): leds[i].off()