While Loops¶
The while statement is used to execute a program in a loop, that is, to execute a program in a loop under certain conditions to handle the same task that needs to be processed repeatedly.
Its basic form is:
while test expression:
Body of while
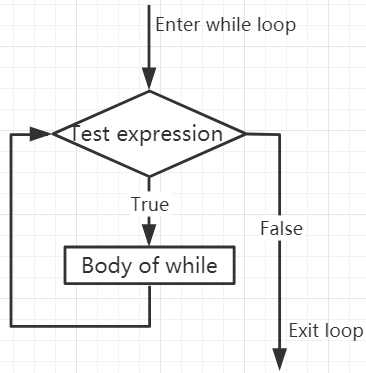
In the while loop, first check the test expression. Only when test expression evaluates to True, enter the body of the while. After one iteration, check the test expression again. This process continues until test expression evaluates to False.
In MicroPython, the body of the while loop is determined by indentation.
The body starts with an indentation and ends with the first unindented line.
Python interprets any non-zero value as True. None and 0 are interpreted as False.
while Loop Flowchart
x = 10
while x > 0:
print(x)
x -= 1
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Break Statement¶
With the break statement we can stop the loop even if the while condition is true:
x = 10
while x > 0:
print(x)
if x == 6:
break
x -= 1
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
10
9
8
7
6
While Loop with Else¶
Like the if loop, the while loop can also have an optional else block.
If the condition in the while loop is evaluated as False, the else part is executed.
x = 10
while x > 0:
print(x)
x -= 1
else:
print("Game Over")
>>> %Run -c $EDITOR_CONTENT
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Game Over