Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
3.1.9 Alarm Bell¶
Introduction¶
In this project, we will make a manual alarm device. You can replace the toggle switch with a thermistor or a photosensitive sensor to make a temperature alarm or a light alarm.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
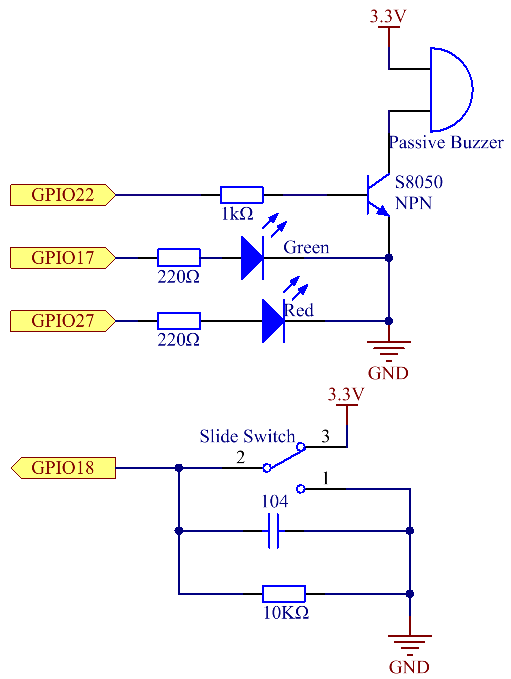
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
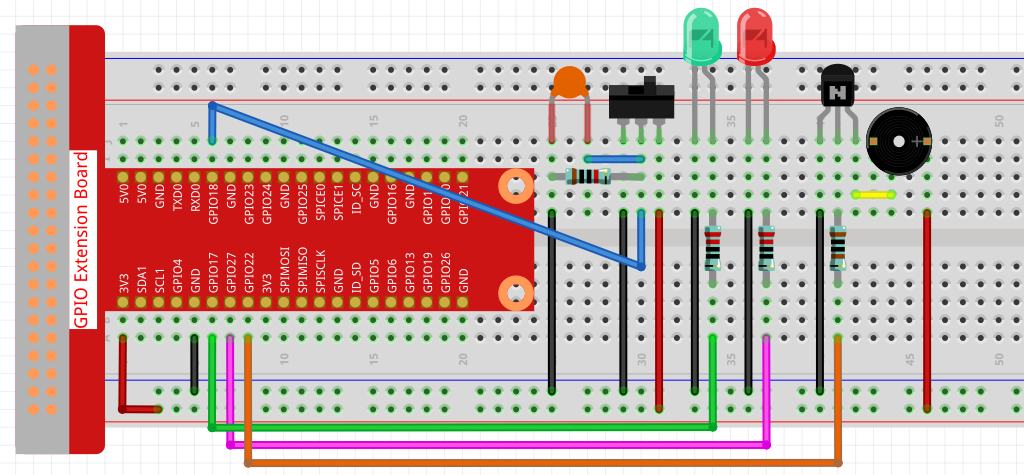
Experimental Procedures¶
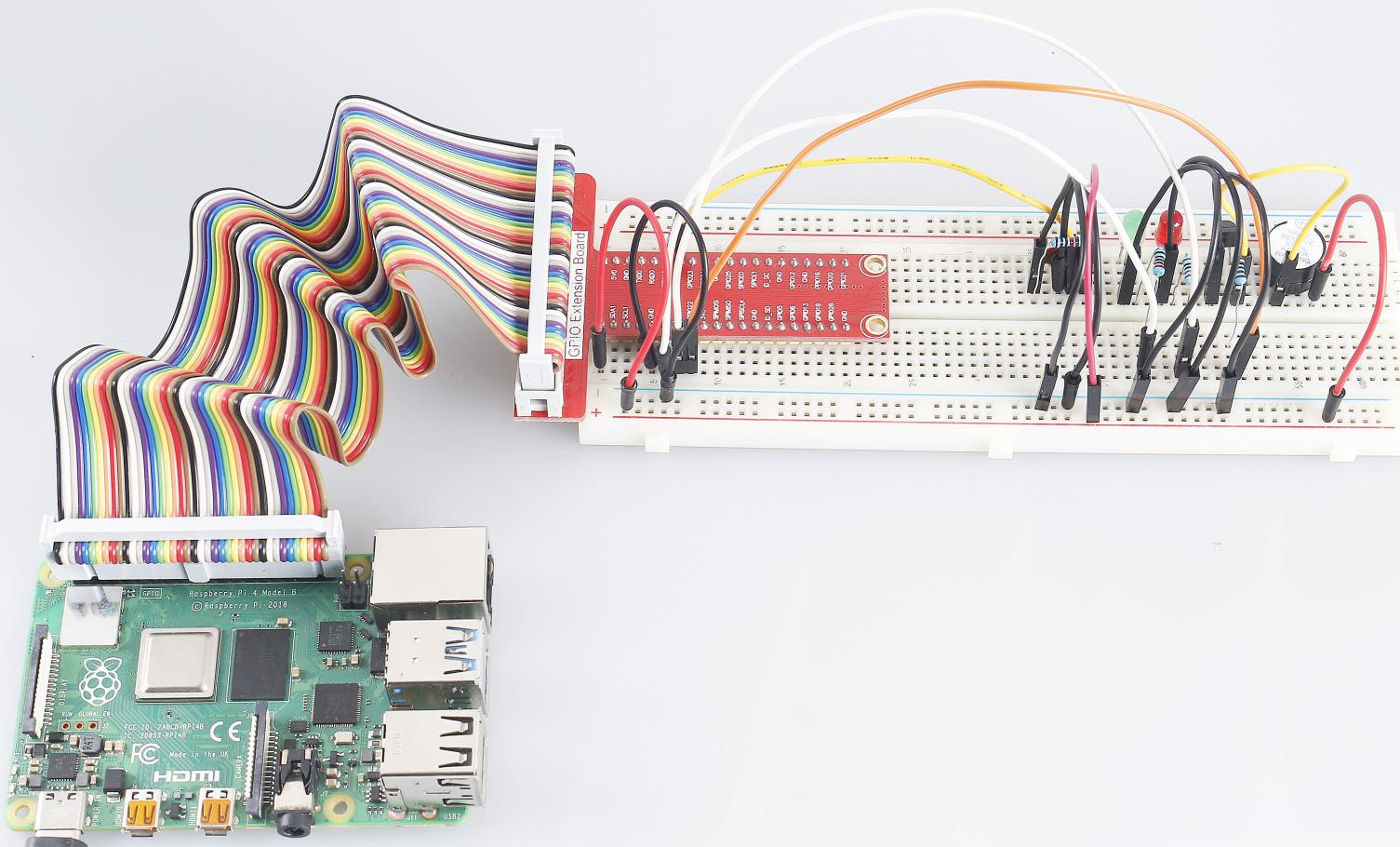
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Change directory.
cd ~/raphael-kit/c/3.1.9/
Step 3: Compile.
gcc 3.1.9_AlarmBell.c -lwiringPi -lpthread
Step 4: Run.
sudo ./a.out
After the program starts, put the slide switch to the right, and the buzzer will give out alarm sounds. At the same time, the red and green LEDs will flash at a certain frequency.
Note
If it does not work after running, or there is an error prompt: "wiringPi.h: No such file or directory", please refer to Install and Check the WiringPi.
Code Explanation
#include <pthread.h>
In this code, you’ll use a new library, pthread.h, which is a set of common thread libraries and can realize multithreading. We add the -lpthread parameter at compile time for the independent working of the LED and the buzzer.
void *ledWork(void *arg){
while(1)
{
if(flag==0){
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
digitalWrite(ALedPin,HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ALedPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(BLedPin,HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(BLedPin,LOW);
}
}
The function ledWork() helps to set the working state of these 2 LEDs:
it keeps the green LED lighting up for 0.5s and then turns off;
similarly, keeps the red LED lighting up for 0.5s and then turns off.
void *buzzWork(void *arg){
while(1)
{
if(flag==0){
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
if((note>=800)||(note<=130)){
pitch = -pitch;
}
note=note+pitch;
softToneWrite(BeepPin,note);
delay(10);
}
}
The function buzzWork() is used to set the working state of the buzzer.
Here we set the frequency as between 130 and 800, to accumulate or decay
at an interval of 20.
void on(){
flag = 1;
if(softToneCreate(BeepPin) == -1){
printf("setup softTone failed !");
return;
}
pthread_t tLed;
pthread_create(&tLed,NULL,ledWork,NULL);
pthread_t tBuzz;
pthread_create(&tBuzz,NULL,buzzWork,NULL);
}
In the function on():
Define the mark
flag=1, indicating the ending of the control thread.Create a software-controlled tone pin
BeepPin.Create two separate threads so that the LED and the buzzer can work at the same time.
pthread_t tLed: Declare a threadtLed.pthread_create(&tLed,NULL,ledWork,NULL): Create the thread and its prototype is as follows:
int pthread_create(pthread_t *restrict tidp,const pthread_attr_t*restrict_attr,void*(*start_rtn)(void*),void *restrict arg);
If successful, return 0 ;otherwise, return the fall number -1.
The first parameter is a pointer to the thread identifier.
The second one is used to set the thread attribute.
The third one is the starting address of the thread running function.
The last one is the one that runs the function.
void off(){
flag = 0;
softToneStop(BeepPin);
digitalWrite(ALedPin,LOW);
digitalWrite(BLedPin,LOW);
}
The function Off() defines “flag=0” so as to exit the threads
ledWork and BuzzWork and then turn off the buzzer and the LED.
int main(){
setup();
int lastState = 0;
while(1){
int currentState = digitalRead(switchPin);
if ((currentState == 1)&&(lastState==0)){
on();
}
else if((currentState == 0)&&(lastState==1)){
off();
}
lastState=currentState;
}
return 0;
}
Main() contains the whole process of the program: firstly read the value
of the slide switch; if the toggle switch is toggled to the right (the
reading is 1), the function on() is called, the buzzer is driven to emit
sounds and the the red and the green LEDs blink. Otherwise, the buzzer
and the LED don’t work.
Phenomenon Picture¶