3.1.2 Welcome¶
Introduction¶
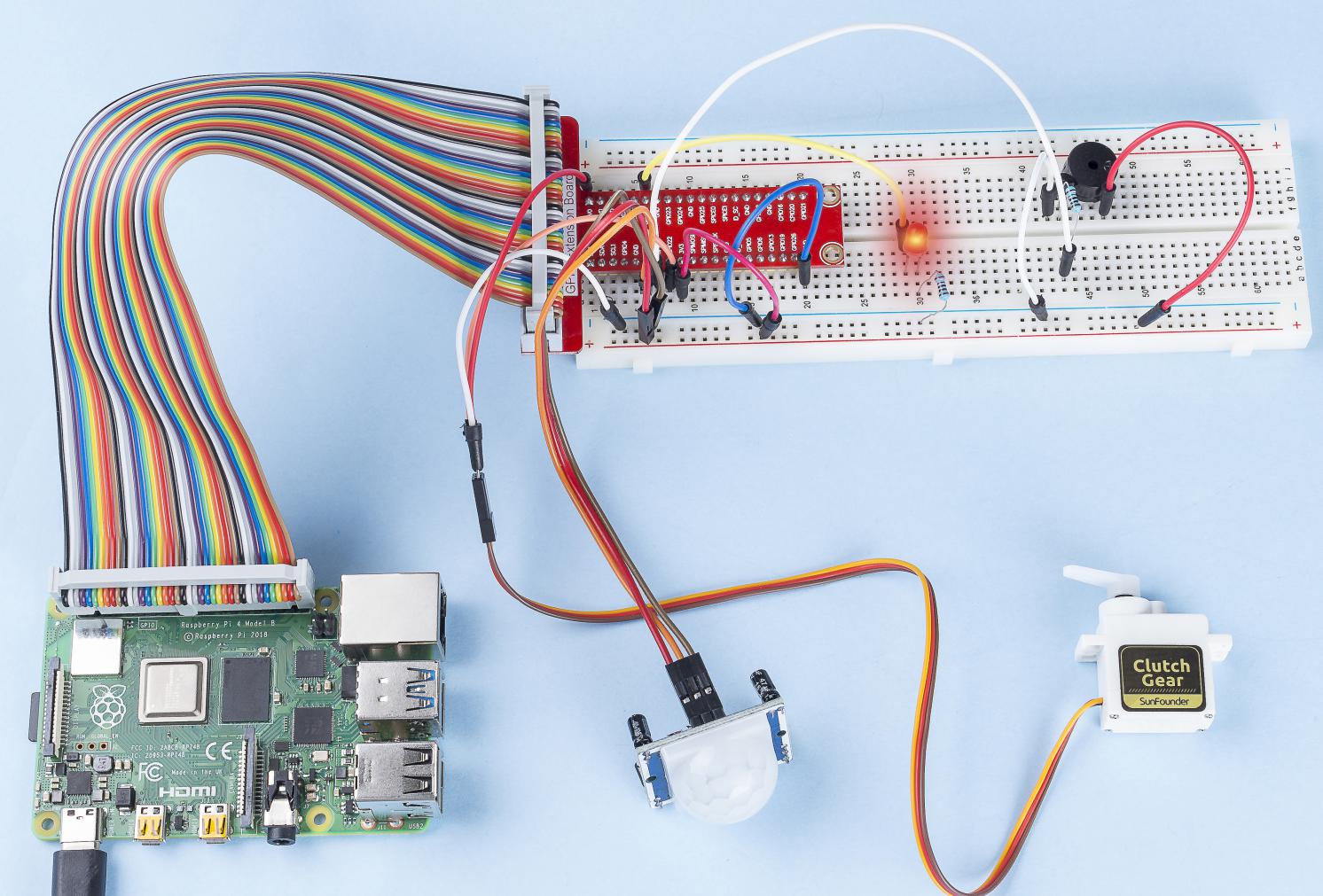
In this project, we will use PIR to sense the movement of pedestrians, and use servos, LED, buzzer to simulate the work of the sensor door of the convenience store. When the pedestrian appears within the sensing range of the PIR, the indicator light will be on, the door will be opened, and the buzzer will play the opening bell.
Components¶
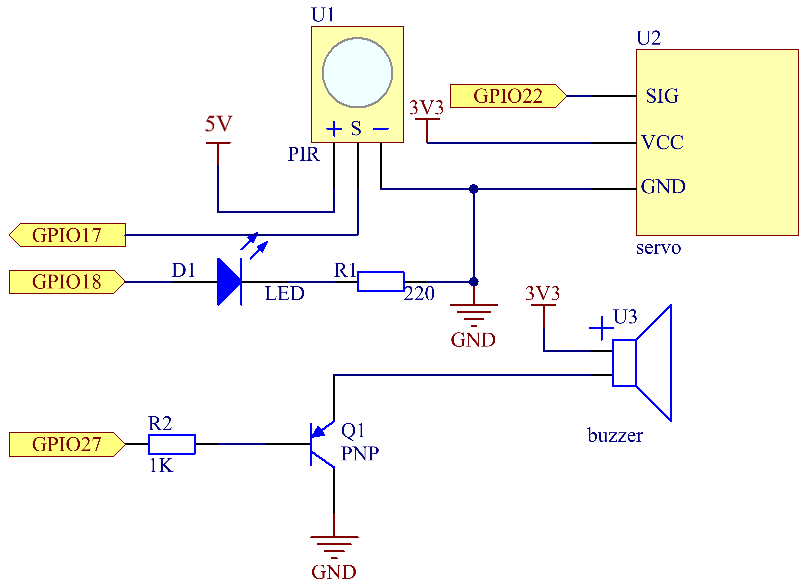
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
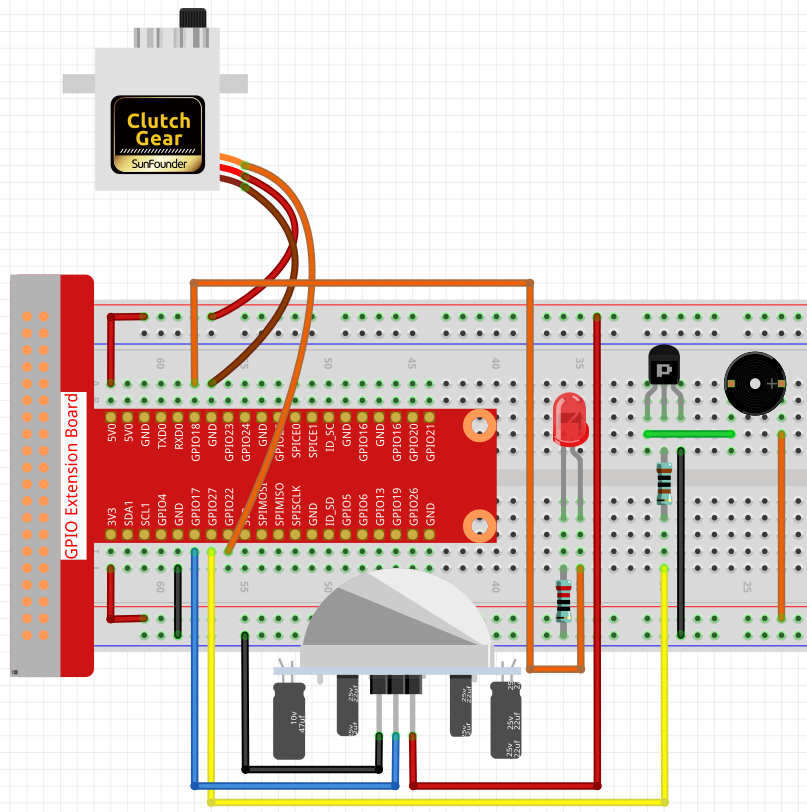
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
For C Language Users¶
Step 2: Change directory.
cd ~/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/c/3.1.2/
Step 3: Compile.
gcc 3.1.2_Welcome.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run.
sudo ./a.out
After the code runs, if the PIR sensor detects someone passing by, the door will automatically open (simulated by the servo), turn on the indicator and play the doorbell music. After the doorbell music plays, the system will automatically close the door and turn off the indicator light, waiting for the next time someone passes by.
There are two potentiometers on the PIR module: one is to adjust sensitivity and the other is to adjust the detection distance. To make the PIR module work better, you You need to turn both of them counterclockwise to the end.
Note
If it does not work after running, or there is an error prompt: "wiringPi.h: No such file or directory", please refer to C code is not working?.
Code Explanation
void setAngle(int pin, int angle){ //Create a funtion to control the angle of the servo.
if(angle < 0)
angle = 0;
if(angle > 180)
angle = 180;
softPwmWrite(pin,Map(angle, 0, 180, 5, 25));
}
Create a function, setAngle to write the angle in the servo that is 0-180.
void doorbell(){
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(song)/4;i++){
softToneWrite(BuzPin, song[i]);
delay(beat[i] * 250);
}
Create a function, doorbell to enable the buzzer to play music.
void closedoor(){
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); //led off
for(int i=180;i>-1;i--){ //make servo rotate from maximum angle to minimum angle
setAngle(servoPin,i);
delay(1);
}
}
Create a closedoor function to simulate closing the door, turn off the LED and let the servo turn from 180 degrees to 0 degree.
void opendoor(){
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); //led on
for(int i=0;i<181;i++){ //make servo rotate from minimum angle to maximum angle
setAngle(servoPin,i);
delay(1);
}
doorbell();
closedoor();
}
The function opendoor() includes several parts: turn on the indicator light, turn the servo (simulate the action of opening the door), play the doorbell music of the convenience store, and call the function closedoor() after playing music.
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print message to screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
if(softToneCreate(BuzPin) == -1){
printf("setup softTone failed !");
return 1;
......
In the function main(), initialize library wiringPi and setup softTone, then set ledPin to output state and pirPin to input state. If the PIR sensor detects someone passing by, the function opendoor will be called to simulate opening the door.
For Python Language Users¶
Step 2: Change directory.
cd ~/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python/
Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 3.1.2_Welcome.py
After the code runs, if the PIR sensor detects someone passing by, the door will automatically open (simulated by the servo), turn on the indicator and play the doorbell music. After the doorbell music plays, the system will automatically close the door and turn off the indicator light, waiting for the next time someone passes by.
There are two potentiometers on the PIR module: one is to adjust sensitivity and the other is to adjust the detection distance. To make the PIR module work better, you You need to turn both of them counterclockwise to the end.
code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python.
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
SERVO_MIN_PULSE = 500
SERVO_MAX_PULSE = 2500
ledPin = 18 # define the ledPin
pirPin = 17 # define the sensorPin
servoPin = 22 # define the servoPin
buzPin = 27 # define the buzzerpin
CL = [0, 131, 147, 165, 175, 196, 211, 248] # Frequency of Low C notes
CM = [0, 262, 294, 330, 350, 393, 441, 495] # Frequency of Middle C notes
CH = [0, 525, 589, 661, 700, 786, 882, 990] # Frequency of High C notes
song = [ CH[5],CH[2],CM[6],CH[2],CH[3],CH[6],CH[3],CH[5],CH[3],CM[6],CH[2] ]
beat = [ 1,1,1,1,1,2,1,1,1,1,1,]
def setup():
global p
global Buzz # Assign a global variable to replace GPIO.PWM
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set ledPin's mode is output
GPIO.setup(pirPin, GPIO.IN) # Set sensorPin's mode is input
GPIO.setup(servoPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set servoPin's mode is output
GPIO.output(servoPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set servoPin to low
GPIO.setup(buzPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pins' mode is output
Buzz = GPIO.PWM(buzPin, 440) # 440 is initial frequency.
Buzz.start(50) # Start Buzzer pin with 50% duty ration
p = GPIO.PWM(servoPin, 50) # set Frequece to 50Hz
p.start(0) # Duty Cycle = 0
def map(value, inMin, inMax, outMin, outMax):
return (outMax - outMin) * (value - inMin) / (inMax - inMin) + outMin
def setAngle(angle): # make the servo rotate to specific angle (0-180 degrees)
angle = max(0, min(180, angle))
pulse_width = map(angle, 0, 180, SERVO_MIN_PULSE, SERVO_MAX_PULSE)
pwm = map(pulse_width, 0, 20000, 0, 100)
p.ChangeDutyCycle(pwm)#map the angle to duty cycle and output it
def doorbell():
for i in range(1, len(song)): # Play song 1
Buzz.ChangeFrequency(song[i]) # Change the frequency along the song note
time.sleep(beat[i] * 0.25) # delay a note for beat * 0.25s
time.sleep(1) # Wait a second for next song.
def closedoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
for i in range(180, -1, -1): #make servo rotate from 180 to 0 deg
setAngle(i)
time.sleep(0.001)
time.sleep(1)
def opendoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
for i in range(0, 181, 1): #make servo rotate from 0 to 180 deg
setAngle(i) # Write to servo
time.sleep(0.001)
time.sleep(1)
doorbell()
closedoor()
def loop():
while True:
if GPIO.input(pirPin)==GPIO.HIGH:
opendoor()
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
p.stop()
Buzz.stop()
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
Code Explanation
def setup():
global p
global Buzz # Assign a global variable to replace GPIO.PWM
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set ledPin's mode is output
GPIO.setup(pirPin, GPIO.IN) # Set sensorPin's mode is input
GPIO.setup(buzPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pins' mode is output
Buzz = GPIO.PWM(buzPin, 440) # 440 is initial frequency.
Buzz.start(50) # Start Buzzer pin with 50% duty ration
GPIO.setup(servoPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set servoPin's mode is output
GPIO.output(servoPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set servoPin to low
p = GPIO.PWM(servoPin, 50) # set Frequece to 50Hz
p.start(0) # Duty Cycle = 0
These statements are used to initialize the pins of each component.
def setAngle(angle): # make the servo rotate to specific angle (0-180 degrees)
angle = max(0, min(180, angle))
pulse_width = map(angle, 0, 180, SERVO_MIN_PULSE, SERVO_MAX_PULSE)
pwm = map(pulse_width, 0, 20000, 0, 100)
p.ChangeDutyCycle(pwm)#map the angle to duty cycle and output it
Create a function, servowrite to write the angle in the servo that is 0-180.
def doorbell():
for i in range(1,len(song)): # Play song1
Buzz.ChangeFrequency(song[i]) # Change the frequency along the song note
time.sleep(beat[i] * 0.25) # delay a note for beat * 0.25s
Create a function, doorbell to enable the buzzer to play music.
def closedoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
Buzz.ChangeFrequency(1)
for i in range(180, -1, -1): #make servo rotate from 180 to 0 deg
setAngle(i)
time.sleep(0.001)
Close the door and turn off the indicator light.
def opendoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
for i in range(0, 181, 1): #make servo rotate from 0 to 180 deg
setAngle(i) # Write to servo
time.sleep(0.001)
doorbell()
closedoor()
The function, opendoor() consists of several parts: turn on the indicator light, turn the servo (to simulate the action of opening the door), play the doorbell music of the convenience store, and call the function , closedoor() after playing music.
def loop():
while True:
if GPIO.input(pirPin)==GPIO.HIGH:
opendoor()
When PIR senses that someone is passing by, it calls the function, opendoor().
Phenomenon Picture¶