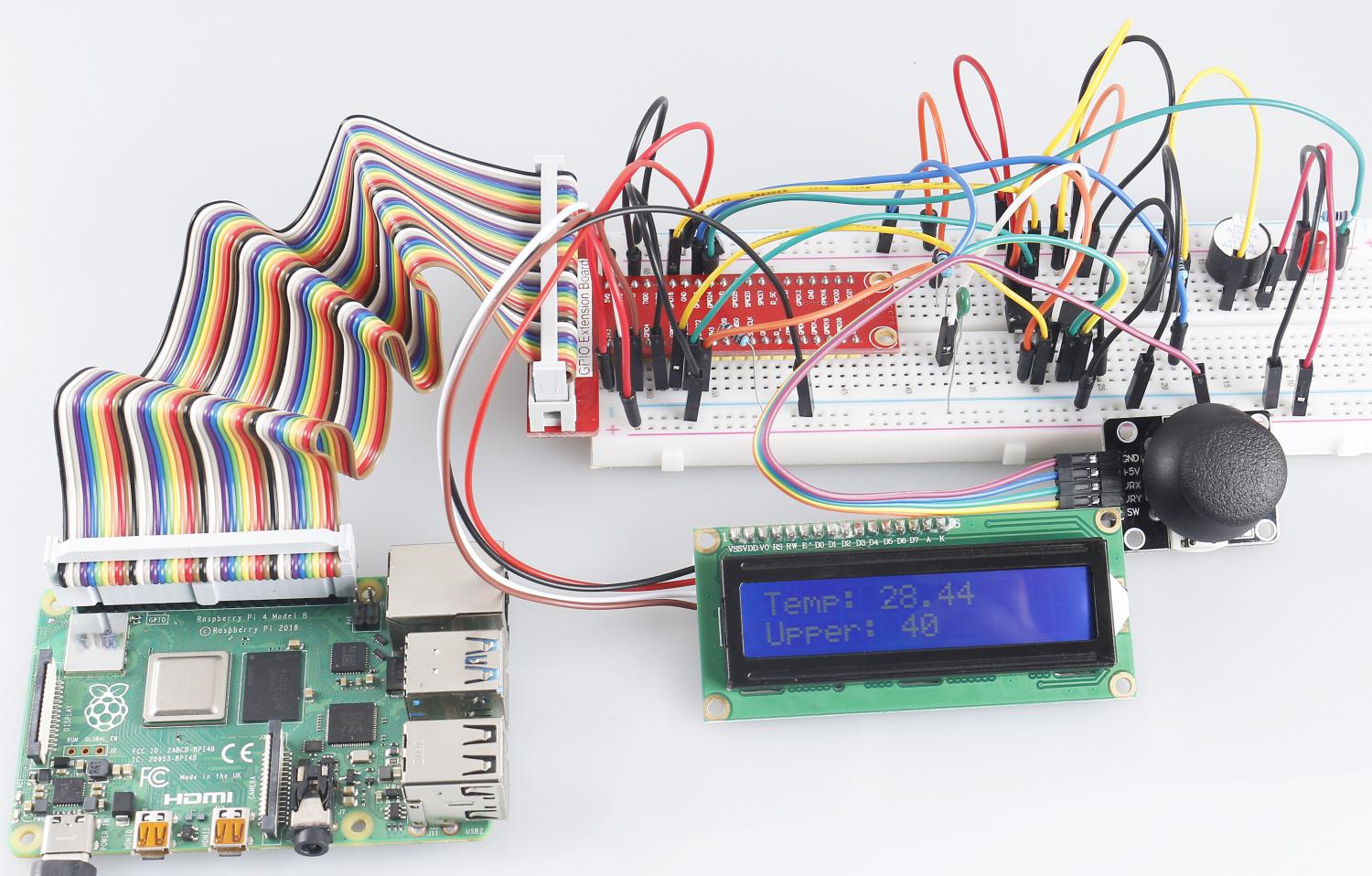
3.1.8 Overheat Monitor¶
Introduction¶
You may want to make an overheat monitoring device that applies to various situations, ex., in the factory, if we want to have an alarm and the timely automatic turning off of the machine when there is a circuit overheating. In this lesson, we will use thermistor, joystick, buzzer, LED and LCD to make an smart temperature monitoring device whose threshold is adjustable.
Components¶
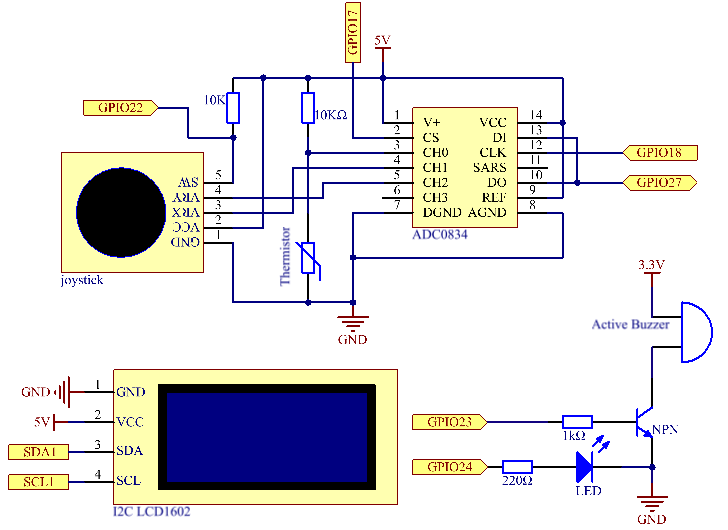
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin15 |
3 |
22 |
GPIO23 |
Pin16 |
4 |
23 |
GPIO24 |
Pin18 |
5 |
24 |
SDA1 |
Pin 3 |
||
SCL1 |
Pin 5 |
Experimental Procedures¶
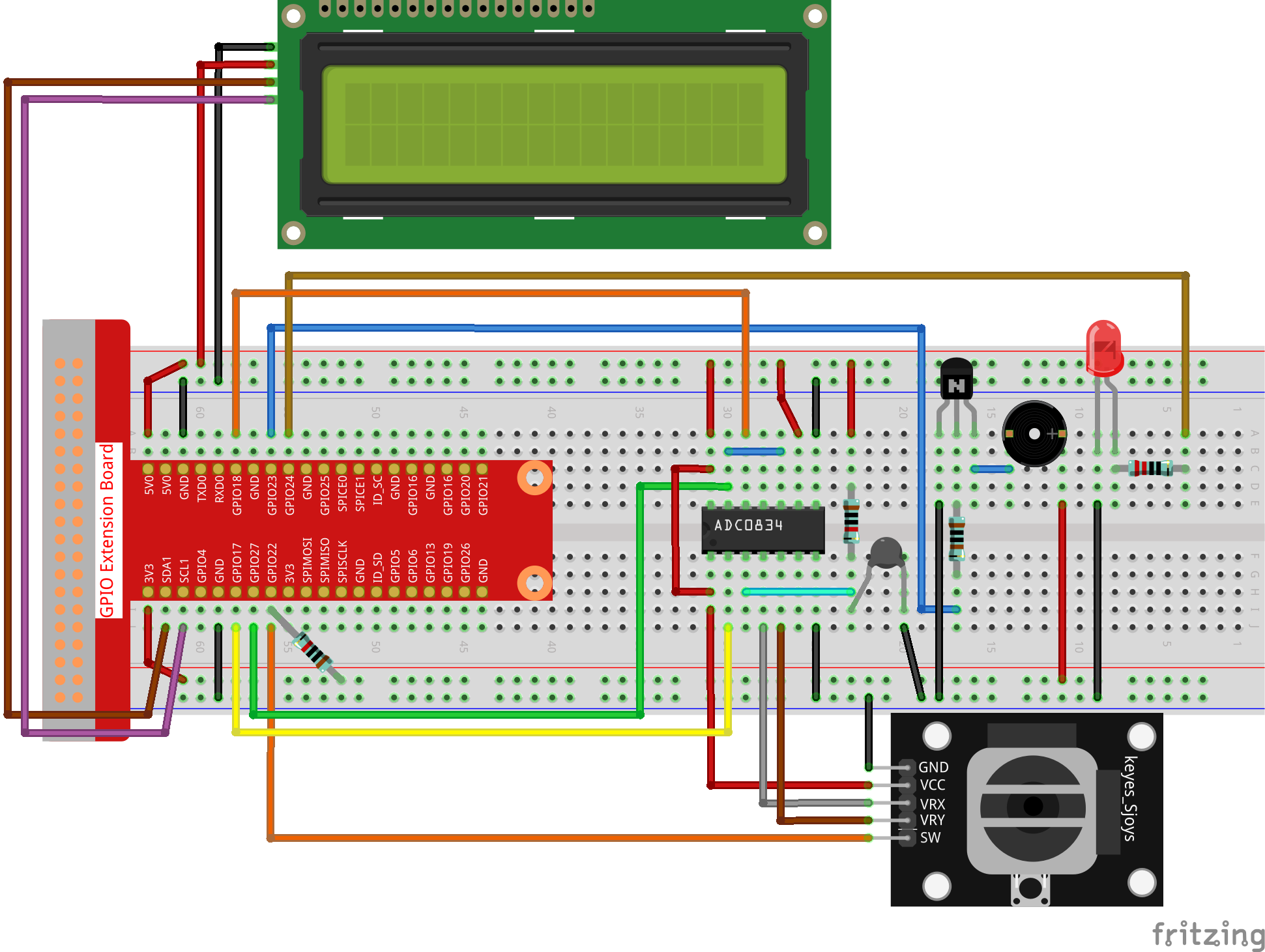
Step 1: Build the circuit.
For C Language Users¶
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/c/3.1.8/
Step 3: Compile the code.
gcc 3.1.8_OverheatMonitor.c -lwiringPi -lm
Step 4: Run the executable file.
sudo ./a.out
As the code runs, the current temperature and the high-temperature threshold 40 are displayed on I2C LCD1602. If the current temperature is larger than the threshold, the buzzer and LED are started to alarm you.
Note
If it does not work after running, or there is an error prompt: "wiringPi.h: No such file or directory", please refer to C code is not working?.
Joystick here is for your pressing to adjust the high-temperature threshold. Toggling the Joystick in the direction of X-axis and Y-axis can adjust (turn up or down) the current high-temperature threshold. Press the Joystick once again to reset the threshold to initial value.
Code Explanation
int get_joystick_value(){
uchar x_val;
uchar y_val;
x_val = get_ADC_Result(1);
y_val = get_ADC_Result(2);
if (x_val > 200){
return 1;
}
else if(x_val < 50){
return -1;
}
else if(y_val > 200){
return -10;
}
else if(y_val < 50){
return 10;
}
else{
return 0;
}
}
This function reads values of X and Y. If X>200, there will return "1"; X<50, return "-1"; y>200, return "-10", and y<50, return "10".
void upper_tem_setting(){
write(0, 0, "Upper Adjust:");
int change = get_joystick_value();
upperTem = upperTem + change;
char str[6];
snprintf(str,3,"%d",upperTem);
write(0,1,str);
int len;
len = strlen(str);
write(len,1," ");
delay(100);
}
This function is for adjusting the threshold and displaying it on the I2C LCD1602.
double temperature(){
unsigned char temp_value;
double Vr, Rt, temp, cel, Fah;
temp_value = get_ADC_Result(0);
Vr = 5 * (double)(temp_value) / 255;
Rt = 10000 * (double)(Vr) / (5 - (double)(Vr));
temp = 1 / (((log(Rt/10000)) / 3950)+(1 / (273.15 + 25)));
cel = temp - 273.15;
Fah = cel * 1.8 +32;
return cel;
}
Read the analog value of the CH0 (thermistor) of ADC0834 and then convert it to temperature value.
void monitoring_temp(){
char str[6];
double cel = temperature();
snprintf(str,6,"%.2f",cel);
write(0, 0, "Temp: ");
write(6, 0, str);
snprintf(str,3,"%d",upperTem);
write(0, 1, "Upper: ");
write(7, 1, str);
delay(100);
if(cel >= upperTem){
digitalWrite(buzzPin, HIGH);
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
}
else if(cel < upperTem){
digitalWrite(buzzPin, LOW);
digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW);
}
}
As the code runs, the current temperature and the high-temperature threshold 40 are displayed on I2C LCD1602. If the current temperature is larger than the threshold, the buzzer and LED are started to alarm you.
int main(void)
{
setup();
int lastState =1;
int stage=0;
while (1)
{
int currentState = digitalRead(Joy_BtnPin);
if(currentState==1 && lastState == 0){
stage=(stage+1)%2;
delay(100);
lcd_clear();
}
lastState=currentState;
if (stage==1){
upper_tem_setting();
}
else{
monitoring_temp();
}
}
return 0;
}
The function main() contains the whole program process as shown:
When the program starts, the initial value of stage is 0, and the current temperature and the high-temperature threshold 40 are displayed on I2C LCD1602. If the current temperature is larger than the threshold, the buzzer and the LED are started to alarm you.
Press the Joystick, and stage will be 1 and you can adjust the high-temperature threshold. Toggling the Joystick in the direction of X-axis and Y-axis can adjust (turn up or down) the current threshold. Press the Joystick once again to reset the threshold to initial value.
For Python Language Users¶
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python/
Step 3: Run the executable file.
sudo python3 3.1.8_OverheatMonitor.py
As the code runs, the current temperature and the high-temperature threshold 40 are displayed on I2C LCD1602. If the current temperature is larger than the threshold, the buzzer and LED are started to alarm you.
Joystick here is for your pressing to adjust the high-temperature threshold. Toggling the Joystick in the direction of X-axis and Y-axis can adjust (turn up or down) the current high-temperature threshold. Press the Joystick once again to reset the threshold to initial value.
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python.
import LCD1602
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import ADC0834
import time
import math
Joy_BtnPin = 22
buzzPin = 23
ledPin = 24
upperTem = 40
def setup():
ADC0834.setup()
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.setup(buzzPin, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.setup(Joy_BtnPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
LCD1602.init(0x27, 1)
def get_joystick_value():
x_val = ADC0834.getResult(1)
y_val = ADC0834.getResult(2)
if(x_val > 200):
return 1
elif(x_val < 50):
return -1
elif(y_val > 200):
return -10
elif(y_val < 50):
return 10
else:
return 0
def upper_tem_setting():
global upperTem
LCD1602.write(0, 0, 'Upper Adjust: ')
change = int(get_joystick_value())
upperTem = upperTem + change
strUpperTem = str(upperTem)
LCD1602.write(0, 1, strUpperTem)
LCD1602.write(len(strUpperTem),1, ' ')
time.sleep(0.1)
def temperature():
analogVal = ADC0834.getResult()
Vr = 5 * float(analogVal) / 255
Rt = 10000 * Vr / (5 - Vr)
temp = 1/(((math.log(Rt / 10000)) / 3950) + (1 / (273.15+25)))
Cel = temp - 273.15
Fah = Cel * 1.8 + 32
return round(Cel,2)
def monitoring_temp():
global upperTem
Cel=temperature()
LCD1602.write(0, 0, 'Temp: ')
LCD1602.write(0, 1, 'Upper: ')
LCD1602.write(6, 0, str(Cel))
LCD1602.write(7, 1, str(upperTem))
time.sleep(0.1)
if Cel >= upperTem:
GPIO.output(buzzPin, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH)
else:
GPIO.output(buzzPin, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
def loop():
lastState=1
stage=0
while True:
currentState=GPIO.input(Joy_BtnPin)
if currentState==1 and lastState ==0:
stage=(stage+1)%2
time.sleep(0.1)
LCD1602.clear()
lastState=currentState
if stage == 1:
upper_tem_setting()
else:
monitoring_temp()
def destroy():
LCD1602.clear()
ADC0834.destroy()
GPIO.cleanup()
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
try:
setup()
while True:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
Code Explanation
def get_joystick_value():
x_val = ADC0834.getResult(1)
y_val = ADC0834.getResult(2)
if(x_val > 200):
return 1
elif(x_val < 50):
return -1
elif(y_val > 200):
return -10
elif(y_val < 50):
return 10
else:
return 0
This function reads values of X and Y. If X>200, there will return "1"; X<50, return "-1"; y>200, return "-10", and y<50, return "10".
def upper_tem_setting():
global upperTem
LCD1602.write(0, 0, 'Upper Adjust: ')
change = int(get_joystick_value())
upperTem = upperTem + change
LCD1602.write(0, 1, str(upperTem))
LCD1602.write(len(strUpperTem),1, ' ')
time.sleep(0.1)
This function is for adjusting the threshold and displaying it on the I2C LCD1602.
def temperature():
analogVal = ADC0834.getResult()
Vr = 5 * float(analogVal) / 255
Rt = 10000 * Vr / (5 - Vr)
temp = 1/(((math.log(Rt / 10000)) / 3950) + (1 / (273.15+25)))
Cel = temp - 273.15
Fah = Cel * 1.8 + 32
return round(Cel,2)
Read the analog value of the CH0 (thermistor) of ADC0834 and then convert it to temperature value.
def monitoring_temp():
global upperTem
Cel=temperature()
LCD1602.write(0, 0, 'Temp: ')
LCD1602.write(0, 1, 'Upper: ')
LCD1602.write(6, 0, str(Cel))
LCD1602.write(7, 1, str(upperTem))
time.sleep(0.1)
if Cel >= upperTem:
GPIO.output(buzzPin, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH)
else:
GPIO.output(buzzPin, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
As the code runs, the current temperature and the high-temperature threshold 40 are displayed on I2C LCD1602. If the current temperature is larger than the threshold, the buzzer and LED are started to alarm you.
def loop():
lastState=1
stage=0
while True:
currentState=GPIO.input(Joy_BtnPin)
if currentState==1 and lastState ==0:
stage=(stage+1)%2
time.sleep(0.1)
LCD1602.clear()
lastState=currentState
if stage == 1:
upper_tem_setting()
else:
monitoring_temp()
The function main() contains the whole program process as shown:
When the program starts, the initial value of stage is 0, and the current temperature and the high-temperature threshold 40 are displayed on I2C LCD1602. If the current temperature is larger than the threshold, the buzzer and the LED are started to alarm you.
Press the Joystick, and stage will be 1 and you can adjust the high-temperature threshold. Toggling the Joystick in the direction of X-axis and Y-axis can adjust (turn up or down) the current high-temperature threshold. Press the Joystick once again to reset the threshold to initial value.
Phenomenon Picture¶