7.8 RFID Music Player¶
Through our previous project, 6.5 Radio Frequency Identification, we learned that the MFRC522 module allows us to write up to 48 letters of information to the card (or key), including both the key and identity information, as well as the music score.
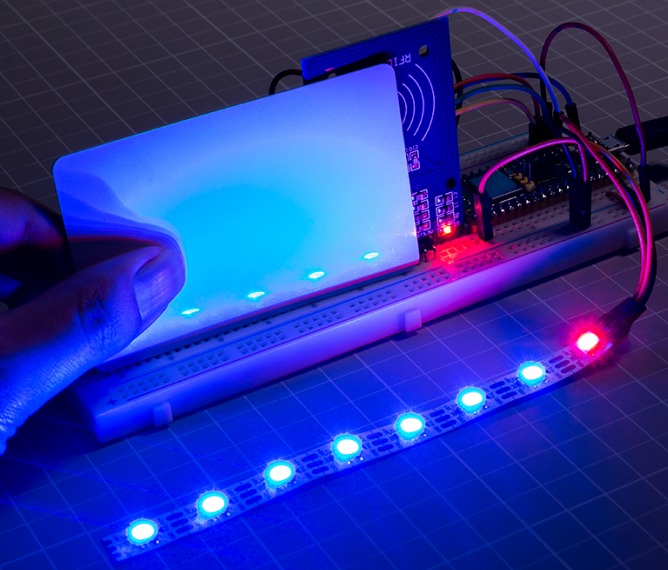
As an example, if you write EEFGGFEDCCDEEDD EEFGGFEDCCDEDCC, the buzzer will play the music when the card (or key) is read again. It can also be equipped with an WS2812 to display amazing effects.
You can find more sheet music on the Internet, or even write your own music, put them into the card (or key), and share them with your friends!
Required Components
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Kepler Kit |
450+ |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
SN |
COMPONENT |
QUANTITY |
LINK |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
1 |
||
2 |
Micro USB Cable |
1 |
|
3 |
1 |
||
4 |
Several |
||
5 |
1(S8050) |
||
6 |
1(1KΩ) |
||
7 |
Passive Buzzer |
1 |
|
8 |
1 |
||
9 |
1 |
Schematic
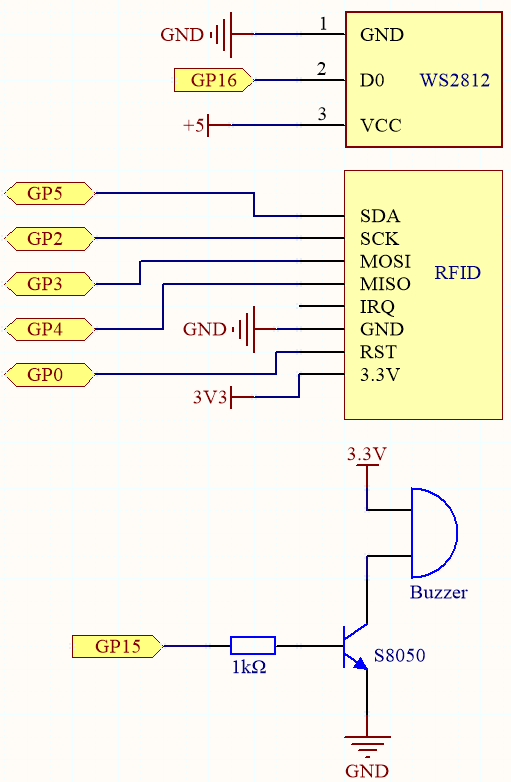
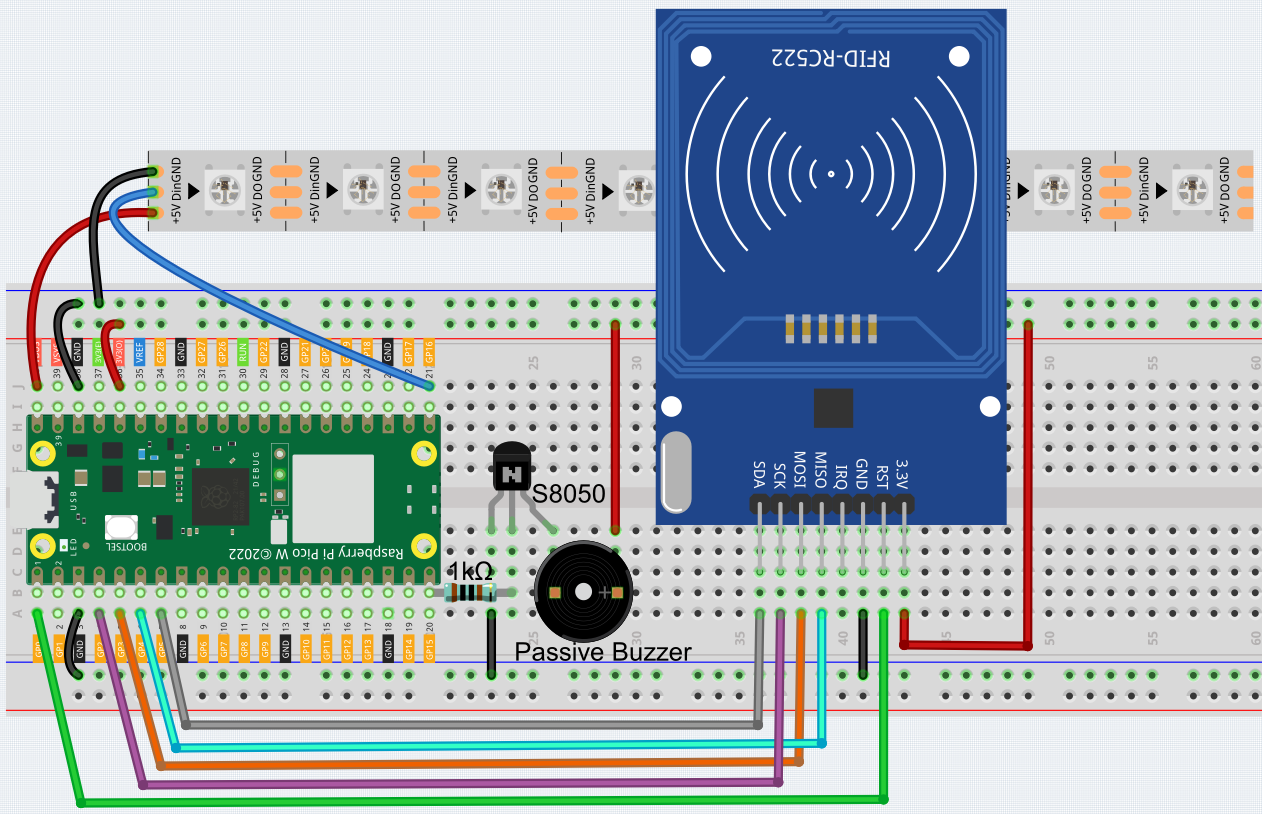
Wiring
Code
Open the
6.5_rfid_write.pyfile under the path ofkepler-kit-main/micropython, then click “Run Current Script” or simply press F5 to run it.After running, type
EEFGGFEDCCDEEDD EEFGGFEDCCDEDCCin the Shell and then put the card (or key) close to the MFRC522 module, this way an Ode an Joy score is stored in.Open the
7.8_rfid_music_player.pyfile under the path ofkepler-kit-main/micropythonor copy this code into Thonny, then click “Run Current Script” or simply press F5 to run it.from mfrc522 import SimpleMFRC522 import machine import time from ws2812 import WS2812 import urandom # ws2812 ws = WS2812(machine.Pin(16),8) # mfrc522 reader = SimpleMFRC522(spi_id=0,sck=2,miso=4,mosi=3,cs=5,rst=0) # buzzer NOTE_C4 = 262 NOTE_D4 = 294 NOTE_E4 = 330 NOTE_F4 = 349 NOTE_G4 = 392 NOTE_A4 = 440 NOTE_B4 = 494 NOTE_C5 = 523 buzzer = machine.PWM(machine.Pin(15)) note=[NOTE_C4,NOTE_D4,NOTE_E4,NOTE_F4,NOTE_G4,NOTE_A4,NOTE_B4,NOTE_C5] def tone(pin,frequency,duration): pin.freq(frequency) pin.duty_u16(30000) time.sleep_ms(duration) pin.duty_u16(0) # lightup def lumi(index): for i in range(8): ws[i] = 0x0000FF ws[index] = 0xFF0000 # int(urandom.uniform(0, 0xFFFFFF)) ws.write() # encode text to index words=["C","D","E","F","G","A","B","N"] def take_text(text): string=text.replace(' ','').upper() while len(string)>0: index=words.index(string[0]) tone(buzzer,note[index],250) lumi(index) new_str="" for i in range(0, len(string)): if i != 0: new_str = new_str + string[i] string=new_str # read card def read(): print("Reading...Please place the card...") id, text = reader.read() print("ID: %s\nText: %s" % (id,text)) take_text(text) read()
By putting the card (or key) close to the MFRC522 module again, the buzzer will play the music stored on the card (or key), and the RGB strip will light up in a random color.