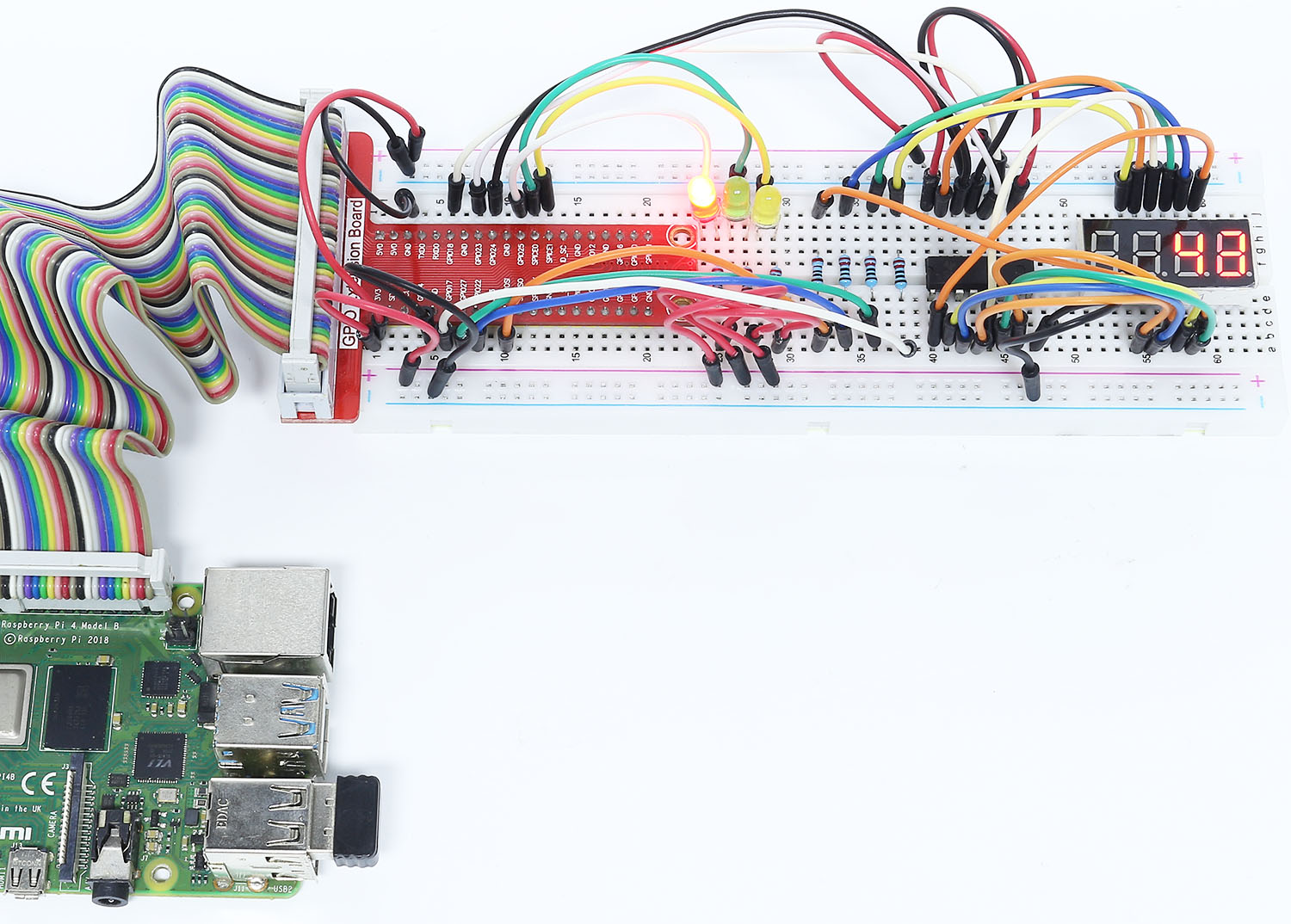
3.1.7 信号機¶
前書き¶
このプロジェクトでは、3色のLEDを使用して交通信号の変化を実現し、 4桁の7セグメントディスプレイを使用して各交通状態のタイミングを表示する。
部品¶
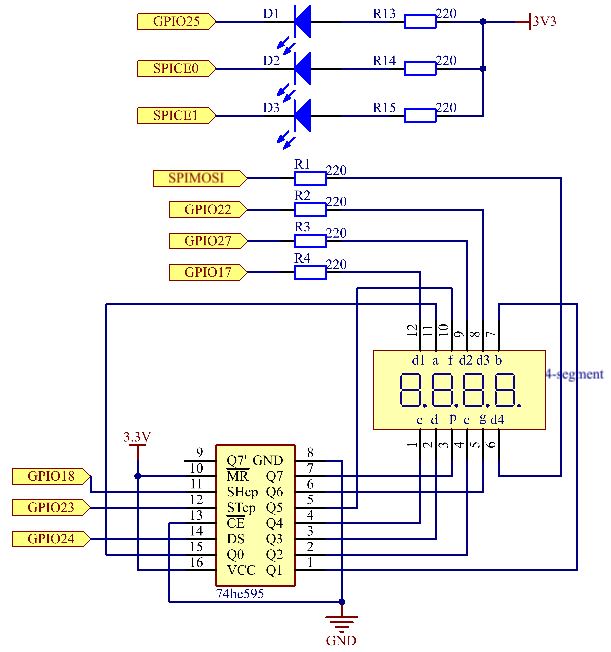
回路図¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
SPIMOSI |
Pin 19 |
12 |
10 |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO23 |
Pin 16 |
4 |
23 |
GPIO24 |
Pin 18 |
5 |
24 |
GPIO25 |
Pin 22 |
6 |
25 |
SPICE0 |
Pin 24 |
10 |
8 |
SPICE1 |
Pin 26 |
11 |
7 |
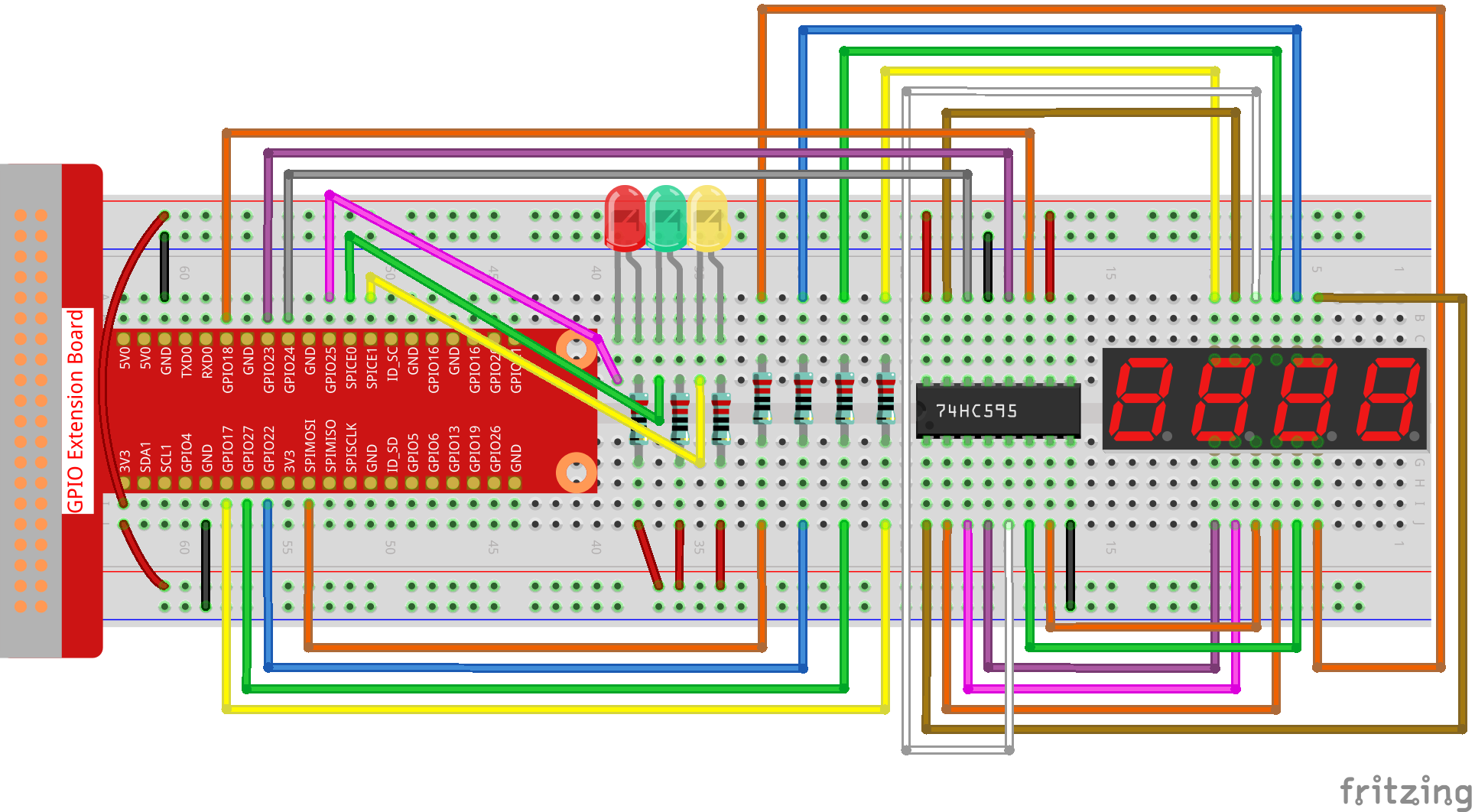
実験手順¶
ステップ1: 回路を作る。
C言語ユーザー向け¶
ステップ2: ディレクトリを変更する。
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/c/3.1.7/
ステップ3: コンパイルする。
gcc 3.1.7_TrafficLight.c -lwiringPi
ステップ4: 実行する。
sudo ./a.out
コードが実行されると、LEDは交通信号の色の変化をシミュレートする。 まず、赤色のLEDが60秒間点灯し、それから緑色のLEDが30秒間点灯し、最後に、黄色のLEDが5秒間点灯する。 その後、赤いLEDが60秒間再び点灯する。 このようにして、この一連のアクションは繰り返し実行される。
コードの説明
#define SDI 5
#define RCLK 4
#define SRCLK 1
const int placePin[] = {12, 3, 2, 0};
unsigned char number[] = {0xc0, 0xf9, 0xa4, 0xb0, 0x99, 0x92, 0x82, 0xf8, 0x80, 0x90};
void pickDigit(int digit);
void hc595_shift(int8_t data);
void clearDisplay();
void display();
これらのコードは、4桁7セグメントディスプレイの数値表示機能を実現するために使用されます。 詳細については、ドキュメントの 1.1.5 4桁7セグメントディスプレイ を参照してください。 ここでは、コードを使用して信号時間のカウントダウンを表示します。
const int ledPin[]={6,10,11};
int colorState = 0;
void lightup()
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
digitalWrite(ledPin[i],HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(ledPin[colorState],LOW);
}
コードはLEDのオンとオフを切り替えるために使用される。
int greenLight = 30;
int yellowLight = 5;
int redLight = 60;
int colorState = 0;
char *lightColor[]={"Red","Green","Yellow"};
int counter = 60;
void timer(int timer1){ //Timer function
if(timer1 == SIGALRM){
counter --;
alarm(1);
if(counter == 0){
if(colorState == 0) counter = greenLight;
if(colorState == 1) counter = yellowLight;
if(colorState == 2) counter = redLight;
colorState = (colorState+1)%3;
}
printf("counter : %d \t light color: %s \n",counter,lightColor[colorState]);
}
}
コードは、タイマーのオンとオフを切り替えるために使用されます。 詳細については、 1.1.5 4桁7セグメントディスプレイ を参照してください。 ここで、タイマーがゼロに戻ると、 colorState が切り替えられてLEDが切り替わり、タイマーが新しい値に割り当てられます。
void loop()
{
while(1){
display();
lightup();
}
}
int main(void)
{
//…
signal(SIGALRM,timer);
alarm(1);
loop();
return 0;
}
タイマーは main() 関数で始まる。
loop() 関数では、 while(1) loopを使用して、4桁7セグメントとLEDの関数を呼び出す。
Python言語ユーザー向け¶
ステップ2: ディレクトリを変更する。
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python/
ステップ3: 実行する。
sudo python3 3.1.7_TrafficLight.py
コードが実行されると、LEDは交通信号の色の変化をシミュレートする。 まず、赤色のLEDが60秒間点灯し、それから緑色のLEDが30秒間点灯し、最後に、黄色のLEDが5秒間点灯する。 その後、赤いLEDが60秒間再び点灯する。このようにして、この一連のアクションは繰り返し実行される。 一方、4桁の7セグメントディスプレイには、カウントダウン時間が連続して表示される。
コード
注釈
以下のコードを 変更/リセット/コピー/実行/停止 できます。 ただし、その前に、 davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python のようなソースコードパスに移動する必要があります。
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import threading
#define the pins connect to 74HC595
SDI = 24 #serial data input(DS)
RCLK = 23 #memory clock input(STCP)
SRCLK = 18 #shift register clock input(SHCP)
number = (0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,0x80,0x90)
placePin = (10,22,27,17)
ledPin =(25,8,7)
greenLight = 30
yellowLight = 5
redLight = 60
lightColor=("Red","Green","Yellow")
colorState=0
counter = 60
timer1 = 0
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(SDI, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(RCLK, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(SRCLK, GPIO.OUT)
for pin in placePin:
GPIO.setup(pin,GPIO.OUT)
for pin in ledPin:
GPIO.setup(pin,GPIO.OUT)
global timer1
timer1 = threading.Timer(1.0,timer)
timer1.start()
def clearDisplay():
for i in range(8):
GPIO.output(SDI, 1)
GPIO.output(SRCLK, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(SRCLK, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(RCLK, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(RCLK, GPIO.LOW)
def hc595_shift(data):
for i in range(8):
GPIO.output(SDI, 0x80 & (data << i))
GPIO.output(SRCLK, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(SRCLK, GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(RCLK, GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(RCLK, GPIO.LOW)
def pickDigit(digit):
for i in placePin:
GPIO.output(i,GPIO.LOW)
GPIO.output(placePin[digit], GPIO.HIGH)
def timer(): #timer function
global counter
global colorState
global timer1
timer1 = threading.Timer(1.0,timer)
timer1.start()
counter-=1
if (counter is 0):
if(colorState is 0):
counter= greenLight
if(colorState is 1):
counter=yellowLight
if (colorState is 2):
counter=redLight
colorState=(colorState+1)%3
print ("counter : %d color: %s "%(counter,lightColor[colorState]))
def lightup():
global colorState
for i in range(0,3):
GPIO.output(ledPin[i], GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(ledPin[colorState], GPIO.LOW)
def display():
global counter
a = counter % 10000//1000 + counter % 1000//100
b = counter % 10000//1000 + counter % 1000//100 + counter % 100//10
c = counter % 10000//1000 + counter % 1000//100 + counter % 100//10 + counter % 10
if (counter % 10000//1000 == 0):
clearDisplay()
else:
clearDisplay()
pickDigit(3)
hc595_shift(number[counter % 10000//1000])
if (a == 0):
clearDisplay()
else:
clearDisplay()
pickDigit(2)
hc595_shift(number[counter % 1000//100])
if (b == 0):
clearDisplay()
else:
clearDisplay()
pickDigit(1)
hc595_shift(number[counter % 100//10])
if(c == 0):
clearDisplay()
else:
clearDisplay()
pickDigit(0)
hc595_shift(number[counter % 10])
def loop():
while True:
display()
lightup()
def destroy(): # When "Ctrl+C" is pressed, the function is executed.
global timer1
GPIO.cleanup()
timer1.cancel() #cancel the timer
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program starting from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
コードの説明
SDI = 24 #serial data input(DS)
RCLK = 23 #memory clock input(STCP)
SRCLK = 18 #shift register clock input(SHCP)
number = (0xc0,0xf9,0xa4,0xb0,0x99,0x92,0x82,0xf8,0x80,0x90)
placePin = (10,22,27,17)
def clearDisplay():
def hc595_shift(data):
def pickDigit(digit):
def display():
これらのコードは、4桁7セグメントの数値表示機能を実現するために使用されます。 詳細については、ドキュメントの 1.1.5 4桁7セグメントディスプレイ を参照してください。 ここでは、コードを使用して信号時間のカウントダウンを表示します。
ledPin =(25,8,7)
colorState=0
def lightup():
global colorState
for i in range(0,3):
GPIO.output(ledPin[i], GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.output(ledPin[colorState], GPIO.LOW)
コードはLEDのオンとオフを切り替えるために使用される。
greenLight = 30
yellowLight = 5
redLight = 60
lightColor=("Red","Green","Yellow")
colorState=0
counter = 60
timer1 = 0
def timer(): #timer function
global counter
global colorState
global timer1
timer1 = threading.Timer(1.0,timer)
timer1.start()
counter-=1
if (counter is 0):
if(colorState is 0):
counter= greenLight
if(colorState is 1):
counter=yellowLight
if (colorState is 2):
counter=redLight
colorState=(colorState+1)%3
print ("counter : %d color: %s "%(counter,lightColor[colorState]))
コードは、タイマーのオンとオフを切り替えるために使用されます。
詳細については、 1.1.5 4桁7セグメントディスプレイ を参照してください。
ここで、タイマーがゼロに戻ると、
colorState が切り替えられてLEDが切り替わり、タイマーが新しい値に割り当てられます。
def setup():
# ...
global timer1
timer1 = threading.Timer(1.0,timer)
timer1.start()
def loop():
while True:
display()
lightup()
def destroy(): # When "Ctrl+C" is pressed, the function is executed.
global timer1
GPIO.cleanup()
timer1.cancel() #cancel the timer
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program starting from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
setup() 関数で、タイマーを開始する。
loop() 関数では、 while True が使用される:4-桁の7-セグメントとLEDの相対関数を循環的に呼び出す。
現象画像¶