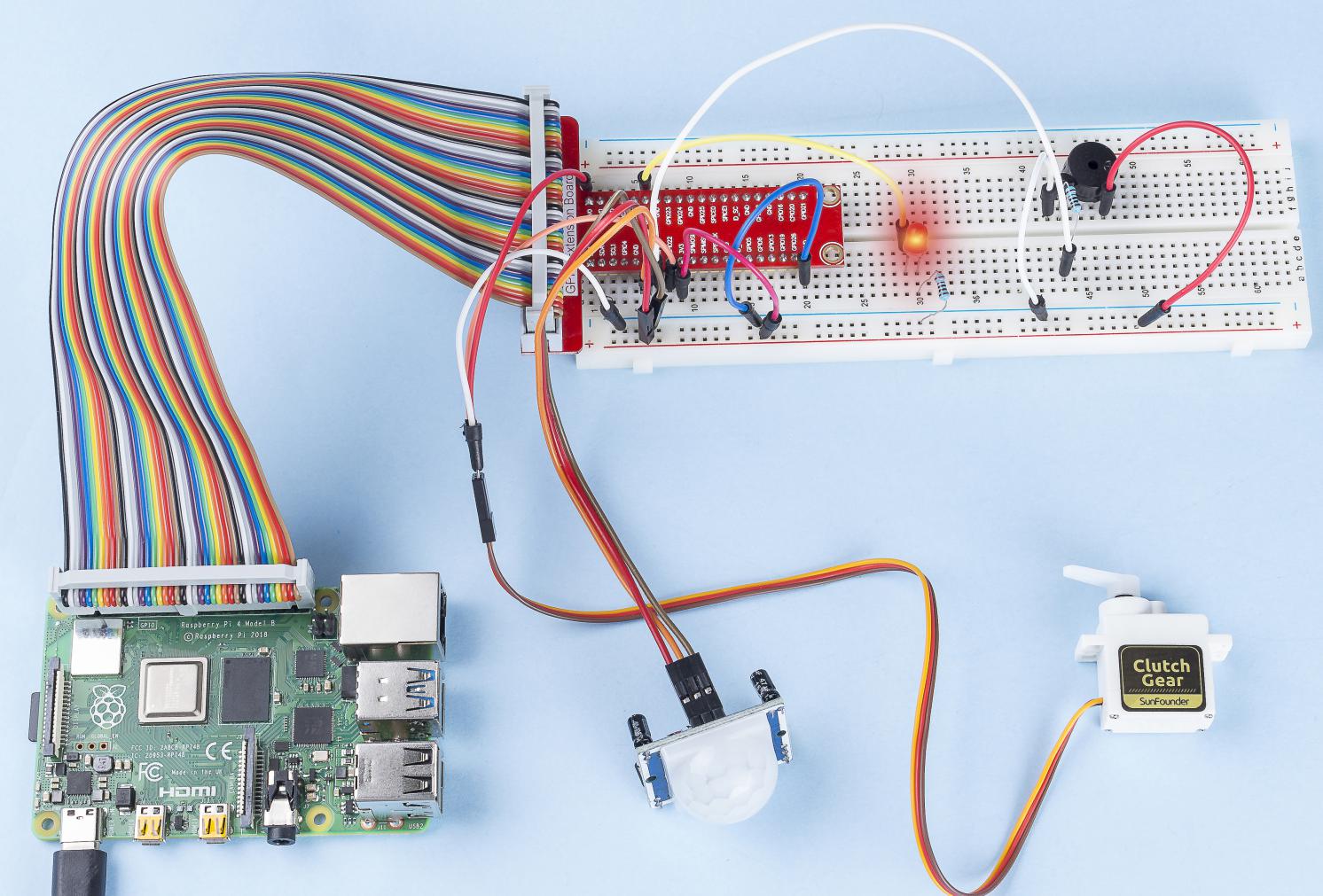
3.1.2 いらっしゃいませ¶
前書き¶
このプロジェクトでは、PIRを使用して歩行者の動きを検知し、サーボ、LED、ブザーを使用してコンビニのセンサードアの動作をシミュレートする。歩行者がPIRの検知範囲内に現れると、インジケータライトが点灯し、ドアが開き、ブザーがオープニングベルを鳴らす。
部品¶
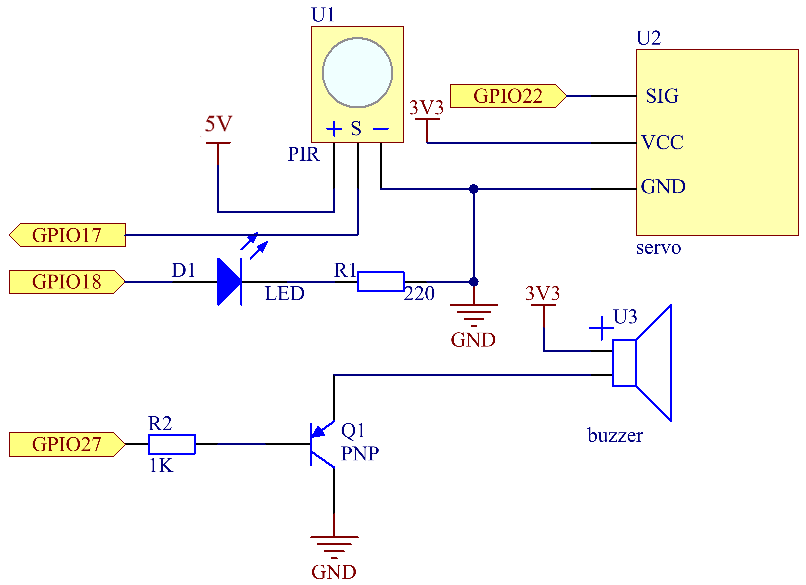
回路図¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO18 |
Pin 12 |
1 |
18 |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
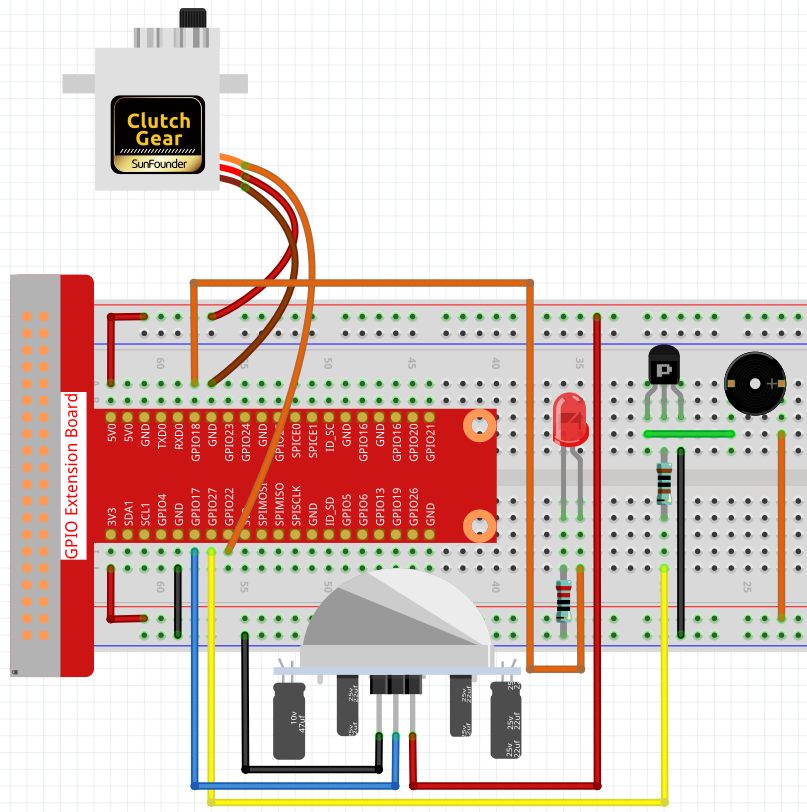
実験手順¶
ステップ1: 回路を作る。
C言語ユーザー向け¶
ステップ2: ディレクトリを変更する。
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/c/3.1.2/
ステップ3: コンパイルする。
gcc 3.1.2_Welcome.c -lwiringPi
ステップ4: 実行する。
sudo ./a.out
コードの実行後、PIRセンサーが通り過ぎる人を検出すると、 ドアが自動的に開き(サーボによってシミュレートされる)、 インジケーターをオンにして、ドアベルの音楽を再生する。ドアベルの音楽が再生されると、 システムは自動的にドアを閉じてインジケータライトをオフにし、次に誰かが通り過ぎることを待つ。
PIR モジュールには 2 つのポテンショメータがあり、 1 つは感度を調整するためのもので、もう 1 つは検出距離を調整するためのものです。 PIR モジュールがうまく機能するためには、両方を完全に反時計回りに回す必要があります。
コードの説明
void setAngle(int pin, int angle){ //Create a funtion to control the angle of the servo.
if(angle < 0)
angle = 0;
if(angle > 180)
angle = 180;
softPwmWrite(pin,Map(angle, 0, 180, 5, 25));
}
0〜180の角度をサーボに書き込むための関数、 setAngle を作成する。
void doorbell(){
for(int i=0;i<sizeof(song)/4;i++){
softToneWrite(BuzPin, song[i]);
delay(beat[i] * 250);
}
ブザーで音楽を再生できるようにする関数、 doorbell を作成する。
void closedoor(){
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); //led off
for(int i=180;i>-1;i--){ //make servo rotate from maximum angle to minimum angle
setAngle(servoPin,i);
delay(1);
}
}
ドアの閉鎖をシミュレートする関数 closedoor を作成し、
LEDをオフにし、サーボを180度から0度に回転させる。
void opendoor(){
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); //led on
for(int i=0;i<181;i++){ //make servo rotate from minimum angle to maximum angle
setAngle(servoPin,i);
delay(1);
}
doorbell();
closedoor();
}
関数 opendoor() にはいくつかの部分が含まれている:インジケータライトをオンにし、
サーボを回転させ(ドアを開く動作をシミュレートする)、
コンビニのドアベル音楽を再生し、音楽を再生した後に関数 closedoor() を呼び出す。
int main(void)
{
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print message to screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
if(softToneCreate(BuzPin) == -1){
printf("setup softTone failed !");
return 1;
......
関数 main() で、ライブラリー wiringPi を初期化し、
softTone をセットアップしてから、 ledPin を出力状態に、
pirPin を入力状態に設定する。PIRセンサーが通り過ぎる人を検出すると、
ドアを開くことをシミュレートするために関数 opendoor が呼び出される。
Python言語ユーザー向け¶
ステップ2: ディレクトリを変更する。
cd /home/pi/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python/
ステップ3: 実行する。
sudo python3 3.1.2_Welcome.py
コードの実行後、PIRセンサーが通り過ぎる人を検出すると、 ドアが自動的に開き(サーボによってシミュレートされる)、 インジケーターをオンにして、ドアベルの音楽を再生する。ドアベルの音楽が再生されると、 システムは自動的にドアを閉じてインジケータライトをオフにし、次に誰かが通り過ぎることを待つ。
PIR モジュールには 2 つのポテンショメータがあり、 1 つは感度を調整するためのもので、もう 1 つは検出距離を調整するためのものです。 PIR モジュールがうまく機能するためには、両方を完全に反時計回りに回す必要があります。
コード
注釈
以下のコードを 変更/リセット/コピー/実行/停止 できます。 ただし、その前に、 davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python のようなソースコードパスに移動する必要があります。
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
SERVO_MIN_PULSE = 500
SERVO_MAX_PULSE = 2500
ledPin = 18 # define the ledPin
pirPin = 17 # define the sensorPin
servoPin = 22 # define the servoPin
buzPin = 27 # define the buzzerpin
CL = [0, 131, 147, 165, 175, 196, 211, 248] # Frequency of Low C notes
CM = [0, 262, 294, 330, 350, 393, 441, 495] # Frequency of Middle C notes
CH = [0, 525, 589, 661, 700, 786, 882, 990] # Frequency of High C notes
song = [ CH[5],CH[2],CM[6],CH[2],CH[3],CH[6],CH[3],CH[5],CH[3],CM[6],CH[2] ]
beat = [ 1,1,1,1,1,2,1,1,1,1,1,]
def setup():
global p
global Buzz # Assign a global variable to replace GPIO.PWM
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set ledPin's mode is output
GPIO.setup(pirPin, GPIO.IN) # Set sensorPin's mode is input
GPIO.setup(servoPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set servoPin's mode is output
GPIO.output(servoPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set servoPin to low
GPIO.setup(buzPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pins' mode is output
Buzz = GPIO.PWM(buzPin, 440) # 440 is initial frequency.
Buzz.start(50) # Start Buzzer pin with 50% duty ration
p = GPIO.PWM(servoPin, 50) # set Frequece to 50Hz
p.start(0) # Duty Cycle = 0
def map(value, inMin, inMax, outMin, outMax):
return (outMax - outMin) * (value - inMin) / (inMax - inMin) + outMin
def setAngle(angle): # make the servo rotate to specific angle (0-180 degrees)
angle = max(0, min(180, angle))
pulse_width = map(angle, 0, 180, SERVO_MIN_PULSE, SERVO_MAX_PULSE)
pwm = map(pulse_width, 0, 20000, 0, 100)
p.ChangeDutyCycle(pwm)#map the angle to duty cycle and output it
def doorbell():
for i in range(1, len(song)): # Play song 1
Buzz.ChangeFrequency(song[i]) # Change the frequency along the song note
time.sleep(beat[i] * 0.25) # delay a note for beat * 0.25s
time.sleep(1) # Wait a second for next song.
def closedoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
for i in range(180, -1, -1): #make servo rotate from 180 to 0 deg
setAngle(i)
time.sleep(0.001)
time.sleep(1)
def opendoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
for i in range(0, 181, 1): #make servo rotate from 0 to 180 deg
setAngle(i) # Write to servo
time.sleep(0.001)
time.sleep(1)
doorbell()
closedoor()
def loop():
while True:
if GPIO.input(pirPin)==GPIO.HIGH:
opendoor()
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
p.stop()
Buzz.stop()
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
コードの説明
def setup():
global p
global Buzz # Assign a global variable to replace GPIO.PWM
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set ledPin's mode is output
GPIO.setup(pirPin, GPIO.IN) # Set sensorPin's mode is input
GPIO.setup(buzPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set pins' mode is output
Buzz = GPIO.PWM(buzPin, 440) # 440 is initial frequency.
Buzz.start(50) # Start Buzzer pin with 50% duty ration
GPIO.setup(servoPin, GPIO.OUT) # Set servoPin's mode is output
GPIO.output(servoPin, GPIO.LOW) # Set servoPin to low
p = GPIO.PWM(servoPin, 50) # set Frequece to 50Hz
p.start(0) # Duty Cycle = 0
これらのステートメントは、各部品のピンを初期化するために使用される。
def setAngle(angle): # make the servo rotate to specific angle (0-180 degrees)
angle = max(0, min(180, angle))
pulse_width = map(angle, 0, 180, SERVO_MIN_PULSE, SERVO_MAX_PULSE)
pwm = map(pulse_width, 0, 20000, 0, 100)
p.ChangeDutyCycle(pwm)#map the angle to duty cycle and output it
0〜180の角度をサーボに書き込むための関数、 setAngle を作成する。
def doorbell():
for i in range(1,len(song)): # Play song1
Buzz.ChangeFrequency(song[i]) # Change the frequency along the song note
time.sleep(beat[i] * 0.25) # delay a note for beat * 0.25s
ブザーで音楽を再生できるようにする関数、 doorbell を作成する。
def closedoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
Buzz.ChangeFrequency(1)
for i in range(180, -1, -1): #make servo rotate from 180 to 0 deg
setAngle(i)
time.sleep(0.001)
ドアを閉じて、インジケータライトをオフにする。
def opendoor():
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
for i in range(0, 181, 1): #make servo rotate from 0 to 180 deg
setAngle(i) # Write to servo
time.sleep(0.001)
doorbell()
closedoor()
関数 opendoor() にはいくつかの部分が含まれている:インジケータライトをオンにし、
サーボを回転させ(ドアを開く動作をシミュレートする)、コンビニのドアベル音楽を再生し、
音楽を再生した後に関数 closedoor() を呼び出す。
def loop():
while True:
if GPIO.input(pirPin)==GPIO.HIGH:
opendoor()
PIRは誰かが通り過ぎることを検知すると、関数 opendoor() を呼び出す。
現象画像¶