2.11 Swinging Servo¶
In this kit, in addition to LED and passive buzzer, there is also a device controlled by PWM signal, Servo.
Servo is a position (angle) servo device, which is suitable for those control systems that require constant angle changes and can be maintained. It has been widely used in high-end remote control toys, such as airplanes, submarine models, and remote control robots.
Now, try to make the servo sway!
Schematic¶
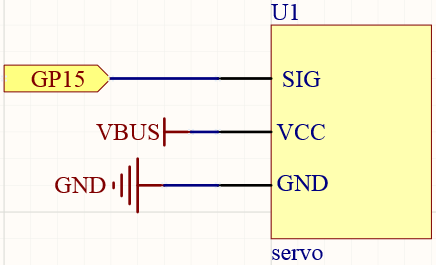
Wiring¶
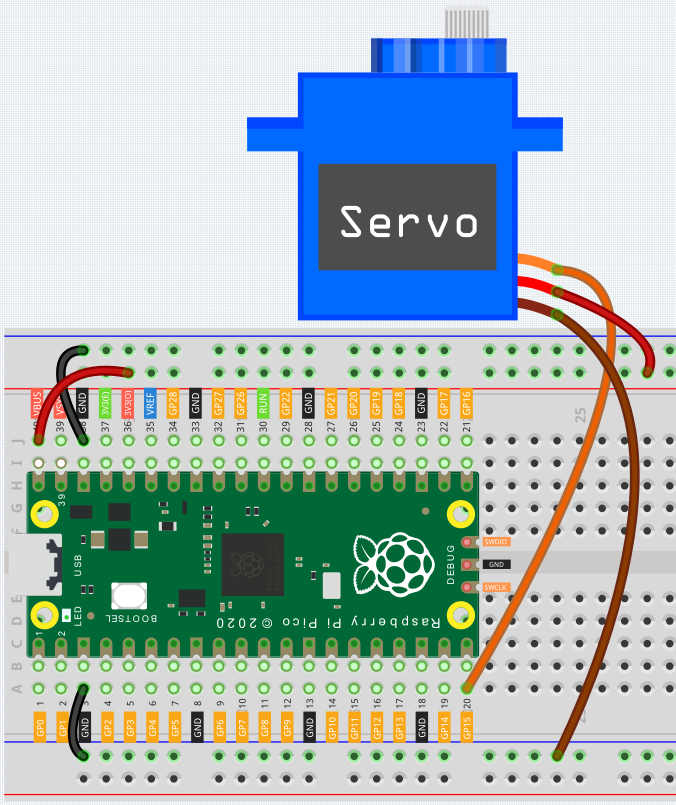
Press the Servo Arm into the Servo output shaft. If necessary, fix it with screws.
Connect VBUS (not 3V3) and GND of Pico to the power bus of the breadboard.
Connect the red lead of the servo to the positive power bus with a jumper.
Connect the yellow lead of the servo to the GP15 pin with a jumper wire.
Connect the brawn lead of the servo to the negative power bus with a jumper wire.
Code¶
When the program is running, we can see the Servo Arm swinging back and forth from 0° to 180°. The program will always run because of the while True loop, we need to press the Stop key to end the program.
import machine
import utime
servo = machine.PWM(machine.Pin(15))
servo.freq(50)
def interval_mapping(x, in_min, in_max, out_min, out_max):
return (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min
def servo_write(pin,angle):
pulse_width=interval_mapping(angle, 0, 180, 0.5,2.5)
duty=int(interval_mapping(pulse_width, 0, 20, 0,65535))
pin.duty_u16(duty)
while True:
for angle in range(180):
servo_write(servo,angle)
utime.sleep_ms(20)
for angle in range(180,-1,-1):
servo_write(servo,angle)
utime.sleep_ms(20)
How it works?¶
We defined the servo_write() function to make the servo run.
This function has two parameters:
pin, the GPIO pin that controls the servo.
Angle, the angle of the shaft output.
In this function, interval_mapping() is called to map the angle range 0 ~ 180 to the pulse width range 0.5 ~ 2.5ms.
pulse_width=interval_mapping(angle, 0, 180, 0.5,2.5)
Why is it 0.5~2.5? This is determined by the working mode of the Servo.
Next, convert the pulse width from period to duty. Since duty_u16() cannot have decimals when used (the value cannot be a float type), we used int() to force the duty to be converted to an int type.
duty=int(interval_mapping(pulse_width, 0, 20, 0,65535))
Finally, write the duty value into duty_u16().