2.13 Thermometer¶
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, and it has two types: Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) and Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC), also known as NTC and PTC. The resistance of PTC thermistor increases with temperature, while the condition of NTC is opposite to the former.
In this experiment we use an NTC thermistor to make a thermometer.
Schematic¶
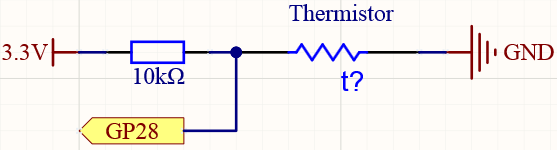
Wiring¶
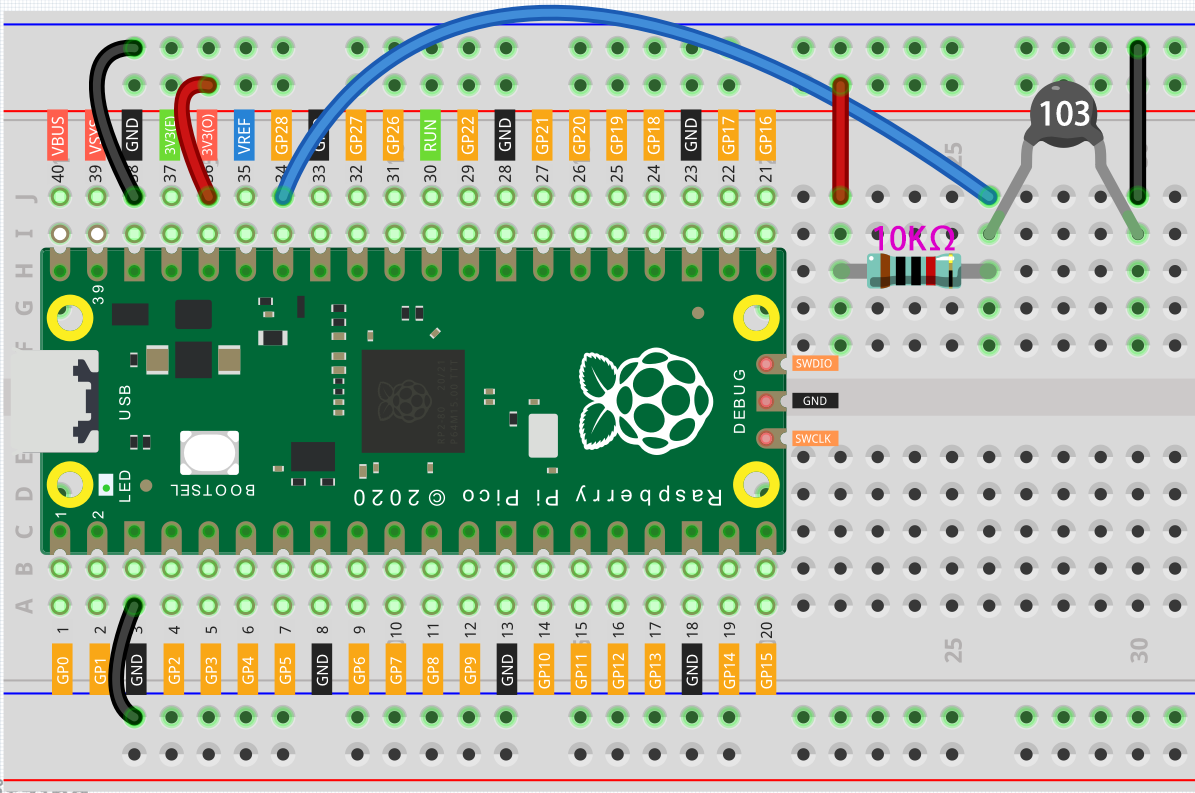
Connect 3V3 and GND of Pico to the power bus of the breadboard.
Connect one lead of the thermistor to the GP28 pin, then connect the same lead to the positive power bus with a 10K ohm resistor.
Connect another lead of thermistor to the negative power bus.
Note
The thermistor is black and marked 103.
The color ring of the 10K ohm resistor is red, black, black, red and brown.
import machine
import utime
import math
thermistor = machine.ADC(28)
while True:
temperature_value = thermistor.read_u16()
Vr = 3.3 * float(temperature_value) / 65535
Rt = 10000 * Vr / (3.3 - Vr)
temp = 1/(((math.log(Rt / 10000)) / 3950) + (1 / (273.15+25)))
Cel = temp - 273.15
Fah = Cel * 1.8 + 32
print ('Celsius: %.2f C Fahrenheit: %.2f F' % (Cel, Fah))
utime.sleep_ms(200)
How it works?¶
Each thermistor has a normal resistance. Here it is 10k ohm, which is measured under 25 degree Celsius. When the temperature gets higher, the resistance of the thermistor decreases. Then the voltage data is converted to digital quantities by the A/D adapter.
The temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit is output via programming.
import math
There is a numerics library which declares a set of functions to compute common mathematical operations and transformations.
temperature_value = thermistor.read_u16()
This function is used to read the value of the thermistor.
Vr = 3.3 * float(temperature_value) / 65535
Rt = 10000 * Vr / (3.3 - Vr)
temp = 1/(((math.log(Rt / 10000)) / 3950) + (1 / (273.15+25)))
Cel = temp - 273.15
Fah = Cel * 1.8 + 32
print ('Celsius: %.2f C Fahrenheit: %.2f F' % (Cel, Fah))
utime.sleep_ms(200)
These calculations convert the thermistor values into centigrade degree and Fahrenheit degree.
Vr = 3.3 * float(temperature_value) / 65535
Rt = 10000 * Vr / (3.3 - Vr)
In the two lines of code above, the voltage is first calculated using the read analoge value, and then get Rt (the resistance of the thermistor).
temp = 1/(((math.log(Rt / 10000)) / 3950) + (1 / (273.15+25)))
Note
Here is the relation between the resistance and temperature:
RT =RN expB(1/TK – 1/TN)
RT is the resistance of the NTC thermistor when the temperature is TK.
RN is the resistance of the NTC thermistor under the rated temperature TN. Here, the numerical value of RN is 10k.
TK is a Kelvin temperature and the unit is K. Here, the numerical value of TK is 273.15 + degree Celsius.
TN is a rated Kelvin temperature; the unit is K too. Here, the numerical value of TN is 273.15+25.
And B(beta), the material constant of NTC thermistor, is also called heat sensitivity index with a numerical value 3950.
exp is the abbreviation of exponential, and the base number e is a natural number and equals 2.7 approximately.
Convert this formula TK=1/(ln(RT/RN)/B+1/TN) to get Kelvin temperature that minus 273.15 equals degree Celsius.
This relation is an empirical formula. It is accurate only when the temperature and resistance are within the effective range.
This code refers to plugging Rt into the formula TK=1/(ln(RT/RN)/B+1/TN) to get Kelvin temperature.
temp = temp - 273.15
Convert Kelvin temperature into centigrade degree.
Fah = Cel * 1.8 + 32
Convert the centigrade degree into Fahrenheit degree.
print ('Celsius: %.2f °C Fahrenheit: %.2f ℉' % (Cel, Fah))
Print centigrade degree, Fahrenheit degree and their units in the shell.