2.10 Custom Tone¶
We have used active buzzer in the previous project, this time we will use passive buzzer.
Like the active buzzer, the passive buzzer also uses the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction to work. The difference is that a passive buzzer does not have oscillating source, so it will not beep if DC signals are used. But this allows the passive buzzer to adjust its own oscillation frequency and can emit different notes such as “doh, re, mi, fa, sol, la, ti”.
Let the passive buzzer emit a melody!
Schematic¶
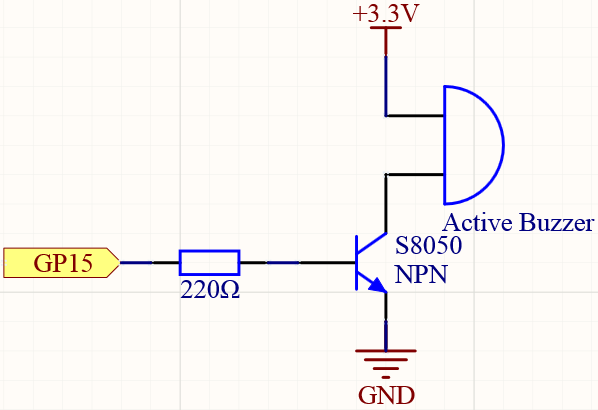
Wiring¶

Two buzzers are included in the kit, we use the one with exposed PCB behind.
The buzzer needs a transistor to work, and here we use S8050.
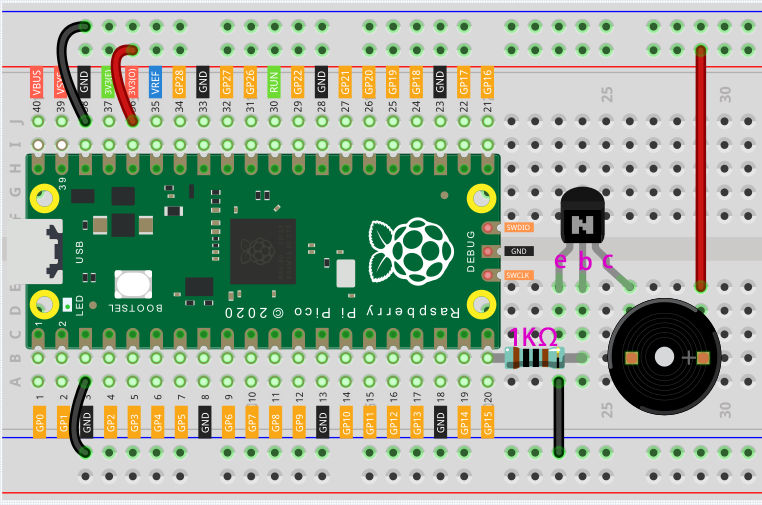
Connect 3V3 and GND of Pico to the power bus of the breadboard.
Connect the positive pin of the buzzer to the positive power bus.
Connect the cathode pin of the buzzer to the collector lead of the transistor.
Connect the base lead of the transistor to the GP15 pin through a 1kΩ resistor.
Connect the emitter lead of the transistor to the negative power bus.
Note
The color ring of the 1k ohm resistor is brown, black, black, brown and brown.
Code¶
import machine
import utime
buzzer = machine.PWM(machine.Pin(15))
def tone(pin,frequency,duration):
pin.freq(frequency)
pin.duty_u16(30000)
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
pin.duty_u16(0)
tone(buzzer,440,250)
utime.sleep_ms(500)
tone(buzzer,494,250)
utime.sleep_ms(500)
tone(buzzer,523,250)
How it works?¶
If the passive buzzer given a digital signal, it can only keep pushing the diaphragm without producing sound.
Therefore, we use the tone() function to generate the PWM signal to make the passive buzzer sound.
This function has three parameters:
pin, the GPIO pin that controls the buzzer.
frequency, the pitch of the buzzer is determined by the frequency, the higher the frequency, the higher the pitch.
Duration, the duration of the tone.
We use the duty_u16() function to set the duty cycle to 30000(about 50%). It can be other numbers, and it only needs to generate a discontinuous electrical signal to oscillate.
What more?¶
We can simulate the specific tone according to the fundamental frequency of the piano, so as to play a complete piece of music.
import machine
import utime
NOTE_C4 = 262
NOTE_G3 = 196
NOTE_A3 = 220
NOTE_B3 = 247
melody =[NOTE_C4,NOTE_G3,NOTE_G3,NOTE_A3,NOTE_G3,NOTE_B3,NOTE_C4]
buzzer = machine.PWM(machine.Pin(15))
def tone(pin,frequency,duration):
pin.freq(frequency)
pin.duty_u16(30000)
utime.sleep_ms(duration)
pin.duty_u16(0)
for note in melody:
tone(buzzer,note,250)
utime.sleep_ms(150)