Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
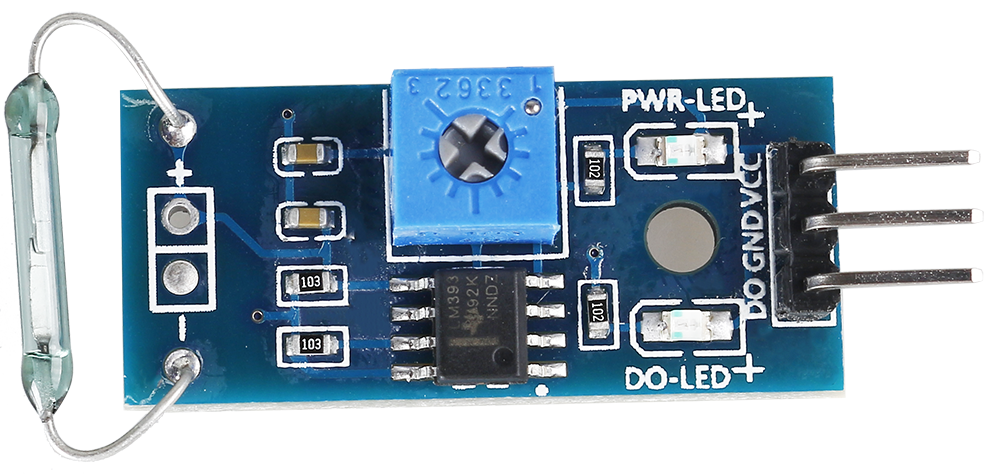
2.2.4 Reed Switch Module¶
Introduction¶
In this project, we will learn about the reed switch, which is an electrical switch that operates by means of an applied magnetic field.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
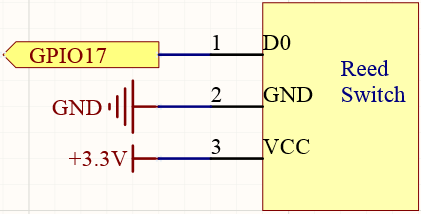
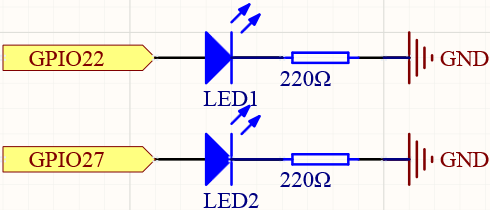
Schematic Diagram¶
T-Board Name |
physical |
wiringPi |
BCM |
GPIO17 |
Pin 11 |
0 |
17 |
GPIO27 |
Pin 13 |
2 |
27 |
GPIO22 |
Pin 15 |
3 |
22 |
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
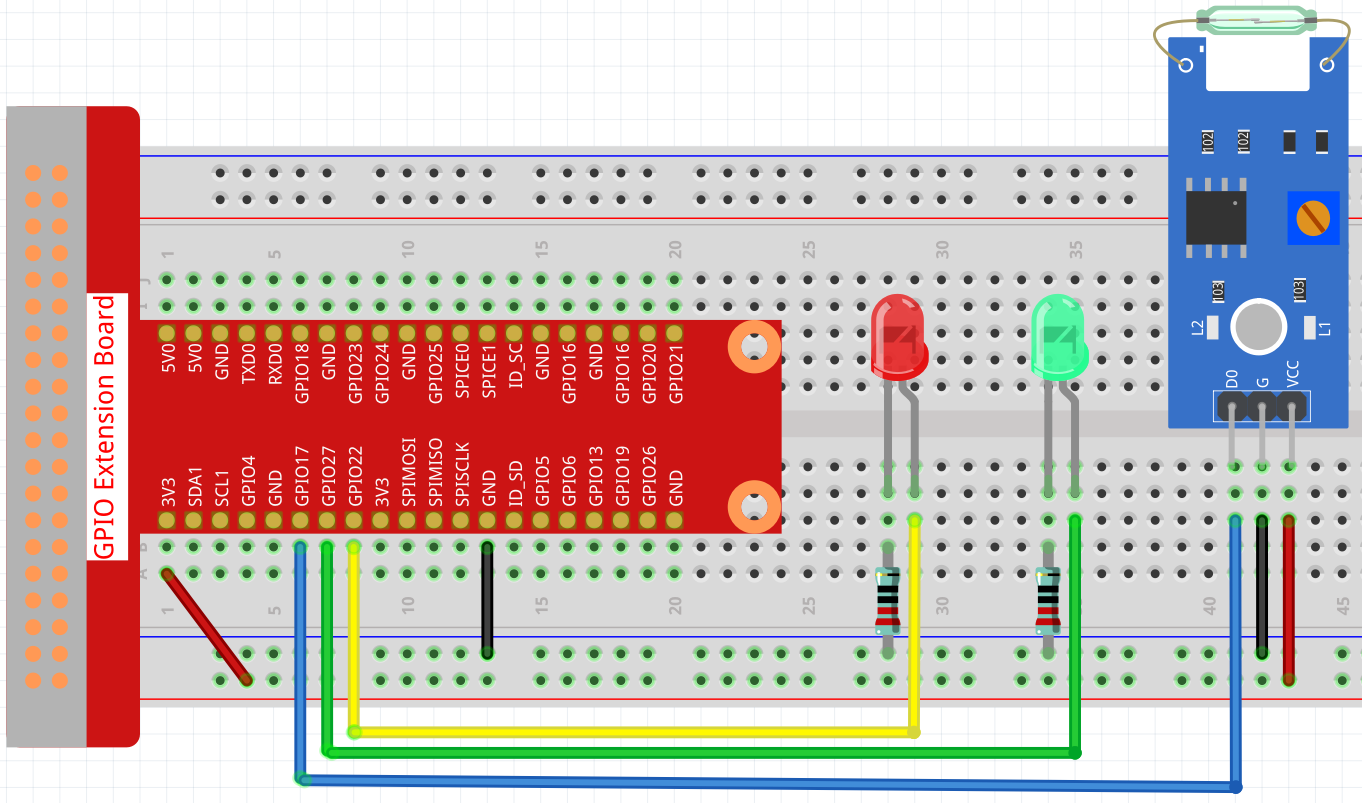
Step 2: Change directory.
cd ~/raphael-kit/python/
Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 2.2.4_ReedSwitch.py
The green LED will light up when the code is run. If a magnet is placed close to the reed switch module, the red LED lights up; take away the magnet and the green LED lights up again.
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like raphael-kit/python. After modifying the code, you can run it directly to see the effect.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
ReedPin = 17
Gpin = 27
Rpin = 22
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) #
GPIO.setup(Gpin, GPIO.OUT) # Set Green Led Pin mode to output
GPIO.setup(Rpin, GPIO.OUT) # Set Red Led Pin mode to output
GPIO.setup(ReedPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Set ReedPin's mode is input, and pull up to high level(3.3V)
GPIO.add_event_detect(ReedPin, GPIO.BOTH, callback=detect, bouncetime=200)
def Led(x):
if x == 0:
GPIO.output(Rpin, 1)
GPIO.output(Gpin, 0)
if x == 1:
GPIO.output(Rpin, 0)
GPIO.output(Gpin, 1)
def detect(self):
Led(GPIO.input(ReedPin))
def loop():
while True:
pass
def destroy():
GPIO.output(Gpin, GPIO.HIGH) # Green led on
GPIO.output(Rpin, GPIO.LOW) # Red led off
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
detect()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
Code Explanation
ReedPin = 17
Gpin = 27
Rpin = 22
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) #
GPIO.setup(Gpin, GPIO.OUT) # Set Green Led Pin mode to output
GPIO.setup(Rpin, GPIO.OUT) # Set Red Led Pin mode to output
GPIO.setup(ReedPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Set ReedPin's mode is input, and pull up to high level(3.3V)
GPIO.add_event_detect(ReedPin, GPIO.BOTH, callback=detect, bouncetime=200)
Set the GPIO modes to BCM Numbering. ReedPin, Gpin and Rpin connects to the GPIO17, GPIO27 and GPIO22.
GPIO.add_event_detect() is used to add an event that is triggered by a change in the value (level) of ReedPin, at which point the callback function detect() is called.
def Led(x):
if x == 0:
GPIO.output(Rpin, 1)
GPIO.output(Gpin, 0)
if x == 1:
GPIO.output(Rpin, 0)
GPIO.output(Gpin, 1)
Define a function Led() to turn the two LEDs on or off. If x=0, the red LED lights up; otherwise, the green LED will be lit.
def detect(self):
Led(GPIO.input(ReedPin))
In this callback function, the value of the reed switch is used to control the 2 LEDs.