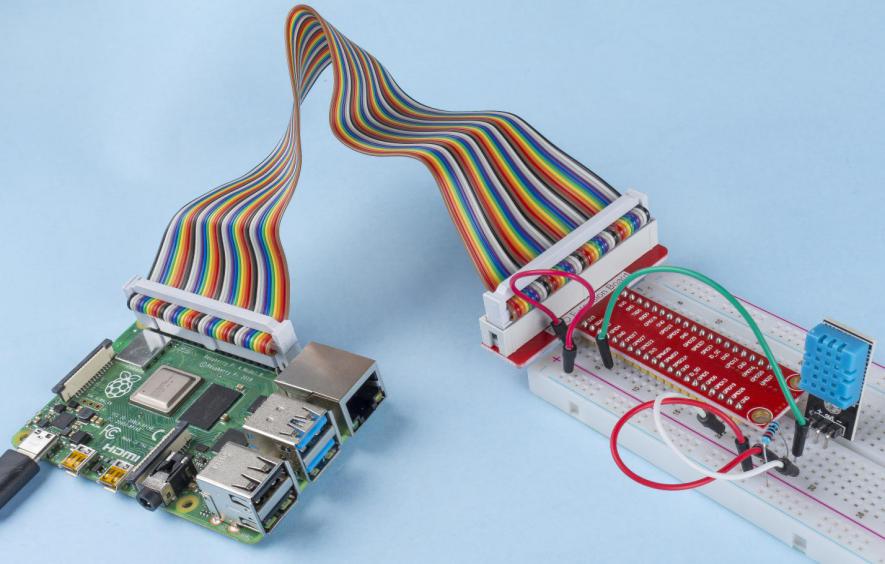
2.2.3 DHT-11¶
Introduction¶
The digital temperature and humidity sensor DHT11 is a composite sensor that contains a calibrated digital signal output of temperature and humidity. The technology of a dedicated digital modules collection and the technology of the temperature and humidity sensing are applied to ensure that the product has high reliability and excellent stability.
The sensors include a wet element resistive sensor and a NTC temperature sensor and they are connected to a high performance 8-bit microcontroller.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
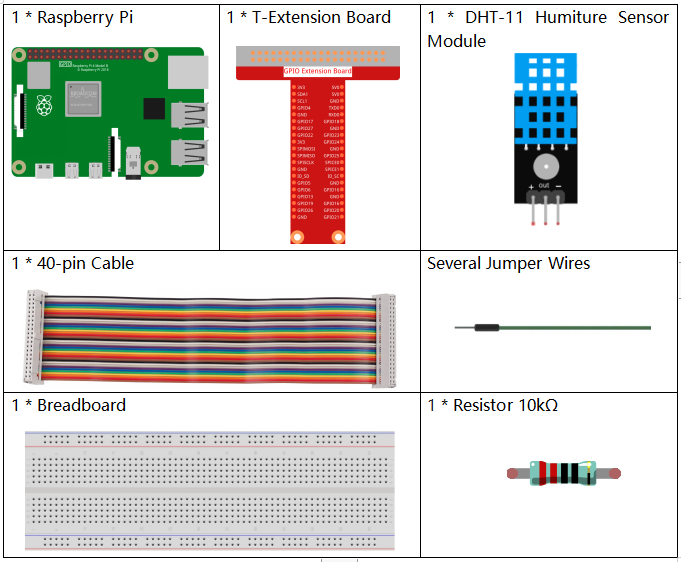
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
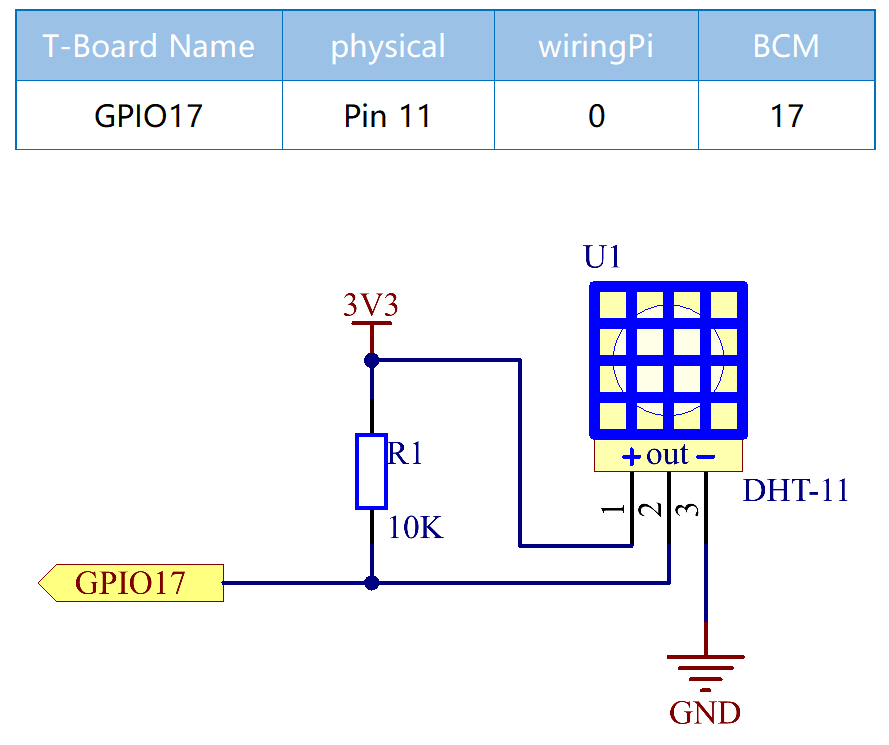
Schematic Diagram¶
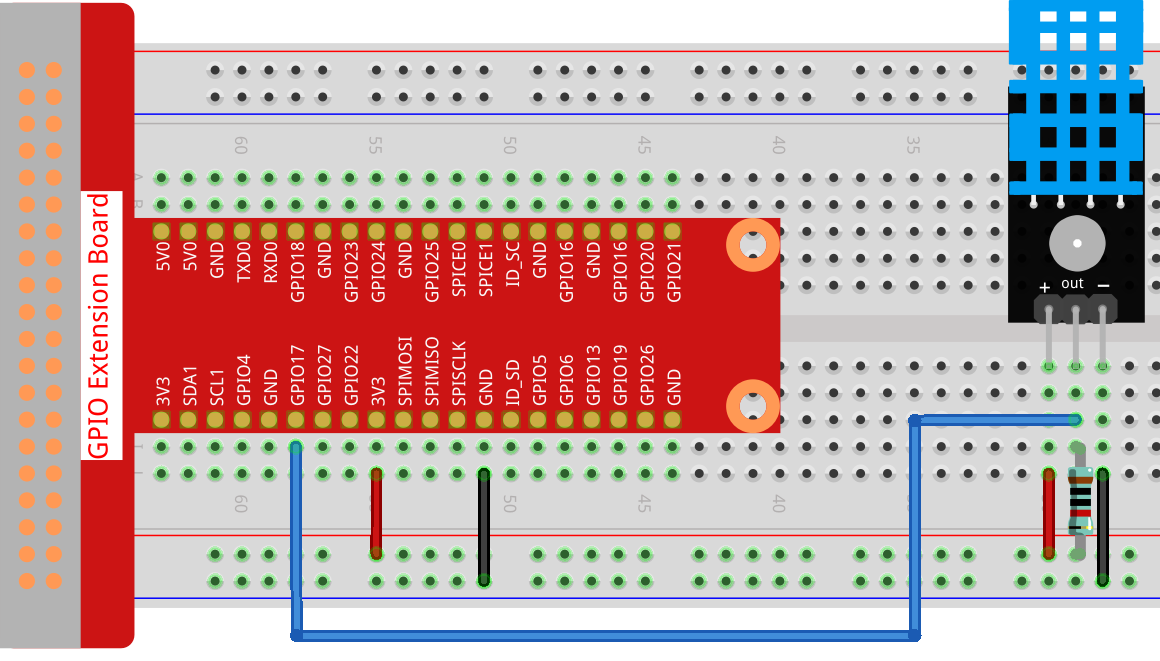
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/python/
Step 3: Run the executable file.
sudo python3 2.2.3_DHT.py
After the code runs, the program will print the temperature and humidity detected by DHT11 on the computer screen.
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like raphael-kit/python. After modifying the code, you can run it directly to see the effect.
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
dhtPin = 17
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
MAX_UNCHANGE_COUNT = 100
STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN = 1
STATE_INIT_PULL_UP = 2
STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN = 3
STATE_DATA_PULL_UP = 4
STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN = 5
def readDht11():
GPIO.setup(dhtPin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(dhtPin, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.05)
GPIO.output(dhtPin, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.02)
GPIO.setup(dhtPin, GPIO.IN, GPIO.PUD_UP)
unchanged_count = 0
last = -1
data = []
while True:
current = GPIO.input(dhtPin)
data.append(current)
if last != current:
unchanged_count = 0
last = current
else:
unchanged_count += 1
if unchanged_count > MAX_UNCHANGE_COUNT:
break
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN
lengths = []
current_length = 0
for current in data:
current_length += 1
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_UP:
if current == GPIO.HIGH:
state = STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_UP:
if current == GPIO.HIGH:
current_length = 0
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN:
if current == GPIO.LOW:
lengths.append(current_length)
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
else:
continue
if len(lengths) != 40:
#print ("Data not good, skip")
return False
shortest_pull_up = min(lengths)
longest_pull_up = max(lengths)
halfway = (longest_pull_up + shortest_pull_up) / 2
bits = []
the_bytes = []
byte = 0
for length in lengths:
bit = 0
if length > halfway:
bit = 1
bits.append(bit)
#print ("bits: %s, length: %d" % (bits, len(bits)))
for i in range(0, len(bits)):
byte = byte << 1
if (bits[i]):
byte = byte | 1
else:
byte = byte | 0
if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0):
the_bytes.append(byte)
byte = 0
#print (the_bytes)
checksum = (the_bytes[0] + the_bytes[1] + the_bytes[2] + the_bytes[3]) & 0xFF
if the_bytes[4] != checksum:
#print ("Data not good, skip")
return False
return the_bytes[0], the_bytes[2]
def main():
while True:
result = readDht11()
if result:
humidity, temperature = result
print ("humidity: %s %%, Temperature: %s ℃" % (humidity, temperature))
time.sleep(1)
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup()
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
main()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
Code Explanation
def readDht11():
GPIO.setup(dhtPin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(dhtPin, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.05)
GPIO.output(dhtPin, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.02)
GPIO.setup(dhtPin, GPIO.IN, GPIO.PUD_UP)
unchanged_count = 0
last = -1
data = []
#...
This function is used to implement the functions of DHT11. It stores the detected data in the the_bytes[] array. DHT11 transmits data of 40 bits at a time. The first 16 bits are related to humidity, the middle 16 bits are related to temperature, and the last eight bits are used for verification. The data format is:
8bit humidity integer data +8bit humidity decimal data +8bit temperature integer data + 8bit temperature decimal data + 8bit check bit.
When the validity is detected via the check bit, the function returns two results: 1. error; 2. humidity and temperature.
checksum = (the_bytes[0] + the_bytes[1] + the_bytes[2] + the_bytes[3]) & 0xFF
if the_bytes[4] != checksum:
#print ("Data not good, skip")
return False
return the_bytes[0], the_bytes[2]
For example, if the received date is 00101011(8-bit value of humidity integer) 00000000 (8-bit value of humidity decimal) 00111100 (8-bit value of temperature integer) 00000000 (8-bit value of temperature decimal) 01100111 (check bit)
Calculation:
00101011+00000000+00111100+00000000=01100111.
If the final result is equal to the check bit data, the data transmission is abnormal: return False.
If the final result is equal to the check bit data, the received data is correct, then there will return the_bytes[0] and the_bytes[2] and output “Humidity =43%,Temperature =60C”.
Phenomenon Picture¶