Bluetooth Piano¶
This project uses an Android app created with MIT App Inventor to enable a straightforward “piano” feature by utilizing a JDY-31 Bluetooth module and a Passive Buzzer Module. The Bluetooth piano project allows users to play different musical notes on a passive buzzer module using a JDY-31 Bluetooth module. By sending specific note instructions via Bluetooth to the Arduino, users can generate corresponding tones on the buzzer.
The Android application will be constructed utilizing a complimentary web-based platform known as MIT App Inventor. The project presents an excellent opportunity to gain familiarity with the interfacing of an Arduino with a smartphone.
1. Build the Circuit¶

2. Create the Android App¶
The Android application will be developed using a free web application known as MIT App Inventor. MIT App Inventor serves as an excellent starting point for Android development, owing to its intuitive drag-and-drop features allowing for the creation of simplistic applications.
Now, let’s begin.
Go to Get Started with MIT App Inventor, and click “online tool” to login. You will require a Google account to register with MIT App Inventor.

After logging in, navigate to Projects -> Import project (.aia) from my computer. Subsequently, upload the
piano.aiafile located in the pathultimate-sensor-kit\iot_project\bluetooth\06-Bluetooth_piano.You can also directly download here:
piano.aia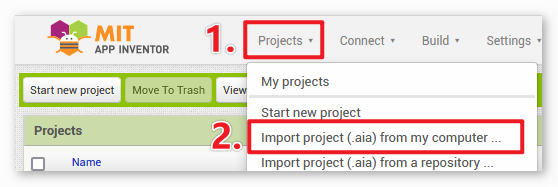
Upon uploading the
.aiafile, you will see the application on the MIT App Inventor software. This is a pre-configured template. You can modify this template after you have familiarized yourself with MIT App Inventor through the following steps.In MIT App Inventor, you have 2 primary sections: the Designer and the Blocks. You can switch between these two sections in the upper right corner of the page.
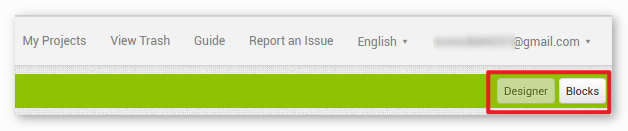
The Designer allows you to add buttons, text, screens, and modify the overall aesthetic of your application.

Next, there’s the Blocks section. This section lets you craft custom functionalities for your app, allowing you to program each component on the app’s GUI to achieve desired features.

To install the application on a smartphone, navigate to the Build tab.

You can generate a
.apkfile. After selecting this option, a page will appear allowing you to choose between downloading a.apkfile or scanning a QR code for installation. Follow the installation guide to complete the application installation.You also download our pre-compiled APK here:
piano.apkIf you wish to upload this app to Google Play or another app marketplace, you can generate a
.aabfile.
3. Upload the Code¶
Open the
06-Bluetooth_piano.inofile under the path ofultimate-sensor-kit\iot_project\bluetooth\06-Bluetooth_piano, or copy this code into Arduino IDE.After selecting the correct board and port, click the Upload button.
Open the Serial monitor(set baudrate to 9600) to view debug messages.
4. App and Bluetooth module Connection¶
Ensure that the application created earlier is installed on your smartphone.
Initially, turn on Bluetooth on your smartphone.
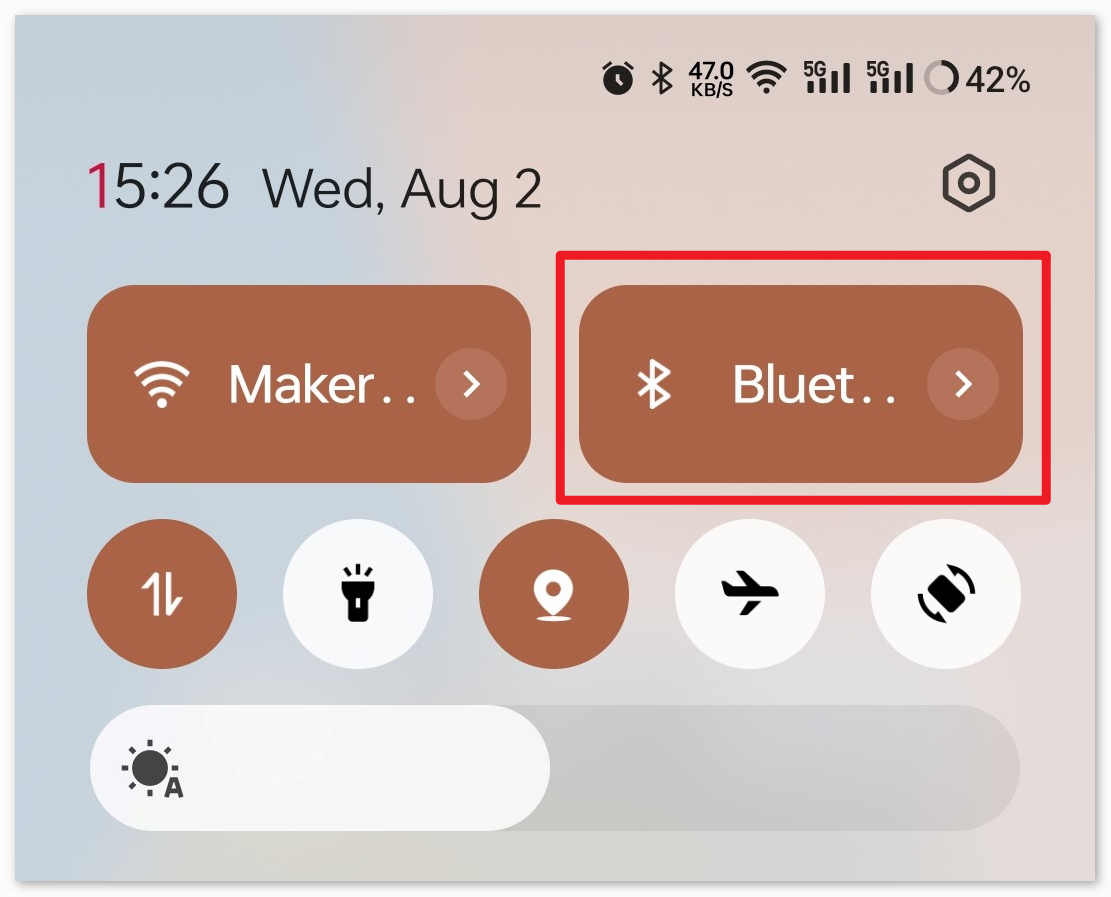
Navigate to the Bluetooth settings on your smartphone and look for names like JDY-31-SPP.

After clicking it, agree to the Pair request in the pop-up window. If prompted for a pairing code, please enter “1234”.

Now open the newly installed Piano APP.

In the APP, click on Connect button to establish a connection between the APP and Bluetooth module.

This page displays a list of all paired Bluetooth devices. Choose the
xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx JDY-31-SPPoption from the list. The name of each device is listed next to its MAC address.
If you don’t see any devices on the page shown above, it could be because this app is not authorized to scan for nearby devices. In such a case, you will need to adjust the settings manually.
To access the APP Info page, long-press the app icon and select it. Alternatively, if you have another method to reach this page, use that instead.

Navigate to the Permissions page.

To enable the APP to scan for nearby devices, go to Nearby devices and select Always.

Now, restart the APP and repeat steps 5 and 6 to successfully connect to Bluetooth.
After a successful connection, you can click on the buttons in the app to play different notes, and even perform some simple songs.

5. Code explanation¶
Setting Up Libraries and Pins
#include "pitches.h" #include <SoftwareSerial.h> const int bluetoothTx = 3; const int bluetoothRx = 4; SoftwareSerial bleSerial(bluetoothTx, bluetoothRx); const int buzzerPin = 2;
pitches.h: This file contains the frequency values for musical notes.
Variable Declarations for Storing Bluetooth Data
char character; String noteType;
character: Stores individual characters received from Bluetooth.noteType: Aggregates the characters to form the full note instruction.
Setup Function - Initializing Serial Communications
void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); bleSerial.begin(9600); }
Initializes serial communication at a baud rate of 9600.
The standard
Serialis for debugging whilebleSerialis specifically for Bluetooth communication.
Main Loop - Reading Bluetooth Data and Playing Corresponding Notes
void loop() { while (bleSerial.available() > 0) { character = bleSerial.read(); noteType = noteType + character; if (character == '*') { noteType = noteType.substring(0, noteType.length() - 1); Serial.println(noteType); if (noteType == "NOTE_C4") { tone(buzzerPin, NOTE_C4); } // ... other notes check similarly ... noteType = ""; delay(200); noTone(buzzerPin); } } }
Reads characters from Bluetooth and assembles the
noteType.If an asterisk (‘*’) is detected, it indicates the end of the note instruction. The note is then played, followed by a short delay and then stopped.