2.1.5 Keypad¶
Introduction¶
A keypad is a rectangular array of buttons. In this project, We will use it input characters.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
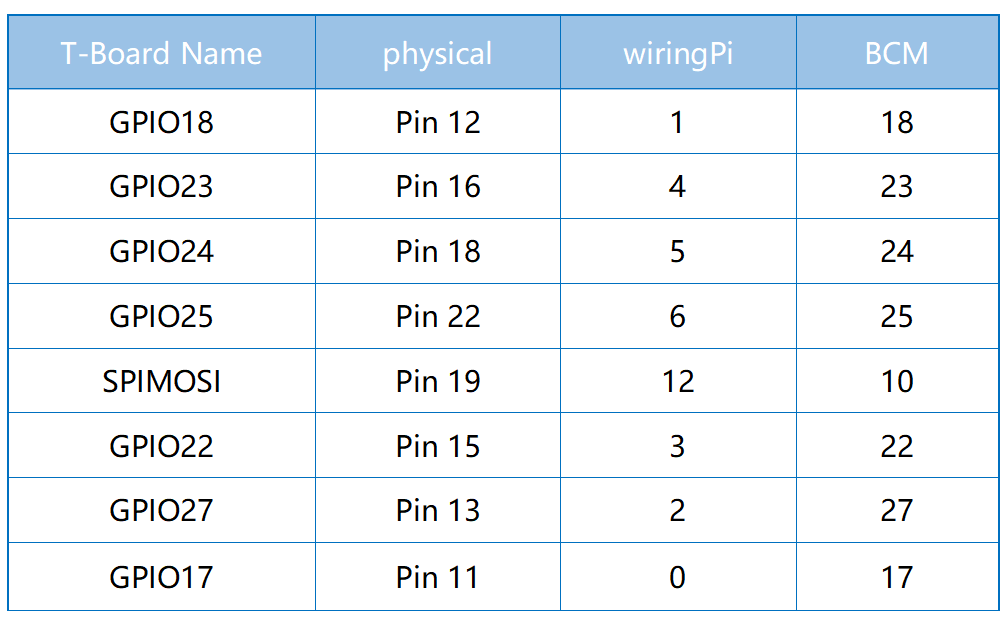
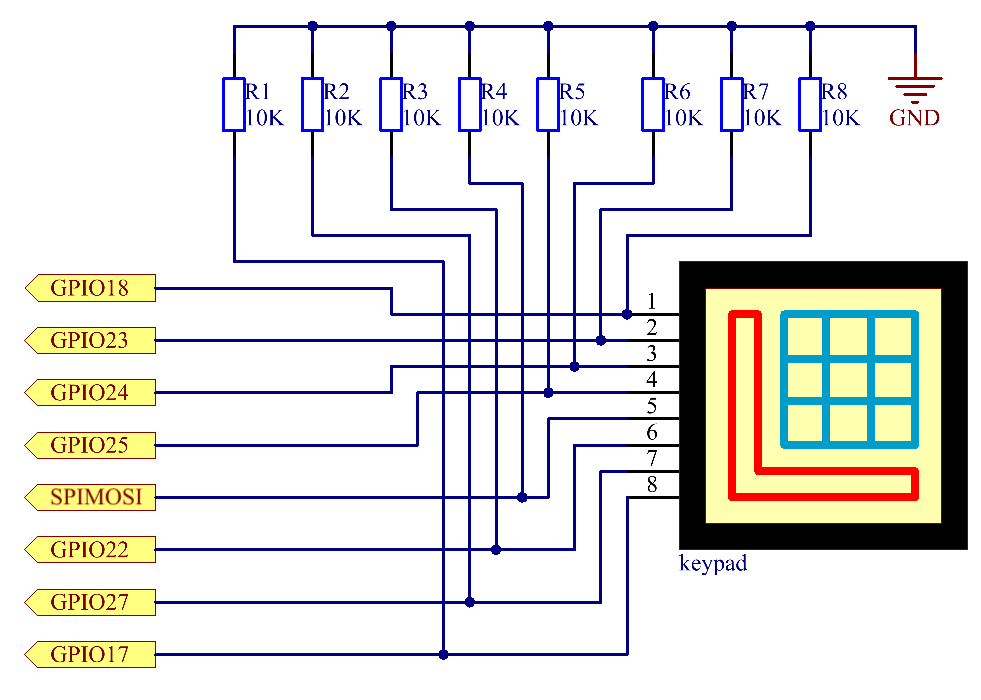
Schematic Diagram¶
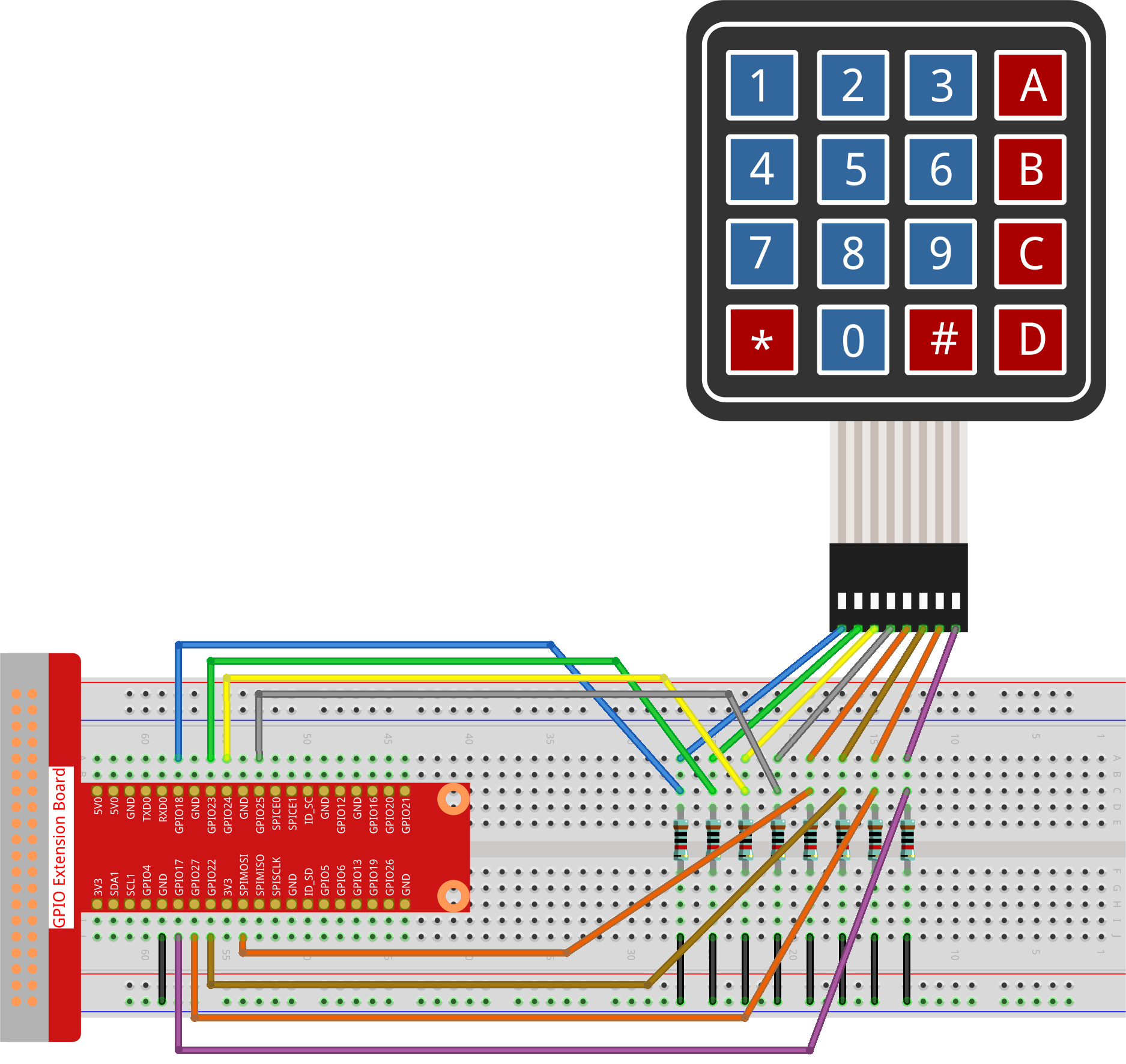
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Open the code file.
cd ~/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python-pi5
Step 3: Run.
sudo python3 2.1.5_Keypad_zero.py
After the code runs, the values of pressed buttons on keypad (button Value) will be printed on the screen.
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/python-pi5. After modifying the code, you can run it directly to see the effect.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from gpiozero import DigitalOutputDevice, Button
from time import sleep
class Keypad:
def __init__(self, rows_pins, cols_pins, keys):
"""
Initialize the Keypad with specified row and column pins and keypad layout.
:param rows_pins: List of GPIO pins for the rows.
:param cols_pins: List of GPIO pins for the columns.
:param keys: List of keys in the keypad layout.
"""
# Initialize row pins as DigitalOutputDevice
self.rows = [DigitalOutputDevice(pin) for pin in rows_pins]
# Initialize column pins as Buttons
self.cols = [Button(pin, pull_up=False) for pin in cols_pins]
self.keys = keys # Set the keypad layout
def read(self):
"""
Read the currently pressed keys on the keypad.
:return: A list of pressed keys.
"""
pressed_keys = []
# Scan each row and column to identify pressed keys
for i, row in enumerate(self.rows):
row.on() # Enable the current row
for j, col in enumerate(self.cols):
if col.is_pressed: # Check if the column button is pressed
# Calculate the key index based on row and column
index = i * len(self.cols) + j
pressed_keys.append(self.keys[index])
row.off() # Disable the current row
return pressed_keys
try:
# Configure rows, columns, and keypad layout
rows_pins = [18, 23, 24, 25]
cols_pins = [10, 22, 27, 17]
keys = ["1", "2", "3", "A",
"4", "5", "6", "B",
"7", "8", "9", "C",
"*", "0", "#", "D"]
# Create an instance of the Keypad class
keypad = Keypad(rows_pins, cols_pins, keys)
last_key_pressed = []
# Continuously read the keypad and print newly pressed keys
while True:
pressed_keys = keypad.read()
if pressed_keys and pressed_keys != last_key_pressed:
print(pressed_keys) # Print the list of pressed keys
last_key_pressed = pressed_keys
sleep(0.1) # Short delay to reduce CPU load
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# Handle a keyboard interrupt (Ctrl+C) for a clean exit
pass
Code Explanation
Imports the
DigitalOutputDeviceandButtonclasses from thegpiozerolibrary, and thesleepfunction for delays.#!/usr/bin/env python3 from gpiozero import DigitalOutputDevice, Button from time import sleep
Defines the
Keypadclass. The__init__method initializes the keypad with given row and column pins and keys. Thereadmethod scans the keypad and returns a list of pressed keys.class Keypad: def __init__(self, rows_pins, cols_pins, keys): """ Initialize the Keypad with specified row and column pins and keypad layout. :param rows_pins: List of GPIO pins for the rows. :param cols_pins: List of GPIO pins for the columns. :param keys: List of keys in the keypad layout. """ # Initialize row pins as DigitalOutputDevice self.rows = [DigitalOutputDevice(pin) for pin in rows_pins] # Initialize column pins as Buttons self.cols = [Button(pin, pull_up=False) for pin in cols_pins] self.keys = keys # Set the keypad layout def read(self): """ Read the currently pressed keys on the keypad. :return: A list of pressed keys. """ pressed_keys = [] # Scan each row and column to identify pressed keys for i, row in enumerate(self.rows): row.on() # Enable the current row for j, col in enumerate(self.cols): if col.is_pressed: # Check if the column button is pressed # Calculate the key index based on row and column index = i * len(self.cols) + j pressed_keys.append(self.keys[index]) row.off() # Disable the current row return pressed_keys
Sets up the GPIO pins for rows and columns and defines the keypad layout.
try: # Configure rows, columns, and keypad layout rows_pins = [18, 23, 24, 25] cols_pins = [10, 22, 27, 17] keys = ["1", "2", "3", "A", "4", "5", "6", "B", "7", "8", "9", "C", "*", "0", "#", "D"]
Creates an instance of the
Keypadclass with the specified configuration.try: ... # Create an instance of the Keypad class keypad = Keypad(rows_pins, cols_pins, keys) last_key_pressed = []
Continuously reads the keypad for pressed keys, prints any changes in the key state, and introduces a short delay to reduce CPU load. Catches a KeyboardInterrupt (like Ctrl+C) to allow for a graceful exit from the script.
try: ... # Continuously read the keypad and print newly pressed keys while True: pressed_keys = keypad.read() if pressed_keys and pressed_keys != last_key_pressed: print(pressed_keys) # Print the list of pressed keys last_key_pressed = pressed_keys sleep(0.1) # Short delay to reduce CPU load except KeyboardInterrupt: # Handle a keyboard interrupt (Ctrl+C) for a clean exit pass