LED¶
Semiconductor light-emitting diode is a type of component which can turn electric energy into light energy via PN junctions. By wavelength, it can be categorized into laser diode, infrared light-emitting diode and visible light-emitting diode which is usually known as light-emitting diode (LED).
Diode has unidirectional conductivity, so the current flow will be as the arrow indicates in figure circuit symbol. You can only provide the anode with a positive power and the cathode with a negative. Thus the LED will light up.
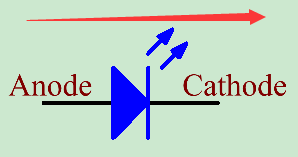
An LED has two pins. The longer one is the anode, and shorter one, the cathode. Pay attention not to connect them inversely. There is fixed forward voltage drop in the LED, so it cannot be connected with the circuit directly because the supply voltage can outweigh this drop and cause the LED to be burnt. The forward voltage of the red, yellow, and green LED is 1.8 V and that of the white one is 2.6 V. Most LEDs can withstand a maximum current of 20 mA, so we need to connect a current limiting resistor in series.
The formula of the resistance value is as follows:
R = (Vsupply - VD)/I
R stands for the resistance value of the current limiting resistor, Vsupply for voltage supply, VD for voltage drop and I for the working current of the LED.
Here is the detailed introduction for the LED: LED - Wikipedia.
Example
Lesson 1 Blinking LED (Mega Board Project)
Lesson 8 Controlling an LED by Potentiometer (Mega Board Project)
Lesson 1 Blinking LED (R3 Board Project)
Lesson 8 Controlling an LED by Potentiometer (R3 Board Project)
2. Table Lamp (Scratch Project)
3. Breathing LED (Scratch Project)