Thermistor¶
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word is a combination of thermal and resistor. Thermistors are widely used as inrush current limiters, temperature sensors (negative temperature coefficient or NTC type typically), self-resetting overcurrent protectors, and self-regulating heating elements (positive temperature coefficient or PTC type typically).
Here is the electronic symbol of thermistor.
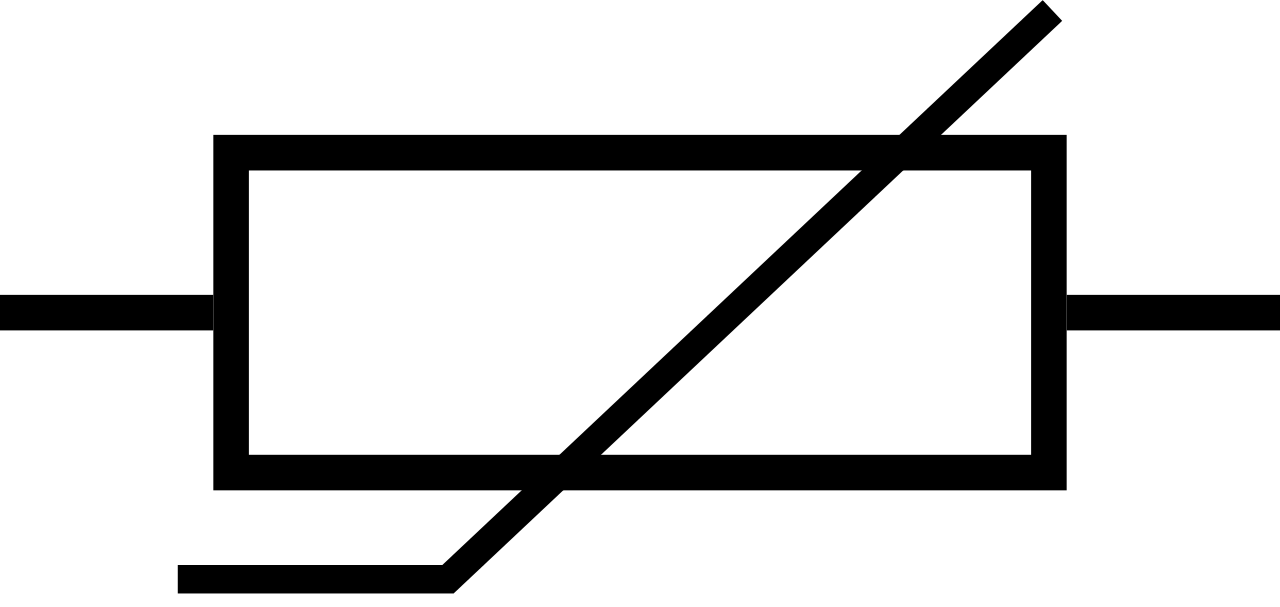
Thermistors are of two opposite fundamental types:
With NTC thermistors, resistance decreases as temperature rises usually due to an increase in conduction electrons bumped up by thermal agitation from valency band. An NTC is commonly used as a temperature sensor, or in series with a circuit as an inrush current limiter.
With PTC thermistors, resistance increases as temperature rises usually due to increased thermal lattice agitations particularly those of impurities and imperfections. PTC thermistors are commonly installed in series with a circuit, and used to protect against overcurrent conditions, as resettable fuses.
In this kit we use an NTC one. Each thermistor has a normal resistance. Here it is 10k ohm, which is measured under 25 degree Celsius.
Here is the relation between the resistance and temperature:
RT = RN * expB(1/TK - 1/TN)
RT is the resistance of the NTC thermistor when the temperature is TK.
RN is the resistance of the NTC thermistor under the rated temperature TN. Here, the numerical value of RN is 10k.
TK is a Kelvin temperature and the unit is K. Here, the numerical value of TK is 273.15 + degree Celsius.
TN is a rated Kelvin temperature; the unit is K too. Here, the numerical value of TN is 273.15+25.
And B(beta), the material constant of NTC thermistor, is also called heat sensitivity index with a numerical value 3950.
exp is the abbreviation of exponential, and the base number e is a natural number and equals 2.7 approximately.
Convert this formula TK=1/(ln(RT/RN)/B+1/TN) to get Kelvin temperature that minus 273.15 equals degree Celsius.
This relation is an empirical formula. It is accurate only when the temperature and resistance are within the effective range.
Example
Lesson 12 Thermistor (Mega Board Project)
Lesson 12 Thermistor (R3 Board Project)
9. Low Temperature Alarm (Scratch Project)