Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
1.3.2 Servo¶
Introduction¶
In this project, we will learn how to make the servo rotate.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
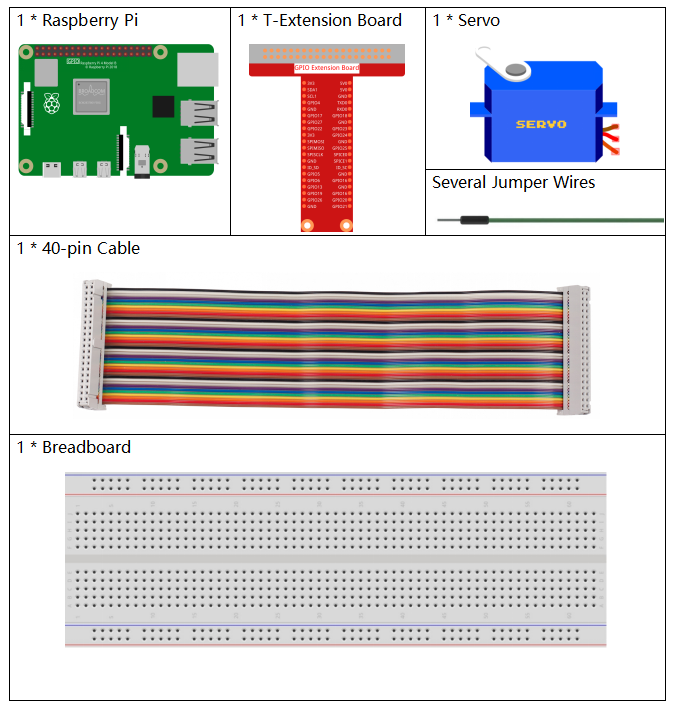
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
Schematic Diagram¶
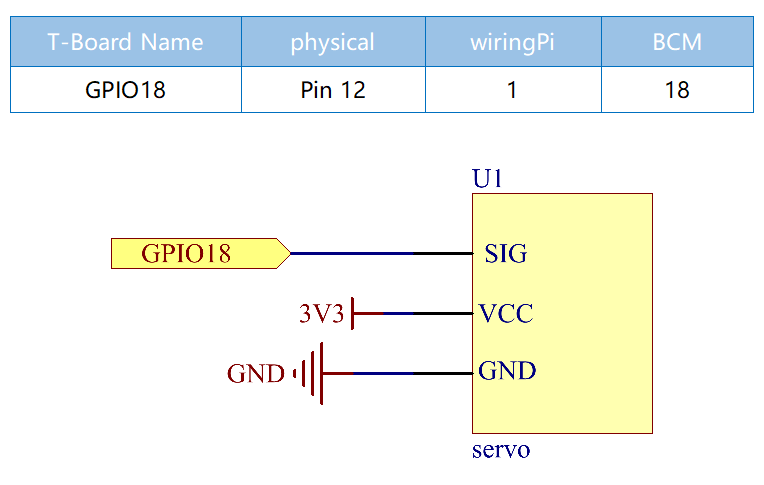
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
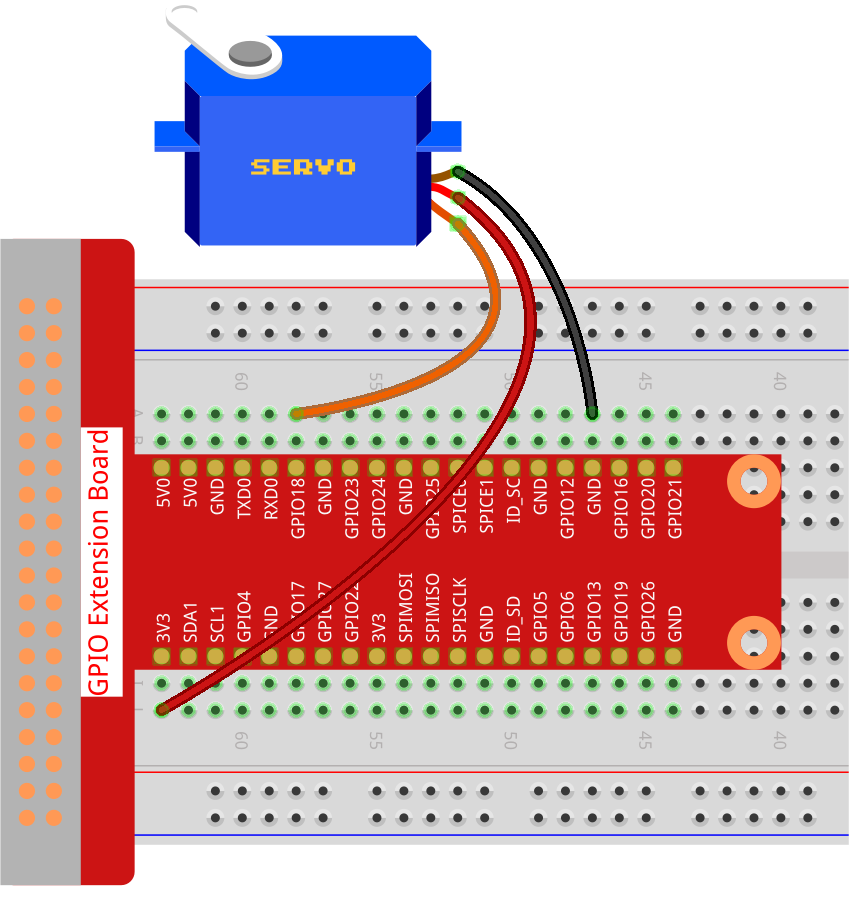
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/python-pi5
Step 3: Run the executable file.
sudo python3 1.3.2_Servo_zero.py
After the program is executed, the servo will rotate from 0 degrees to 90 to 180 degrees, and then from 180 degrees to 90 to 0 degrees, in a circle.
Code
Note
You can Modify/Reset/Copy/Run/Stop the code below. But before that, you need to go to source code path like raphael-kit/python-pi5. After modifying the code, you can run it directly to see the effect.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from gpiozero import Servo
from time import sleep
# Set the GPIO pin number where the servo motor is connected
myGPIO = 18
# Define a correction factor to fine-tune servo pulse width
myCorrection = 0.45
maxPW = (2.0 + myCorrection) / 1000 # Calculate maximum pulse width
minPW = (1.0 - myCorrection) / 1000 # Calculate minimum pulse width
# Initialize the Servo object with custom pulse widths
servo = Servo(myGPIO, min_pulse_width=minPW, max_pulse_width=maxPW)
try:
while True:
# Position the servo at the middle and wait
servo.mid()
print("mid") # Indicate current position
sleep(0.5) # Brief pause for 0.5 seconds
# Move the servo to its minimum position and wait
servo.min()
print("min") # Indicate current position
sleep(1) # Hold position for 1 second
# Return the servo to the middle position and wait
servo.mid()
print("mid") # Indicate current position
sleep(0.5) # Brief pause for 0.5 seconds
# Move the servo to its maximum position and wait
servo.max()
print("max") # Indicate current position
sleep(1) # Hold position for 1 second
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# Gracefully terminate the script on a keyboard interrupt (Ctrl+C)
pass
Code Explanation
These import statements bring in the
Servoclass for servo control and thesleepfunction for timing.#!/usr/bin/env python3 from gpiozero import Servo from time import sleep
Sets the GPIO pin number 18 for connecting the servo motor.
# Set the GPIO pin number where the servo motor is connected myGPIO = 18
These lines define a correction factor and use it to calculate the maximum and minimum pulse widths for the servo, fine-tuning its movement range.
# Define a correction factor to fine-tune servo pulse width myCorrection = 0.45 maxPW = (2.0 + myCorrection) / 1000 # Calculate maximum pulse width minPW = (1.0 - myCorrection) / 1000 # Calculate minimum pulse width
Initializes the Servo object with the specified GPIO pin and custom pulse widths.
# Initialize the Servo object with custom pulse widths servo = Servo(myGPIO, min_pulse_width=minPW, max_pulse_width=maxPW)
The
tryblock contains awhile Trueloop to continuously move the servo. The servo is positioned at mid, min, and max points, with each position printed and held for a specified duration.try: while True: # Position the servo at the middle and wait servo.mid() print("mid") # Indicate current position sleep(0.5) # Brief pause for 0.5 seconds # Move the servo to its minimum position and wait servo.min() print("min") # Indicate current position sleep(1) # Hold position for 1 second # Return the servo to the middle position and wait servo.mid() print("mid") # Indicate current position sleep(0.5) # Brief pause for 0.5 seconds # Move the servo to its maximum position and wait servo.max() print("max") # Indicate current position sleep(1) # Hold position for 1 second except KeyboardInterrupt: # Gracefully terminate the script on a keyboard interrupt (Ctrl+C) pass