1.1.5 4-Digit 7-Segment Display¶
Introduction¶
Next, follow me to try to control the 4-digit 7-segment display.
Components¶
Note
In this projiect, for the 4-Digit 7-Segment Display we should use BS model,if you use AS model it may not light up.
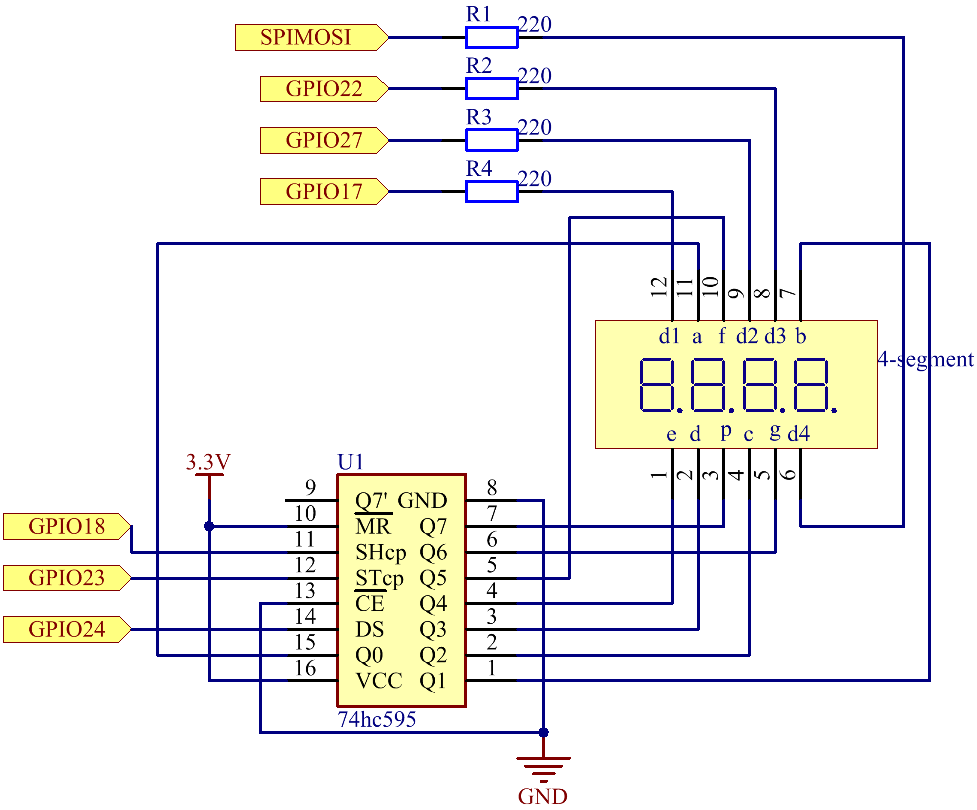
Schematic Diagram¶
Experimental Procedures¶
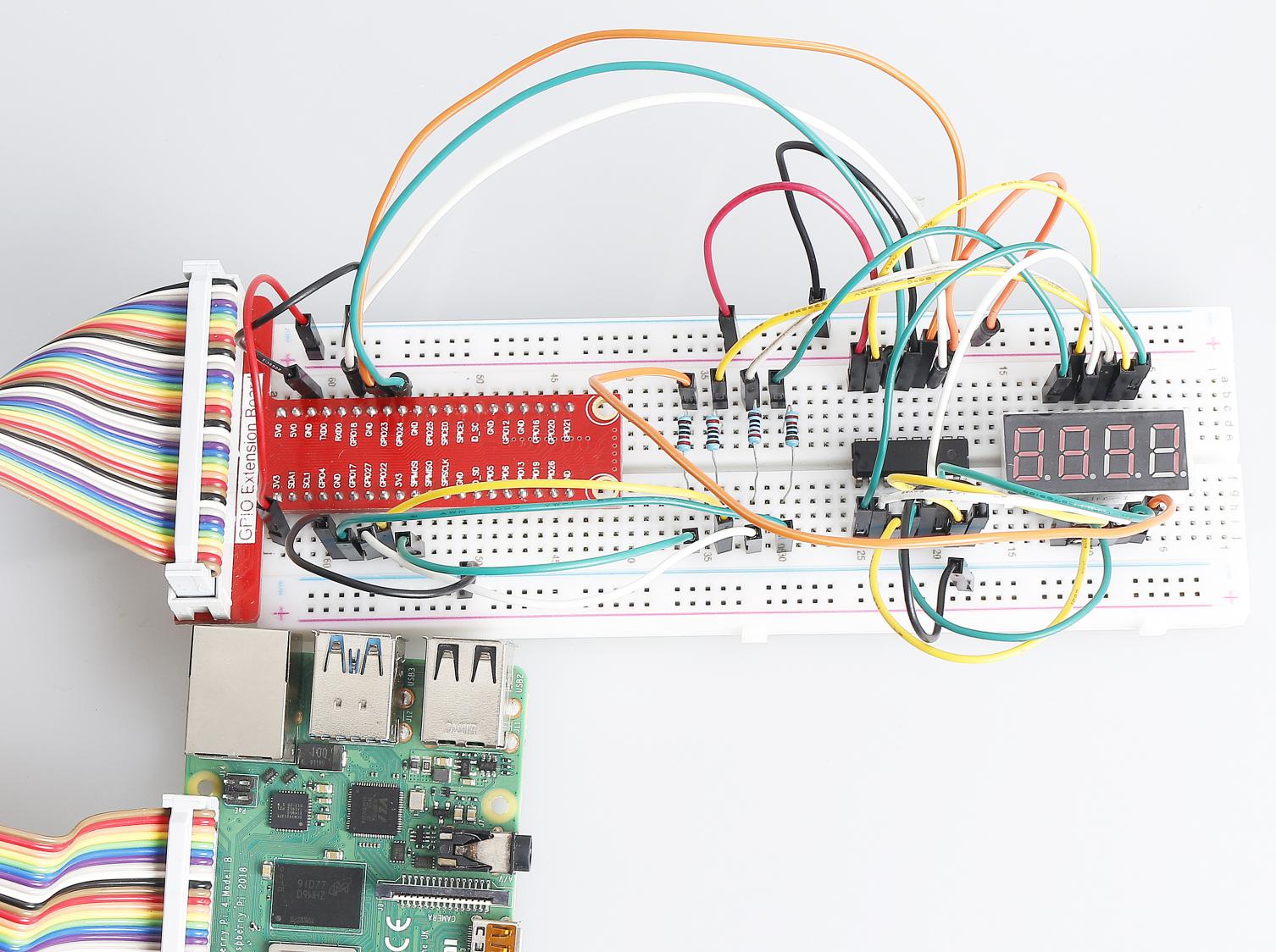
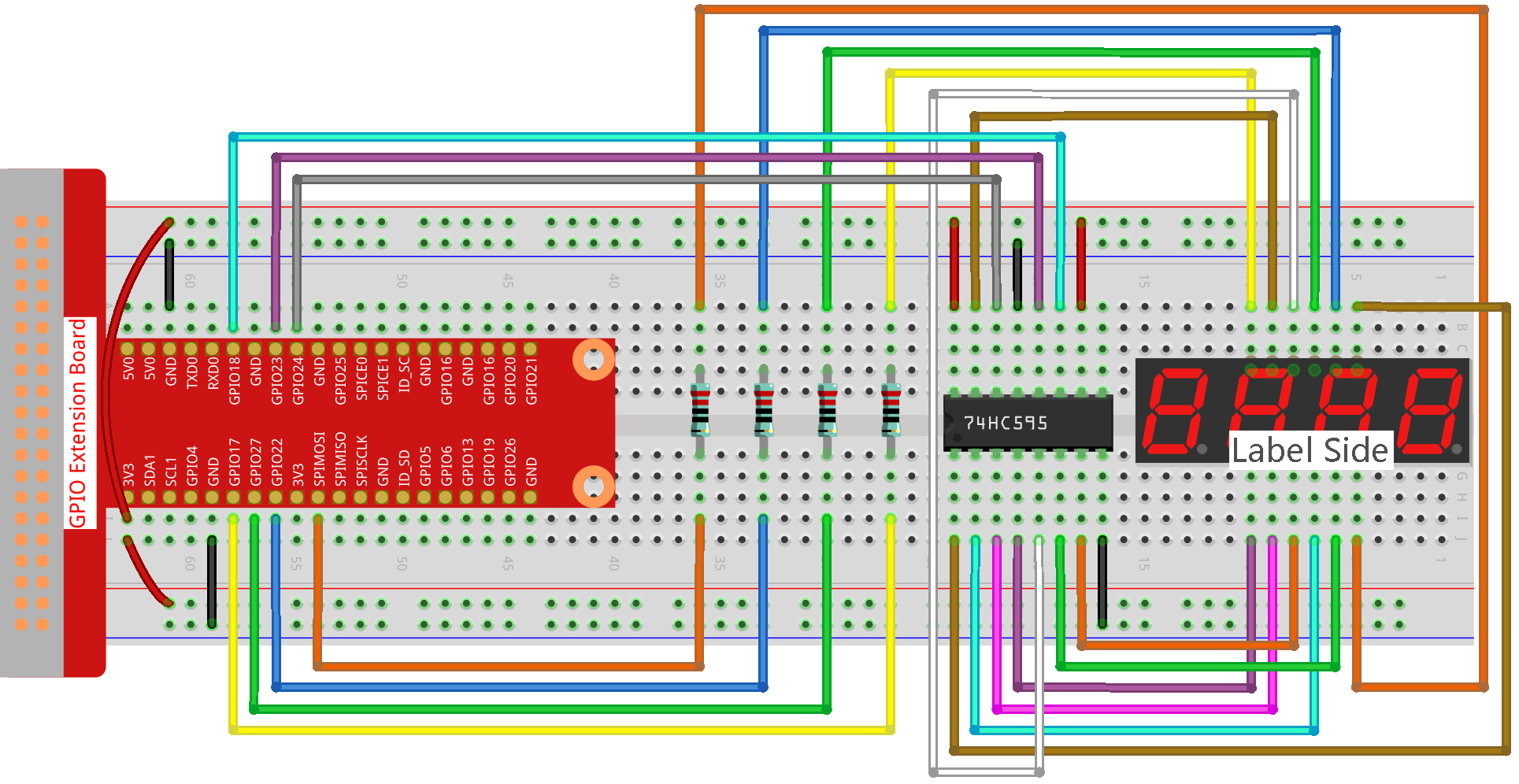
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/davinci-kit-for-raspberry-pi/nodejs/
Step 3: Run the code.
sudo node 4_digit_7_segment_display.js
After the code runs, the program takes a count, increasing by 1 per second, and the 4-digit 7-segment display displays the count.
Code
const Gpio = require('pigpio').Gpio;
var counter = 0;
const number = [0xc0, 0xf9, 0xa4, 0xb0, 0x99, 0x92, 0x82, 0xf8, 0x80, 0x90]; //for BS
const SDI = new Gpio(24, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const RCLK = new Gpio(23, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const SRCLK = new Gpio(18, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const pin1 = new Gpio(10, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const pin2 = new Gpio(22, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const pin3 = new Gpio(27, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const pin4 = new Gpio(17, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const placePin = [pin1, pin2, pin3, pin4];
function clearDisplay() {
hc595_shift(0xff); //for BS
}
function hc595_shift(dat) {
for (let j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
let code = 0x80 & (dat << j);
if (code != 0) {
code = 1;
}
SDI.digitalWrite(code);
SRCLK.trigger(1,1);
}
RCLK.trigger(1,1);
}
function pickDigit(digit) {
for(let i=0;i<4;i++){
placePin[i].digitalWrite(0);
}
placePin[digit].digitalWrite(1);
}
let digit = -1
setInterval(() => {
digit = (digit +1)% 4
clearDisplay();
pickDigit(digit);
switch(digit){
case 0:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 10)]);
break;
case 1:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 100 / 10)]);
break;
case 2:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 1000 / 100)]);
break;
case 3:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 10000 / 1000)]);
break;
}
}, 5);
setInterval(() => {
counter++;
}, 1000);
Code Explanation
const pin1 = new Gpio(10, {mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const pin2 = new Gpio(25, {mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const pin3 = new Gpio(27, {mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const pin4 = new Gpio(17, {mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const placePin = [pin1,pin2,pin3,pin4];
Initialize pins 10, 25, 27, and 17 as output modes and place them in the array placePin to facilitate control of the common anode of the four-digit 7-segment display.
const number = [0xc0, 0xf9, 0xa4, 0xb0, 0x99, 0x92, 0x82, 0xf8, 0x80, 0x90];
Define a constant array number to represent the hexadecimal segment code from 0 to 9 (common anode).
function clearDisplay() {
hc595_shift(0xff);
}
Write 0xff to turn off the digital tube.
function pickDigit(digit) {
for(let i=0;i<4;i++){
placePin[i].digitalWrite(0);
}
placePin[digit].digitalWrite(1);
}
Select the place of the value. there is only one place that should be enable each time. The enabled place will be written high.
let digit = -1
setInterval(() => {
digit = (digit +1)% 4
clearDisplay();
pickDigit(digit);
switch(digit){
case 0:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 10)]);
break;
case 1:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 100 / 10)]);
break;
case 2:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 1000 / 100)]);
break;
case 3:
hc595_shift(number[Math.floor(counter % 10000 / 1000)]);
break;
}
}, 5);
this code is used to set the number displayed on the 4-digit 7-segment Dispaly.
First, start the fourth segment display, write the single-digit number. Then start the third segment display, and type in the tens digit; after that, start the second and the first segment display respectively, and write the hundreds and thousands digits respectively. Because the refreshing speed is very fast, we see a complete four-digit display.
setInterval(() => {
counter++;
}, 1000);
Add one to the counter
(the four-digit digital tube displays the number plus one)
every second that passes.
Phenomenon Picture¶