Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
1.3.2 Servo¶
Introduction¶
In this project, we will learn how to make the servo rotate.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
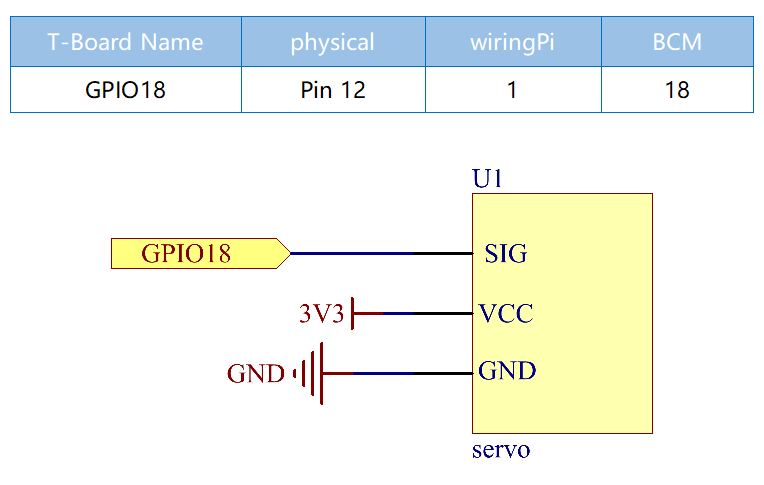
Schematic Diagram¶
Experimental Procedures¶
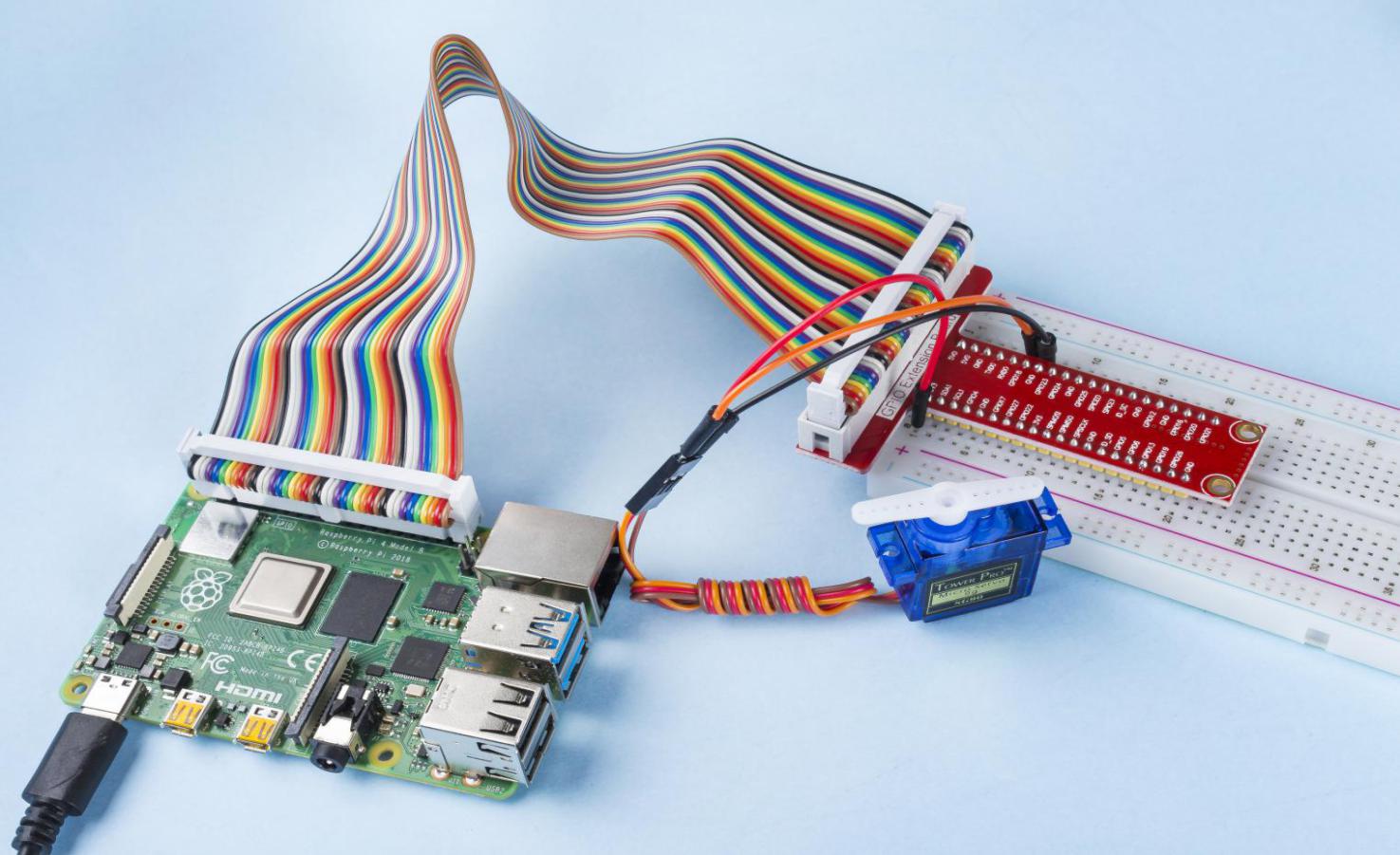
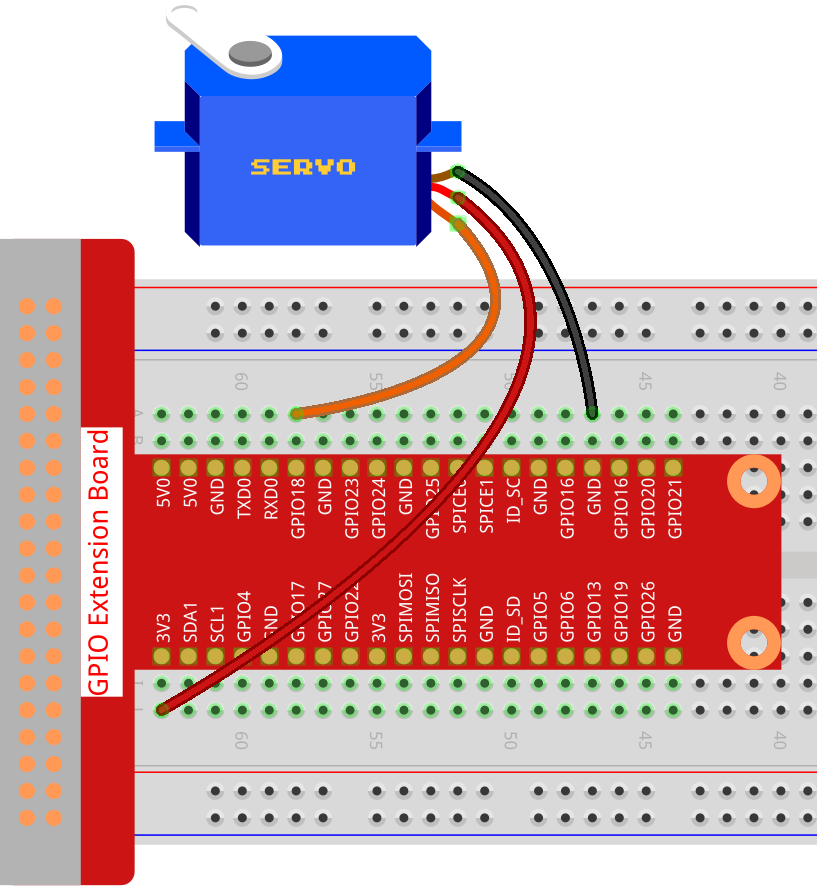
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/nodejs/
Step 3: Run the code.
sudo node servo.js
After the program is executed, the servo will rotate from 0 degrees to 180 degrees, and then from 180 degrees to 0 degrees, circularly.
Code
const Gpio = require('pigpio').Gpio;
SERVO_MIN_ANGLE = 0
SERVO_MAX_ANGLE = 180
SERVO_MIN_PULSE = 500
SERVO_MAX_PULSE = 2500
ServoPin = new Gpio(18,{mode: Gpio.OUTPUT})
function map(value, inMin, inMax, outMin, outMax){
return (outMax - outMin) * (value - inMin) / (inMax - inMin) + outMin
}
function angle2pulse(angle){
return Math.floor(map(angle,SERVO_MIN_ANGLE,SERVO_MAX_ANGLE,SERVO_MIN_PULSE ,SERVO_MAX_PULSE))
}
let angle=90;
let step=5;
setInterval(() => {
if(angle>=180||angle<=0){
step=-step
}
angle+=step;
ServoPin.servoWrite(angle2pulse(angle));
}, 20);
Code Explanation
const Gpio = require('pigpio').Gpio;
ServoPin = new Gpio(18,{mode: Gpio.OUTPUT})
Import the pigpio module and create an object of class Gpio, ServoPin, to control the output of Gpio18.
SERVO_MIN_ANGLE = 0
SERVO_MAX_ANGLE = 180
SERVO_MIN_PULSE = 500
SERVO_MAX_PULSE = 2500
function map(value, inMin, inMax, outMin, outMax){
return (outMax - outMin) * (value - inMin) / (inMax - inMin) + outMin
}
function angle2pulse(angle){
return Math.floor(map(angle,SERVO_MIN_ANGLE,SERVO_MAX_ANGLE,SERVO_MIN_PULSE ,SERVO_MAX_PULSE))
}
The function that maps the angle to the pulse width is defined here.
This is because the servo control function servoWrite(pulseWidth) encapsulated in the Gpio class needs to write pulse width instead of angle.
The angle range of the servo we use is 0~180, which needs to be mapped to the range of pulseWidth, 500~2500.
let angle=90;
let step=5;
setInterval(() => {
if(angle>=180||angle<=0){
step=-step
}
angle+=step;
ServoPin.servoWrite(angle2pulse(angle));
}, 20);
Let the servo angle deflect back and forth from 0 to 180.
Phenomenon Picture¶