1.1.2 RGB LED¶
Introduction¶
In this project, we will control an RGB LED to flash various colors.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
Schematic Diagram¶
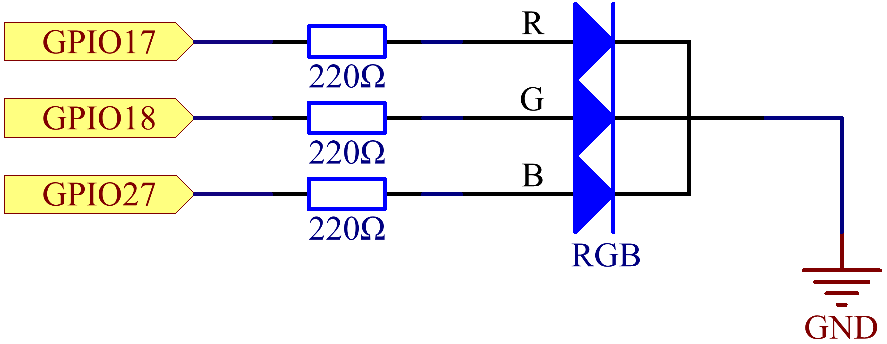
After connecting the pins of R, G, and B to a current limiting resistor, connect them to the GPIO17, GPIO18, and GPIO27 respectively. The longest pin (GND) of the LED connects to the GND of the Raspberry Pi. When the three pins are given different PWM values, the RGB LED will display different colors.
Experimental Procedures¶
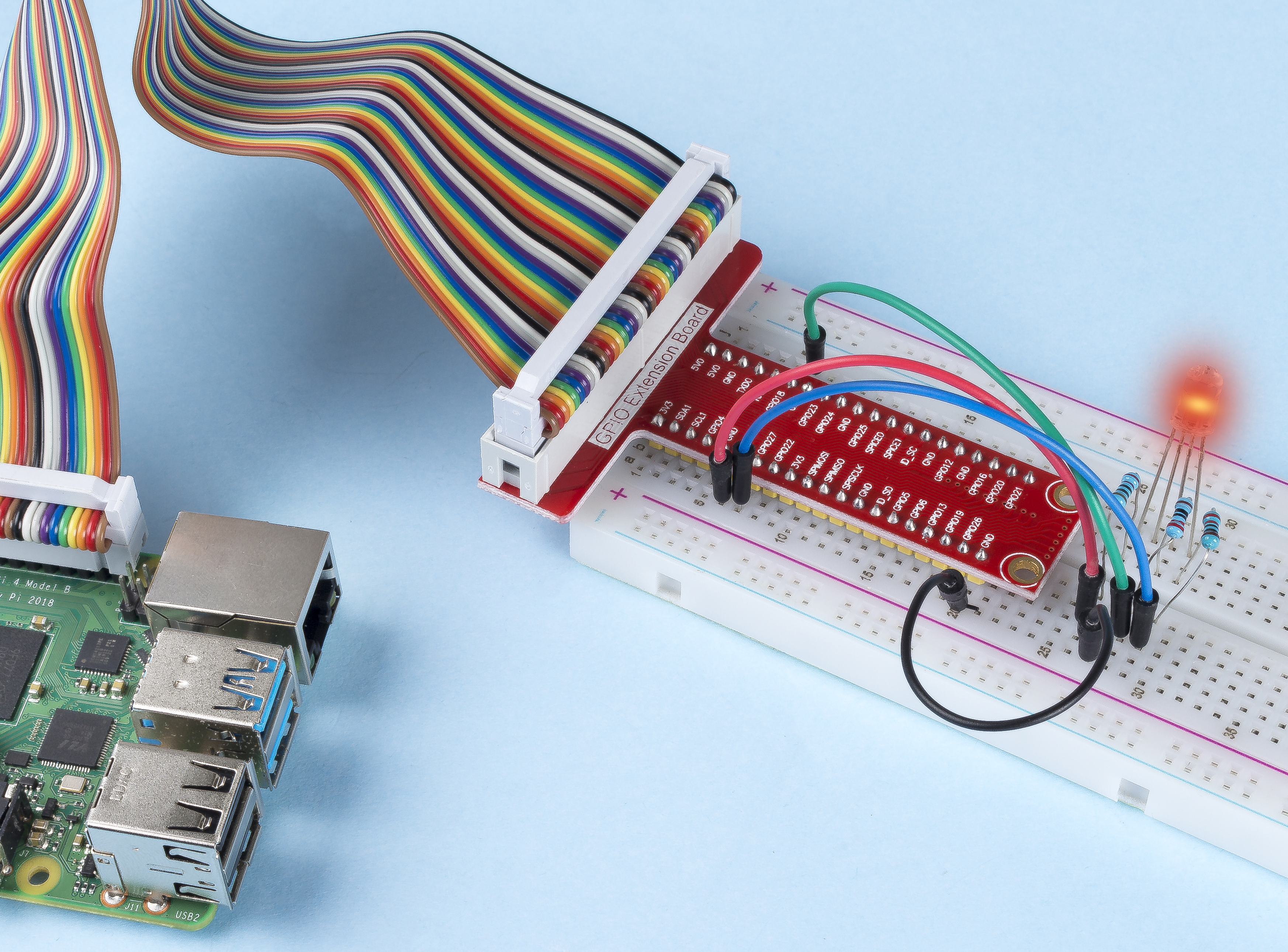
Step 1: Build the circuit.
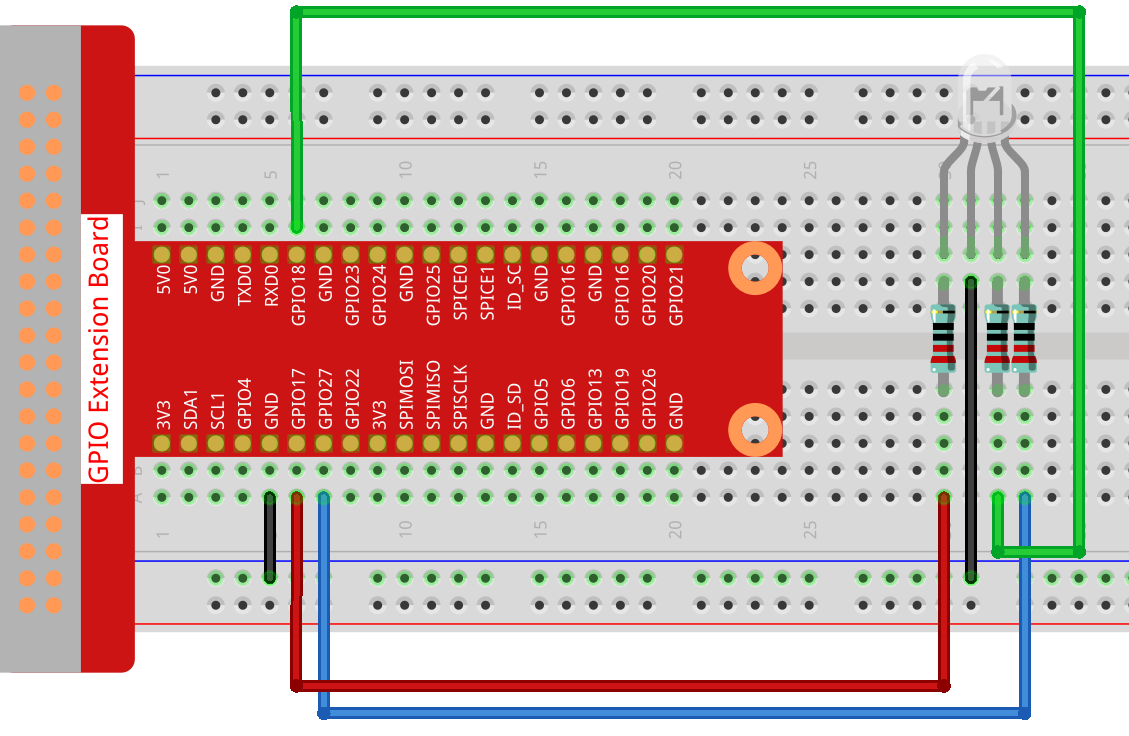
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/nodejs/
Step 3: Run the code.
sudo node rgb_led.js
After the code runs, you will see that RGB displays red, green, blue, yellow, pink, and cyan.
Code
const Gpio = require('pigpio').Gpio;
const ledred = new Gpio(17, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const ledgreen = new Gpio(18, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
const ledblue = new Gpio(27, { mode: Gpio.OUTPUT });
function colorset(r, g, b) {
ledred.pwmWrite(r);
ledgreen.pwmWrite(g);
ledblue.pwmWrite(b);
}
var color_index = -1;
setInterval(() => {
color_index += 1;
switch (color_index) {
case 0:
colorset(0xff, 0x00, 0xFF);
break;
case 1:
colorset(0x00, 0xff, 0x00);
break;
case 2:
colorset(0x00, 0x00, 0xff);
break;
case 3:
colorset(0xff, 0xff, 0x00);
break;
case 4:
colorset(0xff, 0x00, 0xff);
break;
case 5:
colorset(0xc0, 0xff, 0x3e);
break;
default:
color_index=-1;
}
}, 500);
Code Explanation
const ledred = new Gpio(17,{mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const ledgreen = new Gpio(18,{mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const ledblue = new Gpio(27,{mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
Initialize pins 17, 18, and 27 to output mode, and assign them to the constants ledred, ledgreen, and ledblue respectively.
function colorset(r,g,b){
ledred.pwmWrite(r);
ledgreen.pwmWrite(g);
ledblue.pwmWrite(b);
}
Implement a colorset(r,g,b) function, which is used to write pulse values to pins 17, 18, 27. The Gpio library encapsulates the function pwmWrite() to write to pins Pulse value, the value is 0x00 to 0xff. Then you can write RGB values to the RGB LED through the colorset(r,g,b) function, so that it can display a variety of colors.
Note
For questions about RGB, please refer to the website: https://www.rapidtables.com/web/color/RGB_Color.html
var color_index = -1;
setInterval(() => {
color_index += 1;
switch (color_index) {
case 0:
colorset(0xff, 0x00, 0xFF);
break;
case 1:
colorset(0x00, 0xff, 0x00);
break;
case 2:
colorset(0x00, 0x00, 0xff);
break;
case 3:
colorset(0xff, 0xff, 0x00);
break;
case 4:
colorset(0xff, 0x00, 0xff);
break;
case 5:
colorset(0xc0, 0xff, 0x3e);
break;
default:
color_index=-1;
}
}, 500);
The RGB LED is controlled by colorset() executed every 500ms.
A switch case is used here to select the color emitted by the RGB LEDs.
Since color_index is changed by one every cycle, the color of this one RGB LED will change in order.
Phenomenon Picture¶