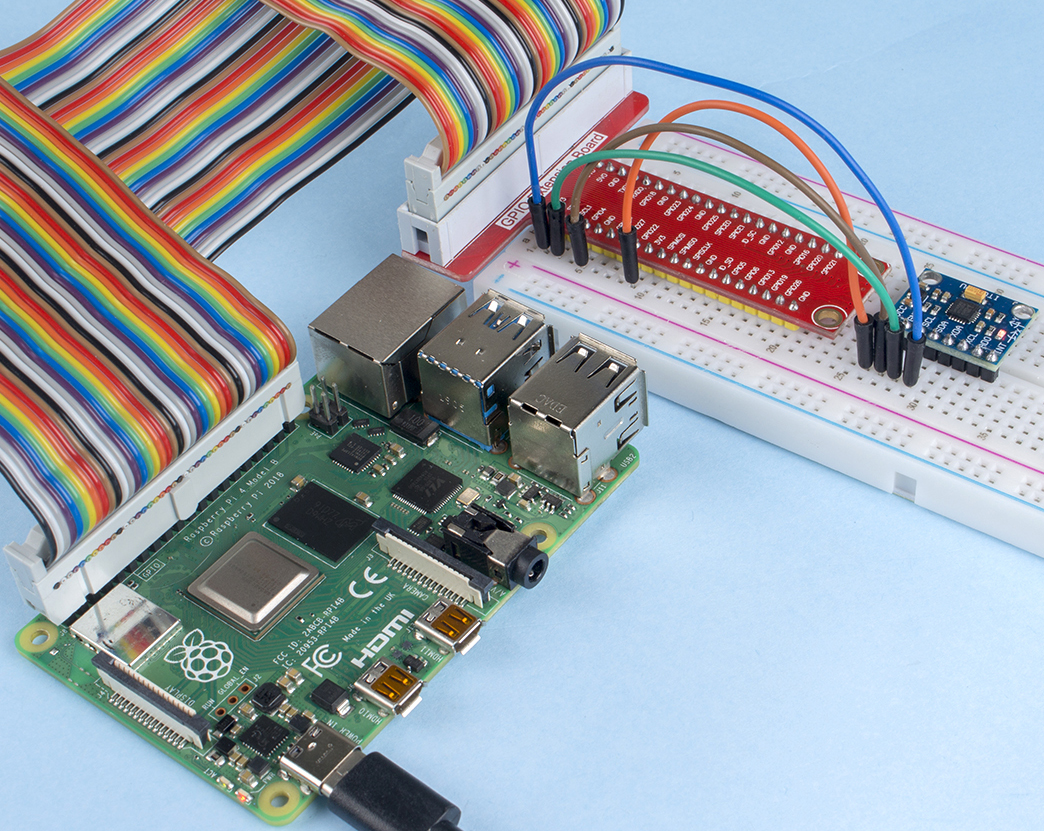
2.2.9 MPU6050 Module¶
Introduction¶
The MPU-6050 is the world’s first and only 6-axis motion tracking devices (3-axis Gyroscope and 3-axis Accelerometer) designed for smartphones, tablets and wearable sensors that have these features, including the low power, low cost, and high performance requirements.
In this experiment, use I2C to obtain the values of the three-axis acceleration sensor and three-axis gyroscope for MPU6050 and display them on the screen.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
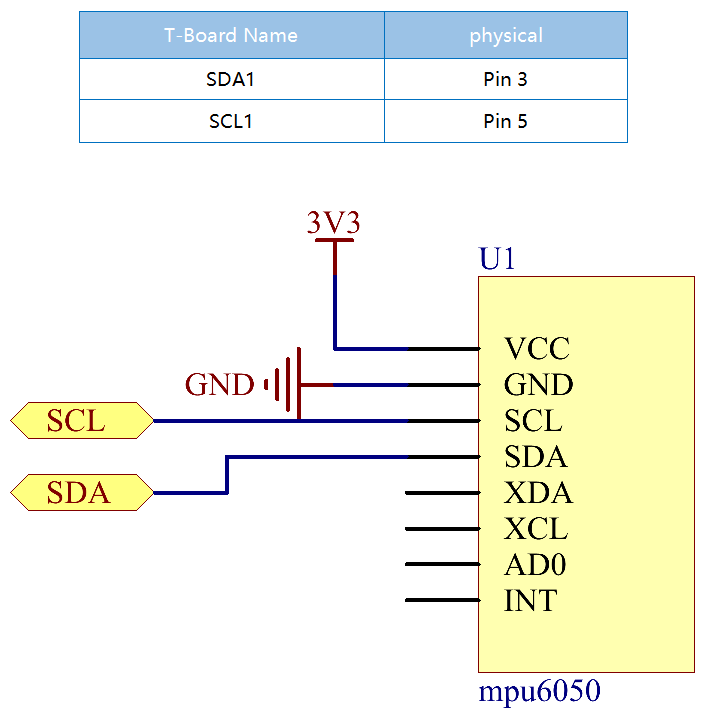
Schematic Diagram¶
MPU6050 communicates with the microcontroller through the I2C bus interface. The SDA1 and SCL1 need to be connected to the corresponding pin.
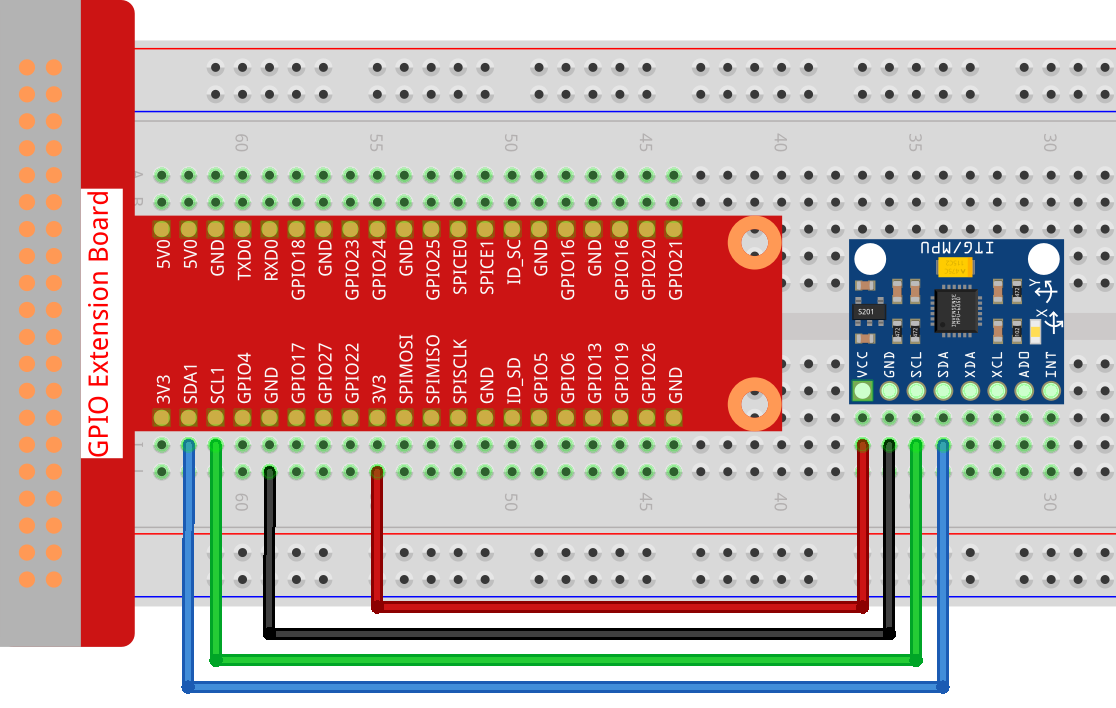
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
Step 2: Setup I2C (see Appendix I2C Configuration. If you have set I2C, skip this step.)
Step 3: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/c/2.2.9/
Step 4: Compile the code.
gcc 2.2.9_mpu6050.c -lwiringPi -lm
Step 5: Run the executable file.
sudo ./a.out
With the code run, deflection angle of x axis, y axis and the acceleration, angular velocity on each axis read by MPU6050 will be printed on the screen after being calculating.
Note
If there is an error prompt
wiringPi.h: No such file or directory, please refer to Install and Check the WiringPi.If you get
Unable to open I2C device: No such file or directoryerror, you need to refer to I2C Configuration to enable I2C and check if the wiring is correct.
Code
#include <wiringPiI2C.h>
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int fd;
int acclX, acclY, acclZ;
int gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ;
double acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled;
double gyroX_scaled, gyroY_scaled, gyroZ_scaled;
int read_word_2c(int addr)
{
int val;
val = wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr);
val = val << 8;
val += wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr+1);
if (val >= 0x8000)
val = -(65536 - val);
return val;
}
double dist(double a, double b)
{
return sqrt((a*a) + (b*b));
}
double get_y_rotation(double x, double y, double z)
{
double radians;
radians = atan2(x, dist(y, z));
return -(radians * (180.0 / M_PI));
}
double get_x_rotation(double x, double y, double z)
{
double radians;
radians = atan2(y, dist(x, z));
return (radians * (180.0 / M_PI));
}
int main()
{
fd = wiringPiI2CSetup (0x68);
wiringPiI2CWriteReg8 (fd,0x6B,0x00);//disable sleep mode
printf("set 0x6B=%X\n",wiringPiI2CReadReg8 (fd,0x6B));
while(1) {
gyroX = read_word_2c(0x43);
gyroY = read_word_2c(0x45);
gyroZ = read_word_2c(0x47);
gyroX_scaled = gyroX / 131.0;
gyroY_scaled = gyroY / 131.0;
gyroZ_scaled = gyroZ / 131.0;
//Print values for the X, Y, and Z axes of the gyroscope sensor.
printf("My gyroX_scaled: %f\n", gyroY X_scaled);
printf("My gyroY_scaled: %f\n", gyroY Y_scaled);
printf("My gyroZ_scaled: %f\n", gyroY Z_scaled);
acclX = read_word_2c(0x3B);
acclY = read_word_2c(0x3D);
acclZ = read_word_2c(0x3F);
acclX_scaled = acclX / 16384.0;
acclY_scaled = acclY / 16384.0;
acclZ_scaled = acclZ / 16384.0;
//Print the X, Y, and Z values of the acceleration sensor.
printf("My acclX_scaled: %f\n", acclX_scaled);
printf("My acclY_scaled: %f\n", acclY_scaled);
printf("My acclZ_scaled: %f\n", acclZ_scaled);
printf("My X rotation: %f\n", get_x_rotation(acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled));
printf("My Y rotation: %f\n", get_y_rotation(acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled));
delay(100);
}
return 0;
}
Code Explanation
int read_word_2c(int addr)
{
int val;
val = wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr);
val = val << 8;
val += wiringPiI2CReadReg8(fd, addr+1);
if (val >= 0x8000)
val = -(65536 - val);
return val;
}
Read sensor data sent from MPU6050.
double get_y_rotation(double x, double y, double z)
{
double radians;
radians = atan2(x, dist(y, z));
return -(radians * (180.0 / M_PI));
}
We get the deflection angle on the Y-axis.
double get_x_rotation(double x, double y, double z)
{
double radians;
radians = atan2(y, dist(x, z));
return (radians * (180.0 / M_PI));
}
Calculate the deflection angle of the X-axis.
gyroX = read_word_2c(0x43);
gyroY = read_word_2c(0x45);
gyroZ = read_word_2c(0x47);
gyroX_scaled = gyroX / 131.0;
gyroY_scaled = gyroY / 131.0;
gyroZ_scaled = gyroZ / 131.0;
//Print values for the X, Y, and Z axes of the gyroscope sensor.
printf("My gyroX_scaled: %f\n", gyroY X_scaled);
printf("My gyroY_scaled: %f\n", gyroY Y_scaled);
printf("My gyroZ_scaled: %f\n", gyroY Z_scaled);
Read the values of the x axis, y axis and z axis on the gyroscope sensor, convert the metadata to angular velocity values, and then print them.
acclX = read_word_2c(0x3B);
acclY = read_word_2c(0x3D);
acclZ = read_word_2c(0x3F);
acclX_scaled = acclX / 16384.0;
acclY_scaled = acclY / 16384.0;
acclZ_scaled = acclZ / 16384.0;
//Print the X, Y, and Z values of the acceleration sensor.
printf("My acclX_scaled: %f\n", acclX_scaled);
printf("My acclY_scaled: %f\n", acclY_scaled);
printf("My acclZ_scaled: %f\n", acclZ_scaled);
Read the values of the x axis, y axis and z axis on the acceleration sensor, convert the metadata to accelerated speed values (gravity unit), and then print them.
printf("My X rotation: %f\n", get_x_rotation(acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled));
printf("My Y rotation: %f\n", get_y_rotation(acclX_scaled, acclY_scaled, acclZ_scaled));
Print the deflection angles of the x-axis and y-axis.
Phenomenon Picture¶