Note
Hello, welcome to the SunFounder Raspberry Pi & Arduino & ESP32 Enthusiasts Community on Facebook! Dive deeper into Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and ESP32 with fellow enthusiasts.
Why Join?
Expert Support: Solve post-sale issues and technical challenges with help from our community and team.
Learn & Share: Exchange tips and tutorials to enhance your skills.
Exclusive Previews: Get early access to new product announcements and sneak peeks.
Special Discounts: Enjoy exclusive discounts on our newest products.
Festive Promotions and Giveaways: Take part in giveaways and holiday promotions.
👉 Ready to explore and create with us? Click [here] and join today!
2.1.7 Potentiometer¶
Introduction¶
The ADC function can be used to convert analog signals to digital signals, and in this experiment, ADC0834 is used to get the function involving ADC. Here, we implement this process by using potentiometer. Potentiometer changes the physical quantity – voltage, which is converted by the ADC function.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
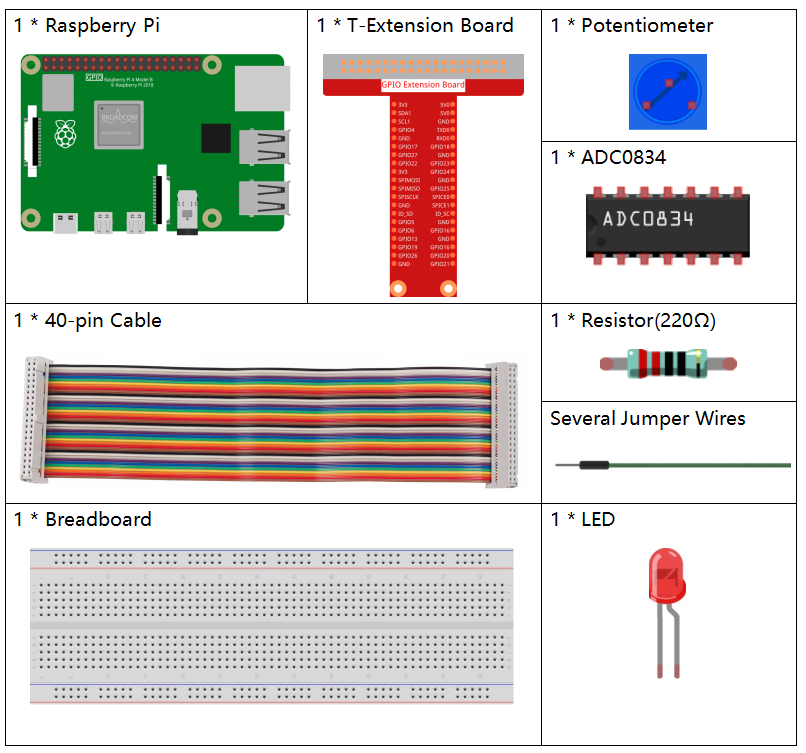
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
- |
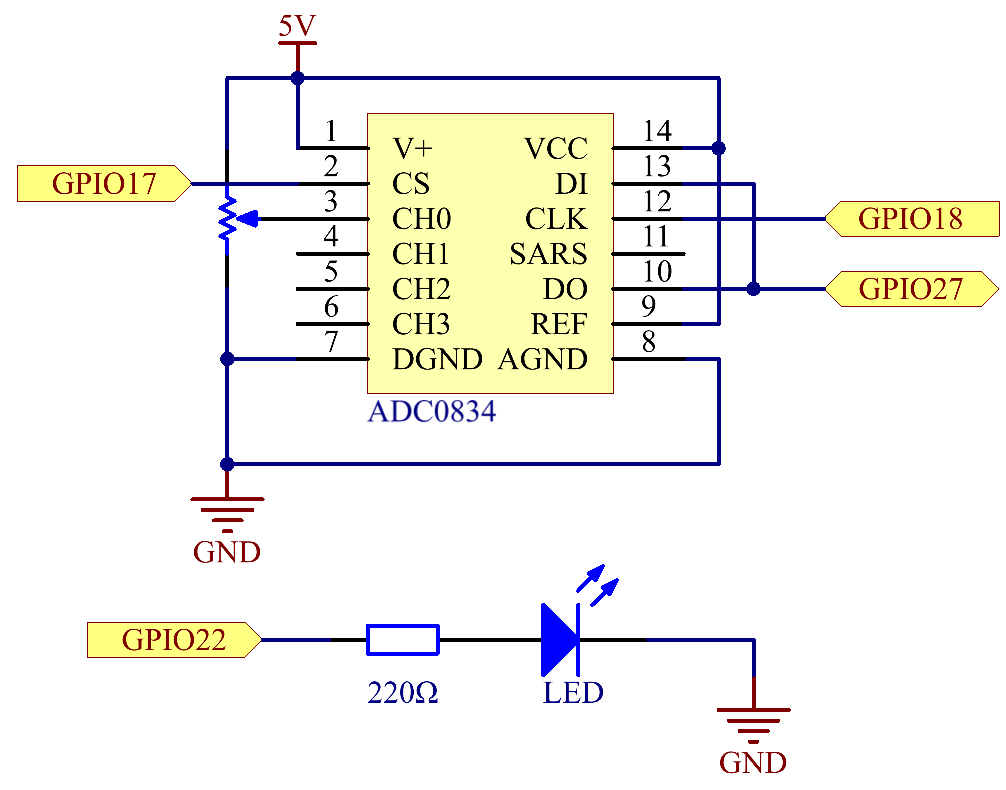
Schematic Diagram¶
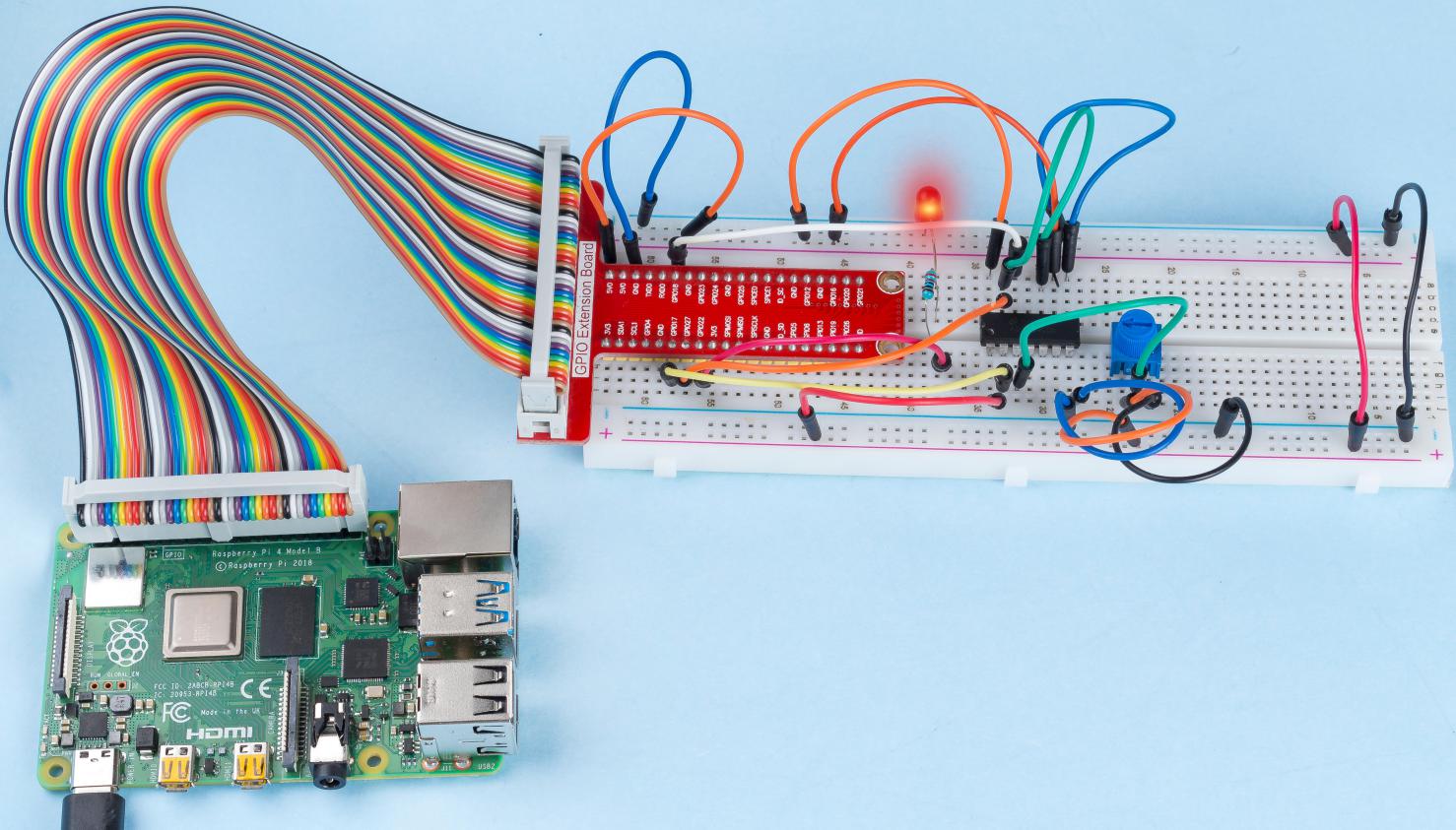
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
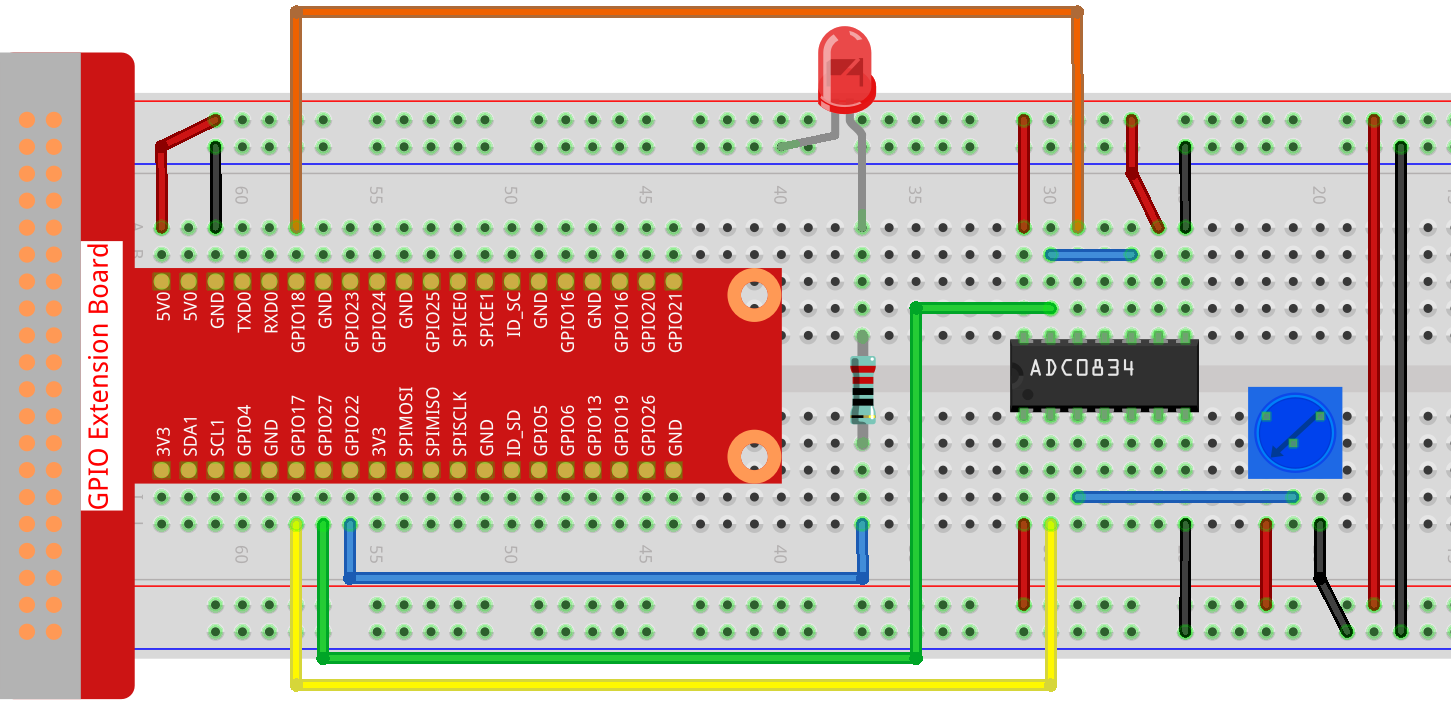
Note
Please place the chip by referring to the corresponding position depicted in the picture. Note that the grooves on the chip should be on the left when it is placed.
Step 2: Open the code file.
cd ~/raphael-kit/c/2.1.7/
Step 3: Compile the code.
gcc 2.1.7_Potentiometer.c -lwiringPi
Step 4: Run.
sudo ./a.out
After the code runs, rotate the knob on the potentiometer, the intensity of LED will change accordingly.
Note
If it does not work after running, or there is an error prompt: "wiringPi.h: No such file or directory", please refer to Install and Check the WiringPi.
Code
#include <wiringPi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <softPwm.h>
typedef unsigned char uchar;
typedef unsigned int uint;
#define ADC_CS 0
#define ADC_CLK 1
#define ADC_DIO 2
#define LedPin 3
uchar get_ADC_Result(uint channel)
{
uchar i;
uchar dat1=0, dat2=0;
int sel = channel > 1 & 1;
int odd = channel & 1;
pinMode(ADC_DIO, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ADC_CS, 0);
// Start bit
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
// Single End mode
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
// ODD
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,odd); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
// Select
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,sel); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0); delayMicroseconds(2);
pinMode(ADC_DIO, INPUT);
dat1=dat1<<1 | digitalRead(ADC_DIO);
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
dat2 = dat2 | ((uchar)(digitalRead(ADC_DIO))<<i);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0); delayMicroseconds(2);
}
digitalWrite(ADC_CS,1);
pinMode(ADC_DIO, OUTPUT);
return(dat1==dat2) ? dat1 : 0;
}
int main(void)
{
uchar analogVal;
if(wiringPiSetup() == -1){ //when initialize wiring failed,print messageto screen
printf("setup wiringPi failed !");
return 1;
}
softPwmCreate(LedPin, 0, 100);
pinMode(ADC_CS, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ADC_CLK, OUTPUT);
while(1){
analogVal = get_ADC_Result(0);
printf("Current analogVal : %d\n", analogVal);
softPwmWrite(LedPin, analogVal);
delay(100);
}
return 0;
}
Code Explanation
#define ADC_CS 0
#define ADC_CLK 1
#define ADC_DIO 2
#define LedPin 3
Define CS, CLK, DIO of ADC0834, and connect them to GPIO0, GPIO1 and GPIO2 respectively. Then attach LED to GPIO3.
uchar get_ADC_Result(uint channel)
{
uchar i;
uchar dat1=0, dat2=0;
int sel = channel > 1 & 1;
int odd = channel & 1;
pinMode(ADC_DIO, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ADC_CS, 0);
// Start bit
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
// Single End mode
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
// ODD
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,odd); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
// Select
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,sel); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0); delayMicroseconds(2);
pinMode(ADC_DIO, INPUT);
dat1=dat1<<1 | digitalRead(ADC_DIO);
}
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
dat2 = dat2 | ((uchar)(digitalRead(ADC_DIO))<<i);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0); delayMicroseconds(2);
}
digitalWrite(ADC_CS,1);
pinMode(ADC_DIO, OUTPUT);
return(dat1==dat2) ? dat1 : 0;
}
There is a function of ADC0834 to get Analog to Digital Conversion. The specific workflow is as follows:
digitalWrite(ADC_CS, 0);
Set CS to low level and start enabling AD conversion.
// Start bit
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
When the low-to-high transition of the clock input occurs at the first time, set DIO to 1 as Start bit. In the following three steps, there are 3 assignment words.
//Single End mode
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
As soon as the low-to-high transition of the clock input occurs for the second time, set DIO to 1 and choose SGL mode.
// ODD
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,odd); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
Once occurs for the third time, the value of DIO is controlled by the variable odd.
//Select
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,sel); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1);
The pulse of CLK converted from low level to high level for the forth time, the value of DIO is controlled by the variable sel.
Under the condition that channel=0, sel=0, odd=0, the operational formulas concerning sel and odd are as follows:
int sel = channel > 1 & 1;
int odd = channel & 1;
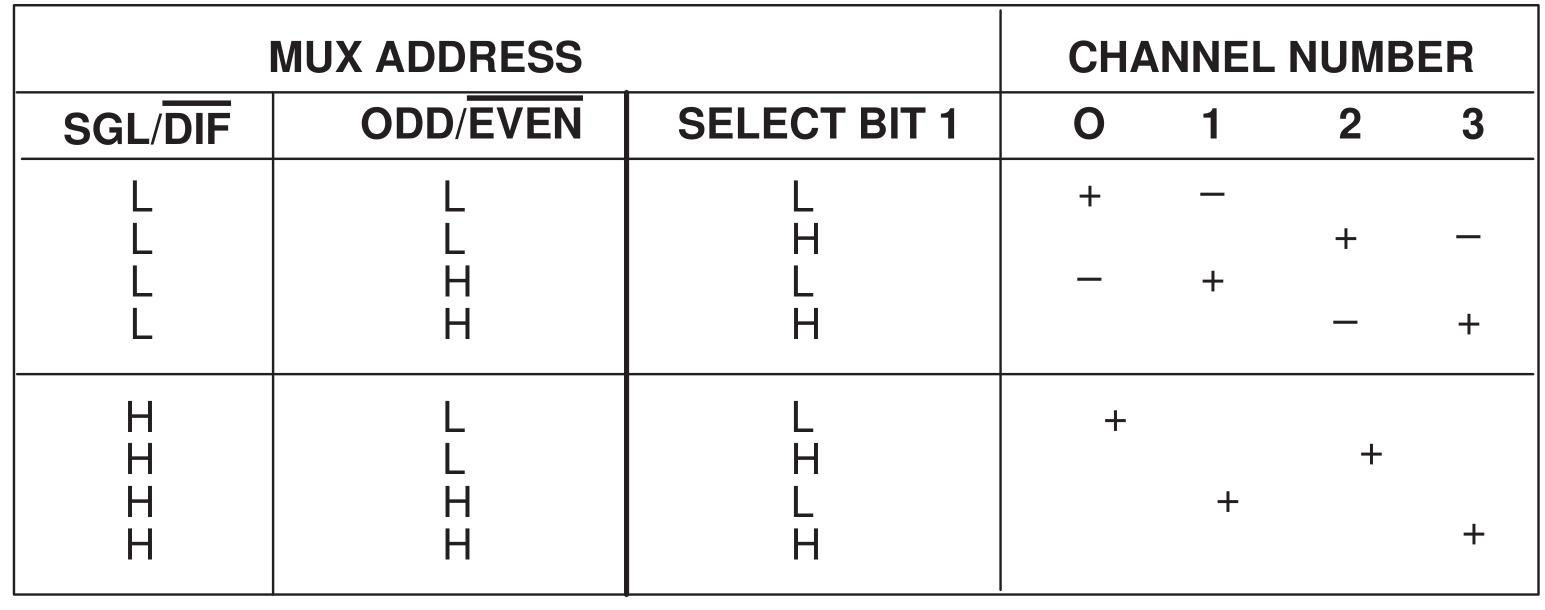
When the condition that channel=1, sel=0, odd=1 is met, please refer to the following address control logic table. Here CH1 is chosen, and the start bit is shifted into the start location of the multiplexer register and conversion starts.
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0);
digitalWrite(ADC_DIO,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
Here, set DIO to 1 twice, please ignore it.
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0); delayMicroseconds(2);
pinMode(ADC_DIO, INPUT);
dat1=dat1<<1 | digitalRead(ADC_DIO);
}
In the first for() statement, as soon as the fifth pulse of CLK is converted from high level to low level, set DIO to input mode. Then the conversion starts and the converted value is stored in the variable dat1. After eight clock periods, the conversion is complete.
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
{
dat2 = dat2 | ((uchar)(digitalRead(ADC_DIO))<<i);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,1); delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(ADC_CLK,0); delayMicroseconds(2);
}
In the second for() statement, output the converted values via DO after other eight clock periods and store them in the variable dat2.
digitalWrite(ADC_CS,1);
pinMode(ADC_DIO, OUTPUT);
return(dat1==dat2) ? dat1 : 0;
return(dat1==dat2) ? dat1 : 0 is used to compare the value gotten during the conversion and the output value. If they are equal to each other, output the converting value dat1; otherwise, output 0. Here, the workflow of ADC0834 is complete.
softPwmCreate(LedPin, 0, 100);
The function is to use software to create a PWM pin, LedPin, then the initial pulse width is set to 0, and the period of PWM is 100 x 100us.
while(1){
analogVal = get_ADC_Result(0);
printf("Current analogVal : %d\n", analogVal);
softPwmWrite(LedPin, analogVal);
delay(100);
}
In the main program, read the value of channel 0 that has been connected with a potentiometer. And store the value in the variable analogVal then write it in LedPin. Now you can see the brightness of LED changing with the value of the potentiometer.
Phenomenon Picture¶