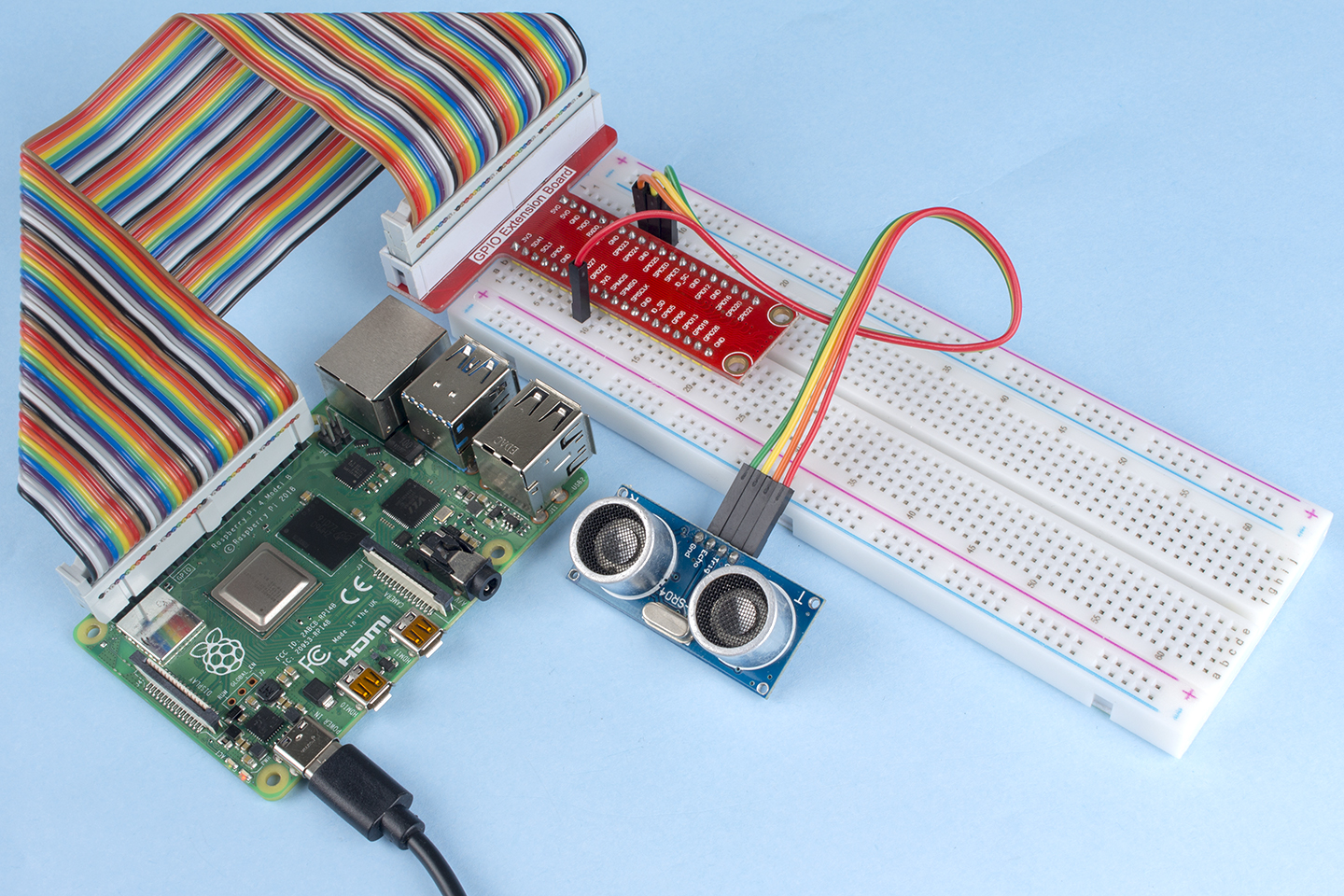
2.2.8 Ultrasonic Sensor Module¶
Introduction¶
The ultrasonic sensor uses ultrasonic to accurately detect objects and measure distances. It sends out ultrasonic waves and converts them into electronic signals.
Required Components¶
In this project, we need the following components.
It’s definitely convenient to buy a whole kit, here’s the link:
Name |
ITEMS IN THIS KIT |
LINK |
|---|---|---|
Raphael Kit |
337 |
You can also buy them separately from the links below.
COMPONENT INTRODUCTION |
PURCHASE LINK |
|---|---|
Schematic Diagram¶
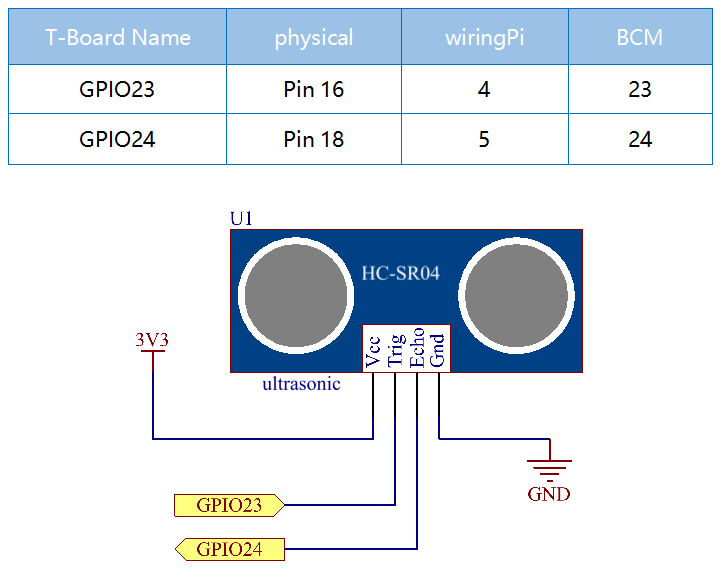
Experimental Procedures¶
Step 1: Build the circuit.
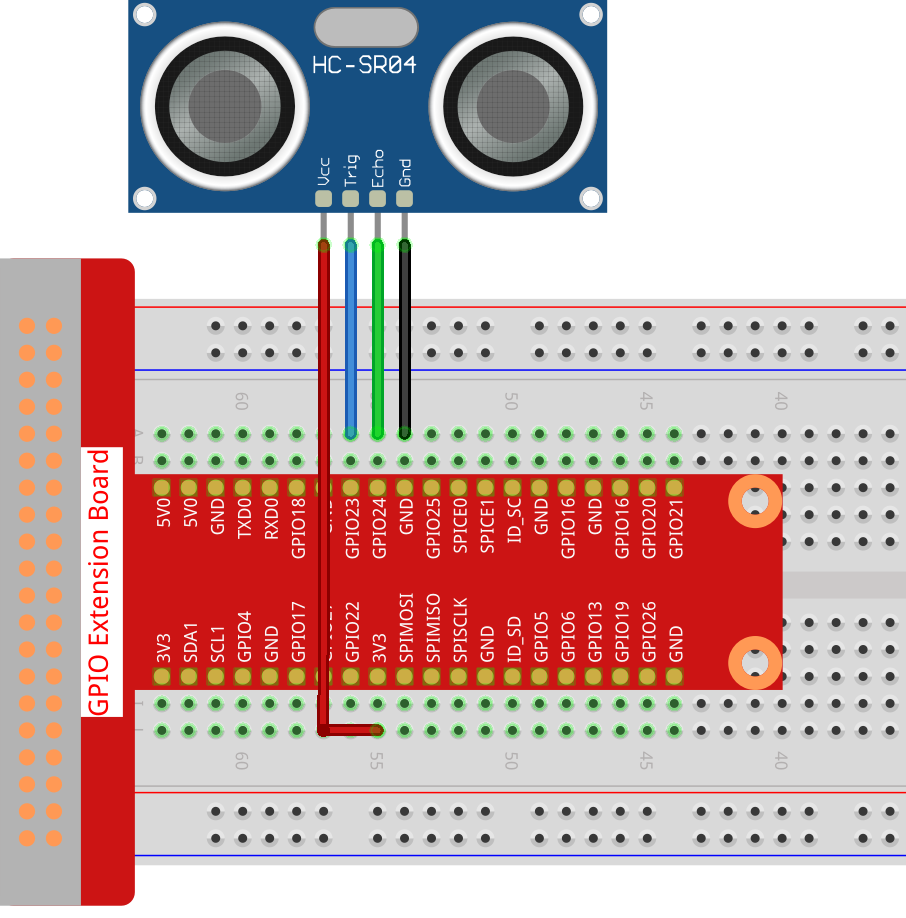
Step 2: Go to the folder of the code.
cd ~/raphael-kit/nodejs/
Step 3: Run the code.
sudo node ultrasonic_sensor.js
With the code run, the ultrasonic sensor module detects the distance between the obstacle ahead and the module itself, then the distance value will be printed on the screen.
Code
const Gpio = require('pigpio').Gpio;
// The number of microseconds it takes sound to travel 1cm at 20 degrees celcius
const MICROSECDONDS_PER_CM = 1e6/34321;
const trigger = new Gpio(23, {mode: Gpio.OUTPUT});
const echo = new Gpio(24, {mode: Gpio.INPUT, alert: true});
trigger.digitalWrite(0); // Make sure trigger is low
const watchHCSR04 = () => {
let startTick;
echo.on('alert', (level, tick) => {
if (level === 1) {
startTick = tick;
} else {
const endTick = tick;
const diff = (endTick >> 0) - (startTick >> 0); // Unsigned 32 bit arithmetic
console.log(diff / 2 / MICROSECDONDS_PER_CM);
}
});
};
watchHCSR04();
// Trigger a distance measurement once per second
setInterval(() => {
trigger.trigger(10, 1); // Set trigger high for 10 microseconds
}, 1000);
Code Explanation
The trigger function can be used to generate a pulse on a GPIO and
alerts can be used to determine the time of a GPIO state change
accurate to a few microseconds.
These two features can be combined to measure distance using a HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor.
setInterval(() => {
trigger.trigger(10, 1); // Set trigger high for 10 microseconds
}, 1000);
This is to periodically send out a 10us ultrasonic pulse.
const watchHCSR04 = () => {
echo.on('alert', (level, tick) => {
if (level === 1) {
startTick = tick;
} else {
const endTick = tick;
const diff = (endTick >> 0) - (startTick >> 0); // Unsigned 32 bit arithmetic
console.log(diff / 2 / MICROSECDONDS_PER_CM);
}
});
};
This function sets an alert that will record the time between sending the pulse (level is 1) and receiving the echo (level is 0). By multiplying the time difference by the speed of sound (and dividing by 2), you can get the distance to the obstacle ahead.
Phenomenon Picture¶