Servo¶
A servo is a specialized motor known for its precision in controlling specific angular positions.

Brown Line: GND
Orange Line: Signal pin, connect to the PWM pin of main board.
Red wire: VCC
Unlike regular motors that spin continuously, a servo can move to a precise position and hold it accurately. It achieves this through a combination of gears, a potentiometer, and control circuitry. Servos are commonly used in various applications that require precise control over the position of objects or mechanisms.
Features
Motor Type: Core motor
Operating Voltage: 4.8~6V DC
Standby Current: ≤4 mA
Consumption Current(at 4.8V No Load): ≦50mA
Consumption Current(at 6 V no load): ≦60mA
Stall Current(at locked 4.8V): ≦550mA
Stall Current(at locked 6V): ≦650mA
Rated Torque: 4.8V, ≥0.6 kgf·cm; 6V, ≥0.7 kgf·cm
Max. Torque: 4.8V, ≥1.4 kgf.cm; 6V, ≥1.6 kgf.cm
No Load Speed: 4.8V, ≦0.14sec/60°; 6V, ≦0.12sec/60°
Note: Torsion protection:≥0.9 kgf.cm;Power failure protection after 5 seconds of continuous
Operating Temperature Range: -10℃~+50℃
Storage Temperature Range: -20℃~+60℃
Operating Humidity Range: ≤ 90%RH
Storage Humidity Range: ≤ 90%RH
Weight: 10± 0.5g
Material: ABS
Operating Angle: 180°±10°(500~2500us)
Mechanical Limit Angle: 360°
Left & Right Travelling Angle: ≤ 6°
Centering deviation: ≤ 1°
Back Lash: ≤ 4 us
Amplifier Type: Digital
Cable Materia: Ф1.08,19 PVC
Cable Length: 245±5mm(Exsert without plugs)
Connector Type: JR2.54mm/3Pin
Operating Principle
Inside a servo, essential components contribute to its unique functionality. At its core, a servo incorporates a conventional motor, this motor is intricately linked to a large gear, which in turn engages with a smaller gear on the motor shaft. This gearing arrangement efficiently converts the motor’s rapid circular motion into slower yet potent movements.
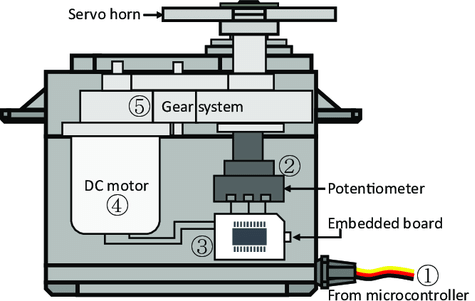
But the real magic happens within the servo, thanks to a minuscule electronic marvel known as a “potentiometer” and sophisticated “control circuitry.” When the servo undergoes movement, the potentiometer rotates, altering its electrical resistance. The control circuitry detects and interprets this change in resistance with remarkable precision, thereby determining the servo’s exact position. This is a testament to its ingenuity.
In the realm of servo control, a unique signaling method called “pulse-width modulation” or PWM comes into play. By skillfully adjusting the width of these pulses, operators can command the servo to move with precision and maintain its position. This is the essence of servo motor technology, a realm where precision and control converge to enable an array of applications.