Face Detection¶
This project is also based on the Computer Vision project, with the addition of face detection algorithms.
Run the Code
cd /home/pi/picar-x/example
sudo python3 human_face_detect.py
Code
import cv2
from picamera.array import PiRGBArray
from picamera import PiCamera
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
def human_face_detect(img):
resize_img = cv2.resize(img, (320,240), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(resize_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 2)
face_num = len(faces)
max_area = 0
if face_num > 0:
for (x,y,w,h) in faces:
x = x*2
y = y*2
w = w*2
h = h*2
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(255,0,0),2)
return img
#init camera
print("start human face detect")
camera = PiCamera()
camera.resolution = (640,480)
camera.framerate = 24
rawCapture = PiRGBArray(camera, size=camera.resolution)
for frame in camera.capture_continuous(rawCapture, format="bgr",use_video_port=True):
img = frame.array
img = human_face_detect(img)
cv2.imshow("video", img)
rawCapture.truncate(0)
k = cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF
if k == 27:
camera.close()
break
How it works?
In the same path as this project (picar-x/example/) , put a file haarcascade_frontalhuman face_default.xml. This file is a face detection model file trained in OpenCV.
This file is called by Cascade Classifier of OpenCV.
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
Object Detection using Haar feature-based cascade classifiers is an effective object detection method proposed by Paul Viola and Michael Jones in their paper, “Rapid Object Detection using a Boosted Cascade of Simple Features” in 2001.
This is a machine learning based approach, where a cascade function is trained from a large quantity of positive and negative images, and then used to detect objects in other images.
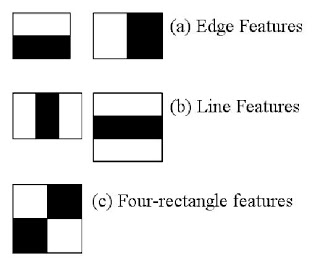
When working with face detection, the algorithm will initially need a large quantity of positive images (images of faces) and negative images (images without faces) to train the classifier. From there, the facial features will then need to be extracted. For this, Haar features shown in the below image are used, similar to the convolutional kernel. Each feature is a single value obtained by subtracting the sum of pixels under the white rectangle, from the sum of pixels under the black rectangle.
The human_human face_detect() function processes pictures in three steps:
Convert picture to grayscale.
Detect the human face on the grayscale image to obtain the bounding rectangle of the detected face.
Draws a frame for the recognized object on the image.
def human_face_detect(img):
resize_img = cv2.resize(img, (320,240), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # To reduce the amount of calculation, the image size is reduced.
gray = cv2.cvtColor(resize_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # Convert picture to grayscale.
faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 2) # Obtain the bounding rectangle of the detected face.
face_num = len(faces)
max_area = 0
if face_num > 0:
for (x,y,w,h) in faces: # Because the picture is reduced during operation, the increase now go back.
x = x*2
y = y*2
w = w*2
h = h*2
cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(255,0,0),2) # Draw a frame for the recognized object on the image.
return img